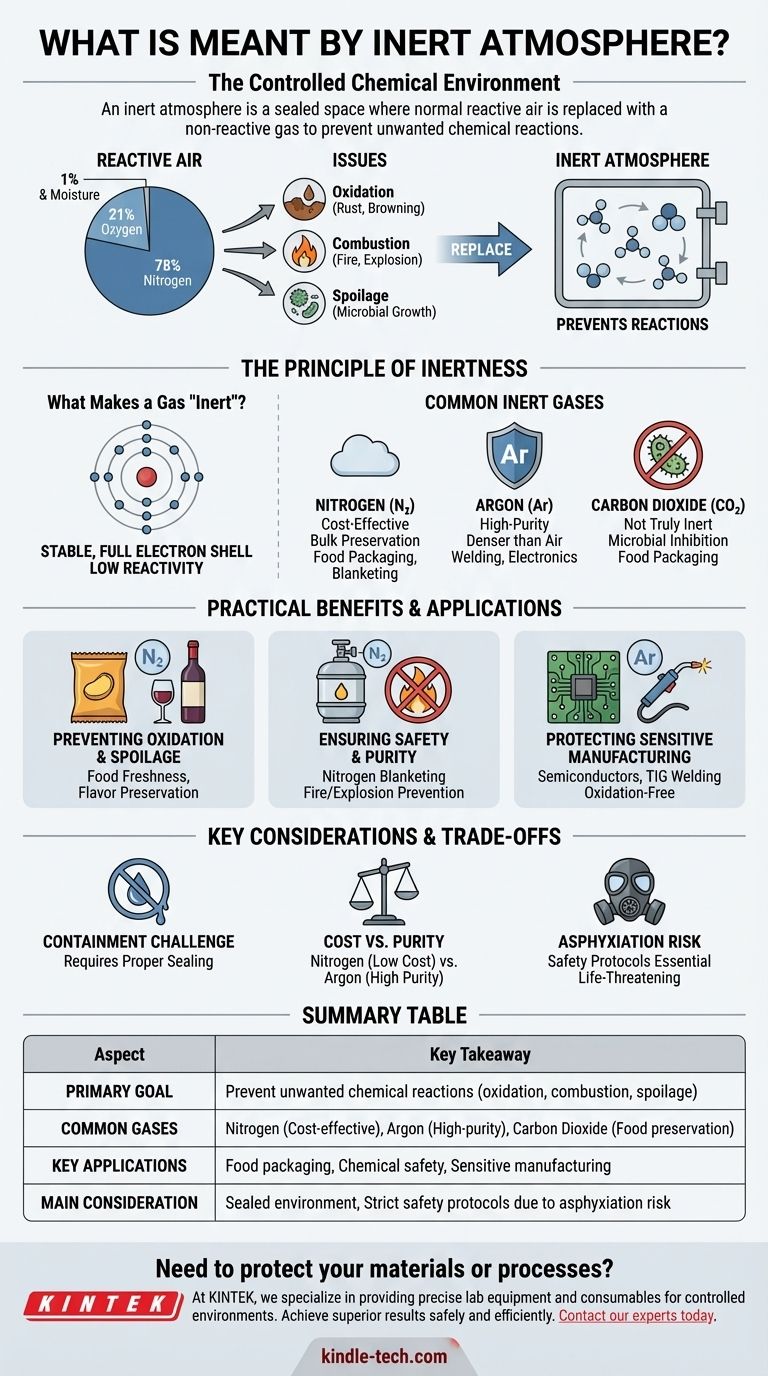
At its core, an inert atmosphere is a controlled environment where the normal, reactive air has been intentionally replaced with a non-reactive (or "inert") gas. This is done to prevent unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation or combustion, that would otherwise occur in the presence of oxygen.
The fundamental purpose of an inert atmosphere is not about the gas itself, but about what it removes: the oxygen and moisture from the air that cause materials to degrade, spoil, rust, or ignite.

The Problem: Reactive Air
The air we breathe is approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and has small amounts of other gases, including water vapor. For many industrial, scientific, and commercial processes, this composition is a significant liability.
Why Oxygen is Often an Issue
Oxygen is a highly reactive element. Its tendency to combine with other substances is responsible for common processes like rusting (oxidation of iron) and the browning of a cut apple. In more volatile situations, it is a key component of fire and explosions.
The Role of Moisture
Water vapor present in the air can also accelerate corrosion and provide an environment for microbial growth, leading to the spoilage of food or the contamination of sensitive materials.
The Principle of Inertness
Creating an inert atmosphere involves purging a sealed space of ambient air and refilling it with a gas that will not interfere with the product or process being protected.
What Makes a Gas "Inert"?
Inert gases are chemically stable because their outermost electron shell is full, meaning they have very little tendency to react with other elements. While true noble gases like Argon are the most inert, other gases like Nitrogen are non-reactive enough for most applications.
Common Gases Used
The choice of gas depends on the required level of inertness and budget.
- Nitrogen (N₂): By far the most common, as it is inexpensive and makes up the majority of our atmosphere, making it easy to source.
- Argon (Ar): More inert than nitrogen and denser than air. It is used for more sensitive applications like high-end welding and electronics manufacturing where even the slight reactivity of nitrogen is unacceptable.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): While not truly inert, it is often used in food packaging because it displaces oxygen and can inhibit the growth of some bacteria and molds.
Practical Benefits and Applications
The value of an inert atmosphere is demonstrated across a wide range of fields where control over the chemical environment is critical.
Preventing Oxidation and Spoilage
This is one of the most common uses. The air inside a bag of potato chips is replaced with nitrogen to prevent the oils from going rancid and to cushion the product. Similarly, winemakers use inert gases to protect wine from oxygen during bottling.
Ensuring Safety and Purity
In chemical processing plants, the air in vessels containing flammable liquids or powders is often replaced with nitrogen. This process, known as "nitrogen blanketing," removes the oxygen required for a fire or explosion, drastically improving safety.
Protecting Sensitive Manufacturing
During the manufacturing of semiconductors and electronics, even microscopic levels of oxidation can ruin a component. These processes are often conducted in chambers filled with a highly pure inert gas like argon. Welders also use a shield of inert gas to protect the molten weld pool from oxygen, which would weaken the final joint.
Key Considerations and Trade-offs
While powerful, implementing an inert atmosphere requires careful planning and understanding of its limitations.
The Challenge of Containment
An inert atmosphere is only effective if the container or room is properly sealed. Any leaks will allow oxygen and moisture to re-enter, defeating the purpose of the system.
Cost vs. Purity
There is a direct trade-off between the cost of the gas and its level of inertness. Nitrogen is sufficient for most bulk applications, but processes requiring absolute chemical purity demand more expensive gases like argon.
Critical Asphyxiation Risk
An atmosphere designed to prevent combustion is also an atmosphere that cannot support life. Any area flooded with an inert gas is an extreme asphyxiation hazard, as it contains little to no oxygen. Strict safety protocols are essential for any personnel working in or near these environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection and application of an inert atmosphere are dictated entirely by the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective preservation: Nitrogen is the standard choice for large-scale applications like food packaging, grain silos, and chemical tank blanketing.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing: Argon is the superior option for sensitive work like TIG welding, scientific research, and silicon wafer manufacturing where absolute non-reactivity is vital.
- If your primary focus is active microbial inhibition: A modified atmosphere including carbon dioxide is often used in meat and produce packaging to extend shelf life beyond simply preventing oxidation.
Ultimately, an inert atmosphere is a powerful tool for taking control of the chemical environment to protect and preserve sensitive materials and processes.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Prevent unwanted chemical reactions (oxidation, combustion, spoilage). |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (cost-effective), Argon (high-purity), Carbon Dioxide (food preservation). |
| Key Applications | Food packaging, chemical safety (blanketing), sensitive manufacturing (welding, electronics). |
| Main Consideration | Requires a sealed environment and strict safety protocols due to asphyxiation risk. |
Need to protect your materials or processes from oxygen and moisture?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to create and maintain controlled environments for your laboratory. Whether your goal is cost-effective preservation or high-purity processing, our solutions can help you achieve superior results safely and efficiently.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application with reliable inert atmosphere solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes



















