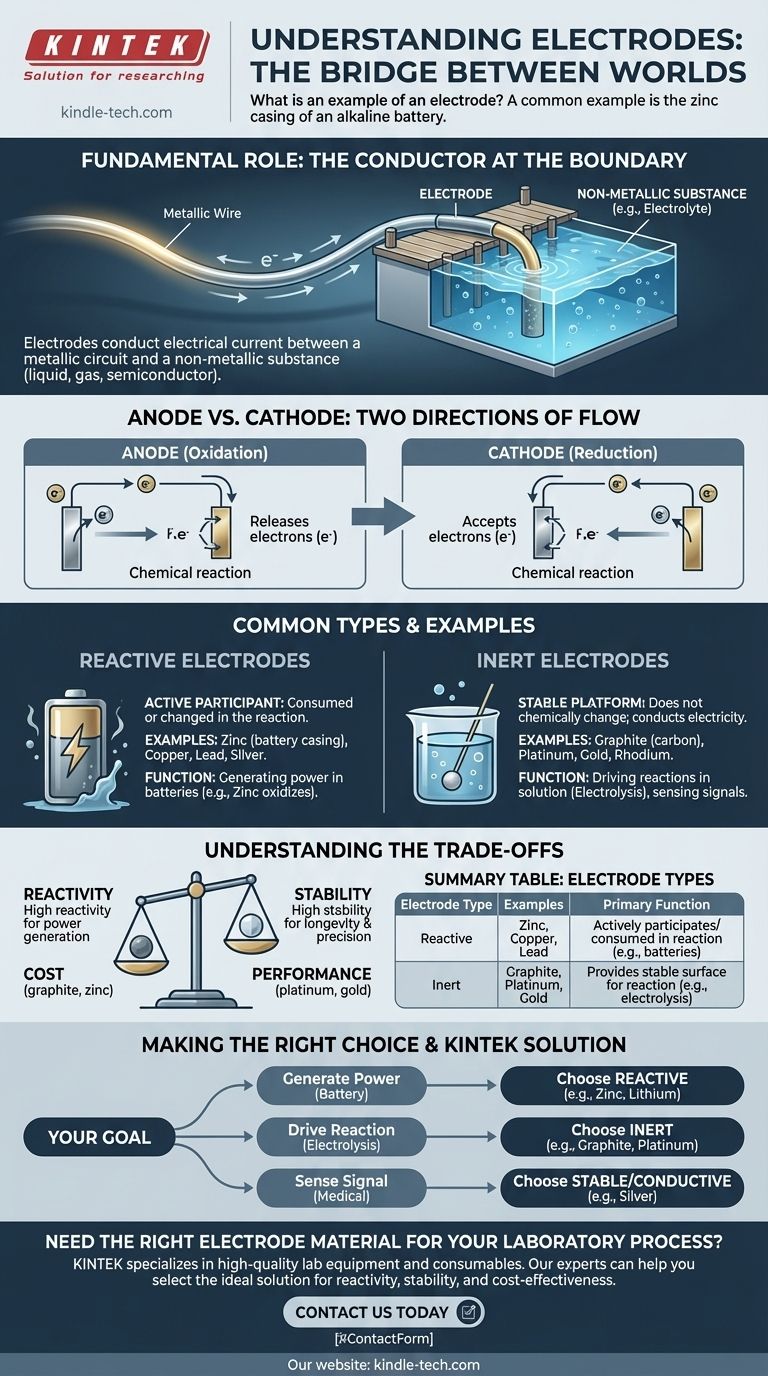
A common example of an electrode is the zinc casing of an alkaline battery or the copper top of a 9-volt battery. These materials act as electrical conductors that make contact with the non-metallic chemical paste (the electrolyte) inside the battery, allowing an electrical current to flow and power your device.
An electrode is fundamentally a bridge. Its job is to conduct electrical current between a standard metallic wire and a non-metallic substance, such as a liquid, gas, or semiconductor, enabling a vast range of chemical and electronic processes.

What Is the Fundamental Role of an Electrode?
An electrode serves as the crucial point of contact where an electrical circuit meets a non-metallic component. Without this bridge, many technologies would be impossible.
The Conductor at the Boundary
Think of an electrode as a dock for electricity. A wire is like a road that brings electricity to the edge of a lake (the non-metallic substance, like an electrolyte). The electrode is the dock that allows the electricity to enter or leave the water.
This non-metallic part can be a liquid electrolyte in a battery, a semiconductor in a diode, or even the human body in a medical device.
Anode vs. Cathode: The Two Directions of Flow
In electrochemical systems like batteries, electrodes are given specific names based on the direction of the reaction.
- An anode is the electrode where oxidation occurs, meaning it releases electrons into the circuit.
- A cathode is the electrode where reduction occurs, meaning it accepts electrons from the circuit.
Common Types and Examples
Electrodes are not all the same; their material is chosen based on whether they should participate in a reaction or simply observe it.
Reactive Electrodes
A reactive electrode is an active participant in a chemical reaction. It is consumed or changed during the process.
The zinc casing of a battery is a perfect example. As the battery discharges, the zinc metal oxidizes and slowly dissolves into the electrolyte, releasing the electrons that power your device. Other common reactive electrodes include copper, lead, and silver.
Inert Electrodes
An inert electrode acts as a stable, non-participating platform for a reaction to occur upon. It conducts electricity but does not chemically change itself.
Graphite (a form of carbon) is a widely used inert electrode because it is an excellent conductor and is relatively inexpensive. Platinum, gold, and rhodium are also used for their extreme resistance to reaction, though they are much more costly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of electrode material is a critical engineering decision based on the intended function and environment.
Reactivity vs. Stability
The primary trade-off is between reactivity and stability. For a single-use battery, you want a reactive electrode that can be consumed to generate power.
However, for a process like electrolysis (using electricity to split water), you need an inert electrode like platinum or graphite. Using a reactive electrode like zinc would cause the electrode itself to react with the water instead of splitting it.
Cost vs. Performance
Highly inert metals like gold and platinum offer superior performance and longevity, as they resist corrosion and unwanted side reactions.
However, their high cost makes them unsuitable for many applications. Graphite offers a good balance of inertness and conductivity at a fraction of the price, making it ideal for large-scale industrial processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
By observing the material and its application, you can quickly understand the purpose of a given electrode.
- If your primary focus is generating power in a battery: The electrodes will be made of reactive materials like zinc, lithium, or lead, chosen specifically to be consumed in a chemical reaction.
- If your primary focus is driving a reaction in a solution (electrolysis): The electrodes will be inert materials like graphite or platinum that can conduct current without interfering.
- If your primary focus is sensing an electrical signal: The electrodes (like in medical devices) will be made of conductive, stable materials like silver that can accurately transmit small currents from a non-metallic source like the body.
Ultimately, viewing an electrode as the bridge between the metallic and non-metallic worlds is the key to understanding its function in any device.
Summary Table:
| Electrode Type | Common Examples | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Reactive | Zinc, Copper, Lead | Actively participates in and is consumed by a chemical reaction (e.g., in batteries). |
| Inert | Graphite, Platinum, Gold | Provides a stable surface for a reaction without being consumed (e.g., in electrolysis). |
Need the right electrode material for your laboratory process? Choosing the correct electrode is critical for the success and efficiency of your experiments, whether you're developing new battery technologies or running precise electrolysis. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of electrode materials. Our experts can help you select the ideal solution for reactivity, stability, and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and let us be your partner in innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- How should a graphite electrode be cleaned and stored after an experiment? Ensure Reliable Electrochemical Data
- What are the properties of graphite rods? Leverage High Conductivity for Extreme Applications
- What are the properties and applications of a graphite disk electrode? Precision Tools for Electroanalysis
- Why is a high-purity graphite rod preferred as a counter electrode? Ensure Uncontaminated Electrochemical Analysis
- What technical advantages do carbon graphite electrodes offer for electroactive biofilms? Optimize Your Bio-Research



















