At its core, ceramic powder is the fundamental building block for advanced technical ceramics. These powders are the starting point for creating solid components that are essential in fields ranging from aerospace and electronics to medicine and industrial manufacturing, valued for properties that metals and plastics cannot match.
The true purpose of ceramic powder is not its use as a powder, but its potential to be transformed. Through processes like pressing and sintering (heating), these fine particles are fused into a dense, solid object, unlocking exceptional hardness, heat resistance, and chemical stability that are impossible to achieve in the powder's initial state.
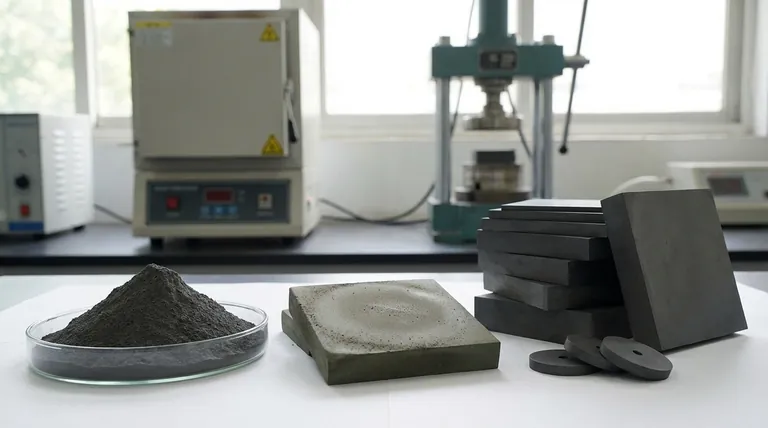

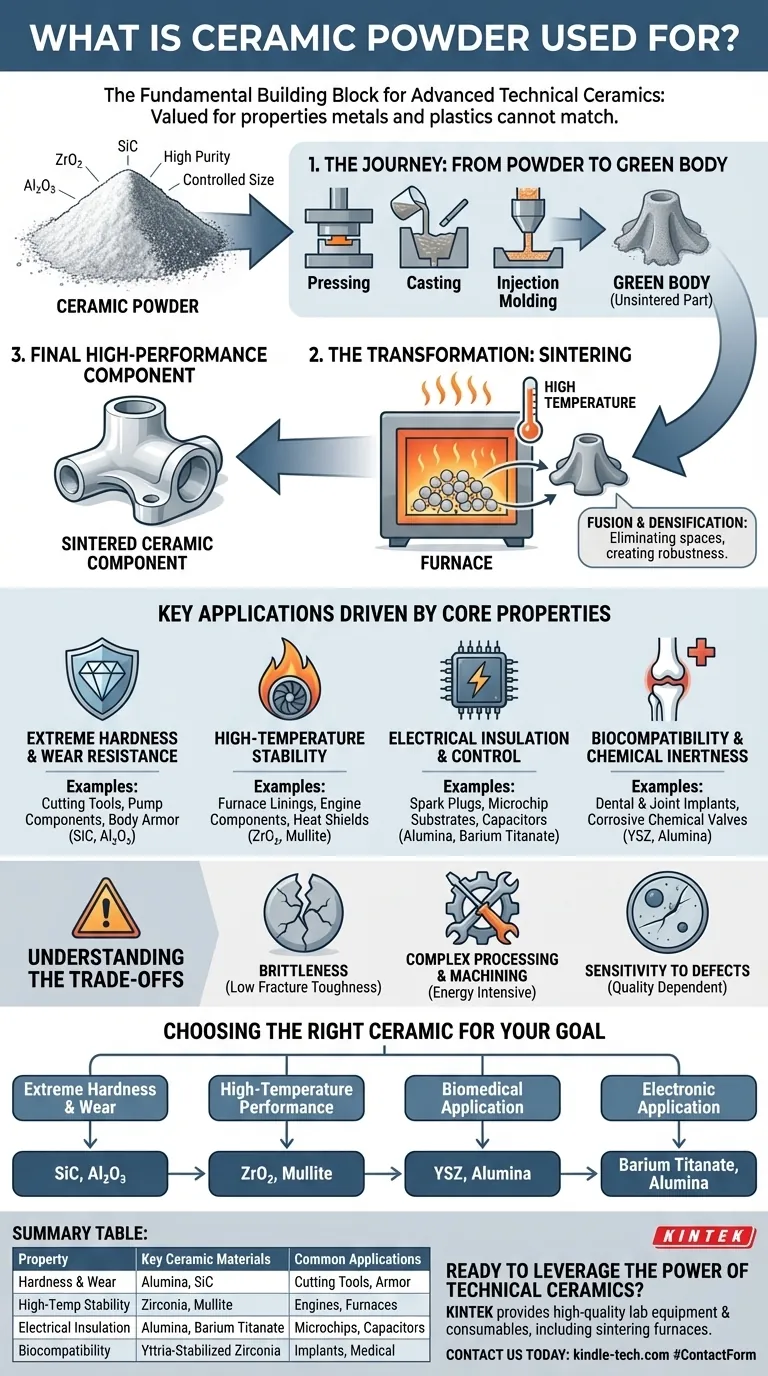
The Journey: From Powder to High-Performance Component
The value of a ceramic part is defined long before it becomes a solid object. The process begins with the precise characteristics of the initial powder, which dictate the final properties of the component.
The Starting Material: Purity is Paramount
Ceramic powders, such as alumina (Al₂O₃), zirconia (ZrO₂), and silicon carbide (SiC), are synthesized to achieve extreme purity and controlled particle sizes.
The size and shape of these microscopic particles are critical. They determine how densely the powder can be packed and, ultimately, the strength and integrity of the finished product.
The Shaping Process: Forming the "Green Body"
The powder is mixed with a binder to create a workable mass, which is then shaped into the desired geometry. This initial, unsintered part is known as a "green body."
Common forming methods include:
- Pressing: Compacting the powder in a die to form simple shapes.
- Casting: Pouring a ceramic slurry into a mold, ideal for complex shapes.
- Injection Molding: Forcing the ceramic mixture into a mold for high-volume, intricate parts.
The Transformation: Sintering
The green body is heated in a high-temperature furnace to a point below its melting temperature. This process, called sintering, causes the individual powder particles to fuse together.
During sintering, the spaces between particles are eliminated, causing the part to shrink and become incredibly dense and strong. This is the step that transforms the fragile green body into a robust technical ceramic.
Key Applications Driven by Core Properties
The final applications for ceramic components are a direct result of the unique properties locked in during the sintering process.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
Ceramics are among the hardest materials known. This makes them ideal for applications involving high friction and abrasion.
Examples include cutting tools, industrial pump components, ball bearings, and body armor plates. Materials like silicon carbide and alumina excel here.
High-Temperature Stability
Most ceramics maintain their strength and shape at temperatures that would cause metals to melt or deform.
This property is crucial for furnace linings, gas turbine engine components, heat shields on spacecraft, and crucibles for molten metal.
Electrical Insulation and Control
While most ceramics are excellent electrical insulators, some are engineered to have specific dielectric or piezoelectric properties.
They are foundational to electronics, used in spark plug insulators, substrates for microchips, capacitors, and sensors.
Biocompatibility and Chemical Inertness
Many advanced ceramics are non-reactive and are not rejected by the human body, making them ideal for medical use. Their chemical stability also makes them perfect for harsh industrial environments.
This leads to their use in dental implants, hip and knee joint replacements, and valves and pipes for handling corrosive chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. The exceptional strengths of ceramics come with inherent challenges that are critical to understand.
The Challenge of Brittleness
The primary drawback of ceramics is their low fracture toughness, or brittleness. While incredibly hard, they can fail suddenly and catastrophically when subjected to sharp impacts, unlike metals which tend to bend and deform.
Complexity in Processing and Machining
Sintering is an energy-intensive process that requires precise control. Furthermore, once a ceramic part is fully sintered, its extreme hardness makes it very difficult and expensive to machine or finish. Critical dimensions must be designed into the part before firing.
Sensitivity to Defects
The reliability of a ceramic component is highly dependent on the quality of the starting powder and the forming process. A tiny impurity, void, or microcrack introduced in the powder or green body can become a failure point in the final part.
Choosing the Right Ceramic for Your Goal
The selection process is about matching a material's inherent properties to the primary challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: Choose dense, fine-grained materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or alumina (Al₂O₃).
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: Prioritize materials with high melting points and thermal stability, such as zirconia (ZrO₂) or mullite.
- If your primary focus is a biomedical application: Select high-purity, proven biocompatible materials like yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) or specific grades of alumina.
- If your primary focus is an electronic application: Look for materials with specific dielectric strengths or constants, such as barium titanate for capacitors or alumina for insulators.
Understanding the journey from powder to solid part empowers you to leverage the extraordinary capabilities of technical ceramics for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Ceramic Materials | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Hardness & Wear Resistance | Alumina (Al₂O₃), Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Cutting tools, industrial pumps, body armor |
| High-Temperature Stability | Zirconia (ZrO₂), Mullite | Furnace linings, turbine engines, heat shields |
| Electrical Insulation/Control | Alumina, Barium Titanate | Spark plugs, microchip substrates, capacitors |
| Biocompatibility & Chemical Inertness | Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) | Dental/medical implants, valves for corrosive chemicals |
Ready to leverage the power of technical ceramics in your lab or production process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced material processing, including the precise furnaces essential for sintering ceramic powders. Whether you're in R&D or manufacturing, our solutions help you achieve the material properties critical for success in aerospace, medical, electronics, and industrial applications.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how we can support your specific ceramic processing needs and help you unlock superior performance and durability in your components.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Ceramic Sheet
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
People Also Ask
- Why are Beta-Al2O3 pellets covered with powder during sintering? Master Volatility Control for Better Ceramics
- What is the primary purpose of using zirconia coatings in W-Cu infiltration? Ensure Dense, Void-Free Composites
- Why is high-purity alumina (Al2O3) preferred over quartz for steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity at 1773 K
- What temperature is alumina activated? Unlock Optimal Porosity for Adsorption
- What physical changes occur during sintering of ceramic powders? Master the Transformation to Dense, Strong Parts
- What is SiC melting point? Discover the Extreme Thermal Stability of Silicon Carbide
- Why is ceramic sintering used? To transform fragile powder into a strong, dense solid.
- Why is density important in ceramics? It's the Key to Mechanical Strength and Performance



















