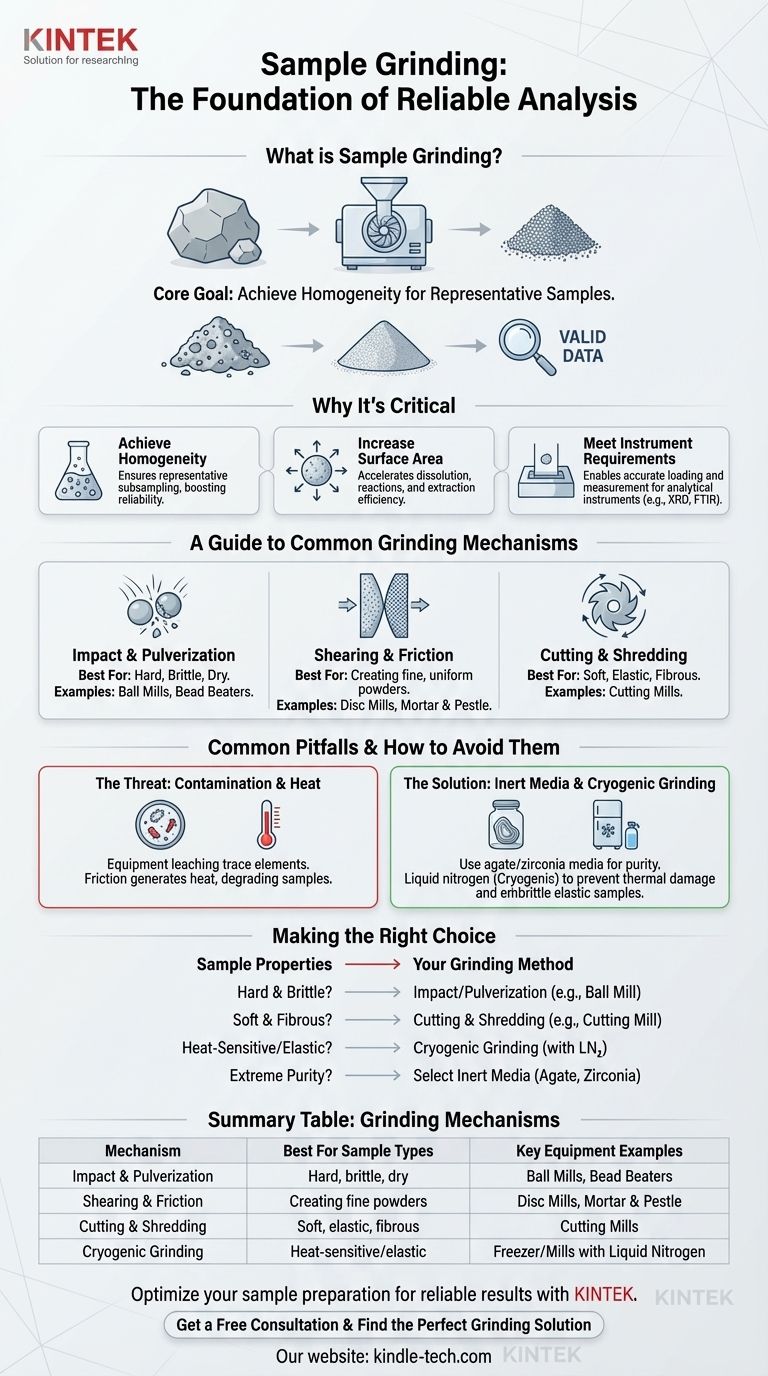
At its core, sample grinding is a mechanical process for reducing the size of a solid substance. It is a foundational sample preparation technique that transforms a large, potentially inconsistent material into a fine, homogenous powder. This ensures that any small portion taken for subsequent analysis is truly representative of the bulk material.
The primary goal of sample grinding isn't just to make things smaller; it's to achieve homogeneity. An improperly ground sample leads to non-representative subsampling, which invalidates even the most precise analytical results.

Why Sample Grinding is a Critical Step
Proper sample preparation is the bedrock of accurate analysis. Grinding is often the most important part of that preparation, directly influencing the quality and reliability of your data.
Achieving True Homogeneity
Most bulk materials are heterogeneous, meaning their composition varies from one point to another. Taking a small scoop from a bag of un-ground material is a gamble.
Grinding and mixing create a homogenous powder. This drastically increases the probability that a small subsample has the exact same chemical and physical composition as the original material.
Increasing Surface Area
Breaking a sample into smaller particles dramatically increases its total surface area. This is critical for processes that depend on surface interactions.
A larger surface area accelerates dissolution rates, improves the efficiency of chemical extractions, and can speed up reaction kinetics.
Meeting Instrument Requirements
Many analytical instruments simply cannot accept large or irregularly shaped samples.
Techniques like X-ray diffraction (XRD), infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and various chromatographic methods require samples to be fine, uniform powders to ensure proper loading and accurate measurement.
A Guide to Common Grinding Mechanisms
The ideal grinding method depends entirely on the physical properties of your sample. The primary mechanisms are based on applying different types of force.
Impact and Pulverization
This method uses high-speed collisions to shatter material. It is highly effective for hard, brittle, and dry samples.
Common examples include ball mills (where grinding balls tumble in a rotating jar) and bead beaters (using tiny beads for smaller, often biological, samples).
Shearing and Friction
Shearing involves grinding particles between two solid surfaces moving relative to one another. This is excellent for creating very fine, uniform powders.
The classic mortar and pestle is a manual example. Automated disc mills operate on the same principle for higher throughput.
Cutting and Shredding
This mechanism is essential for samples that are soft, elastic, or fibrous. Impact or friction would simply cause these materials to deform, melt, or tangle.
Cutting mills use rotating knives against stationary blades to cleanly chop the material, making them ideal for plant matter, polymers, and textiles.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
The process of grinding can introduce its own errors and artifacts if not managed carefully. Awareness of these trade-offs is key to generating reliable data.
The Threat of Contamination
The grinding equipment itself can be a source of contamination. A steel ball mill can leach trace amounts of iron, chromium, and nickel into your sample.
To avoid this, select grinding media made from a material that will not interfere with your downstream analysis. Common choices include agate, zirconia, tungsten carbide, and polymers.
The Problem of Heat Generation
All grinding methods generate heat through friction. This heat can be intense enough to degrade thermally sensitive samples.
This can lead to the loss of volatile compounds, changes in crystalline structure, or the degradation of biological molecules like proteins and RNA.
The Solution: Cryogenic Grinding
For heat-sensitive or highly elastic samples (like rubber), cryogenic grinding is the solution.
The sample is embrittled by immersing it in liquid nitrogen before and during the grinding process. This makes it hard and brittle for easy shattering while also keeping it frozen, preventing any thermal damage.
Controlling Final Particle Size
The final particle size is a critical parameter. It is controlled by the grinding time, the energy input, and the type of equipment used.
For many applications, grinding is followed by sieving to isolate a specific and narrow particle size range, further ensuring uniformity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sample
Your sample's physical properties are the ultimate guide to selecting the correct grinding method. Consider your material and your analytical goal to make an informed decision.
- If your sample is hard and brittle (e.g., minerals, ceramics): Focus on impact-based methods like ball milling or use a jaw crusher for initial large-scale reduction.
- If your sample is soft and fibrous (e.g., plant tissue, paper): A cutting mill is necessary to cleanly shred the material without melting or tangling it.
- If your sample is heat-sensitive or elastic (e.g., polymers, fatty tissues): Cryogenic grinding is almost certainly required to make the material brittle and prevent thermal degradation.
- If your analysis requires extreme purity (e.g., trace metal analysis): Choose your grinding media carefully (e.g., agate or zirconia) to avoid elemental contamination from steel components.
Ultimately, mastering sample grinding is mastering the first and most critical step towards reliable and reproducible scientific data.
Summary Table:
| Grinding Mechanism | Best For Sample Types | Key Equipment Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Impact & Pulverization | Hard, brittle, dry materials | Ball Mills, Bead Beaters |
| Shearing & Friction | Creating fine, uniform powders | Disc Mills, Mortar & Pestle |
| Cutting & Shredding | Soft, elastic, fibrous materials | Cutting Mills |
| Cryogenic Grinding | Heat-sensitive or elastic materials | Freezer/Mills with Liquid Nitrogen |
Ready to optimize your sample preparation for reliable results?
Proper grinding is the foundation of accurate analysis. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of mills and grinding media tailored to your specific sample type—from hard ceramics to heat-sensitive polymers.
We can help you select the right equipment to prevent contamination, control particle size, and achieve true sample homogeneity. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and ensure your lab's success from the very first step.
Get a Free Consultation & Find the Perfect Grinding Solution
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.
- Why is a ball mill jar lined with Y-ZrO2 required for Na3PS4 synthesis? Ensuring Purity in Sulfide Electrolytes
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) milling jars recommended for sulfide electrolytes? Ensure Purity in Li6PS5Cl Synthesis



















