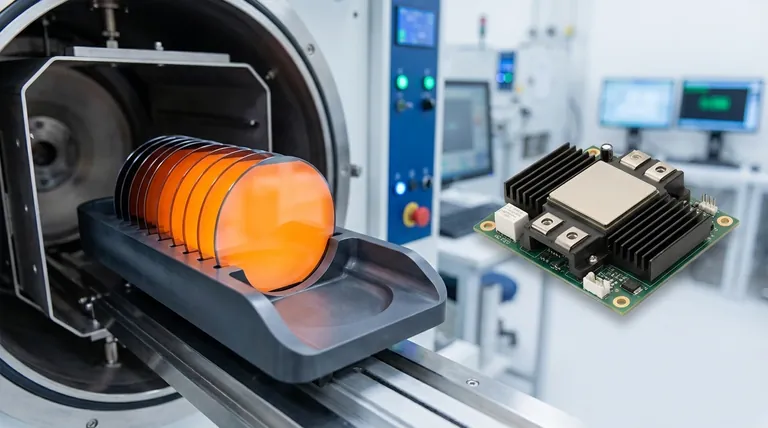
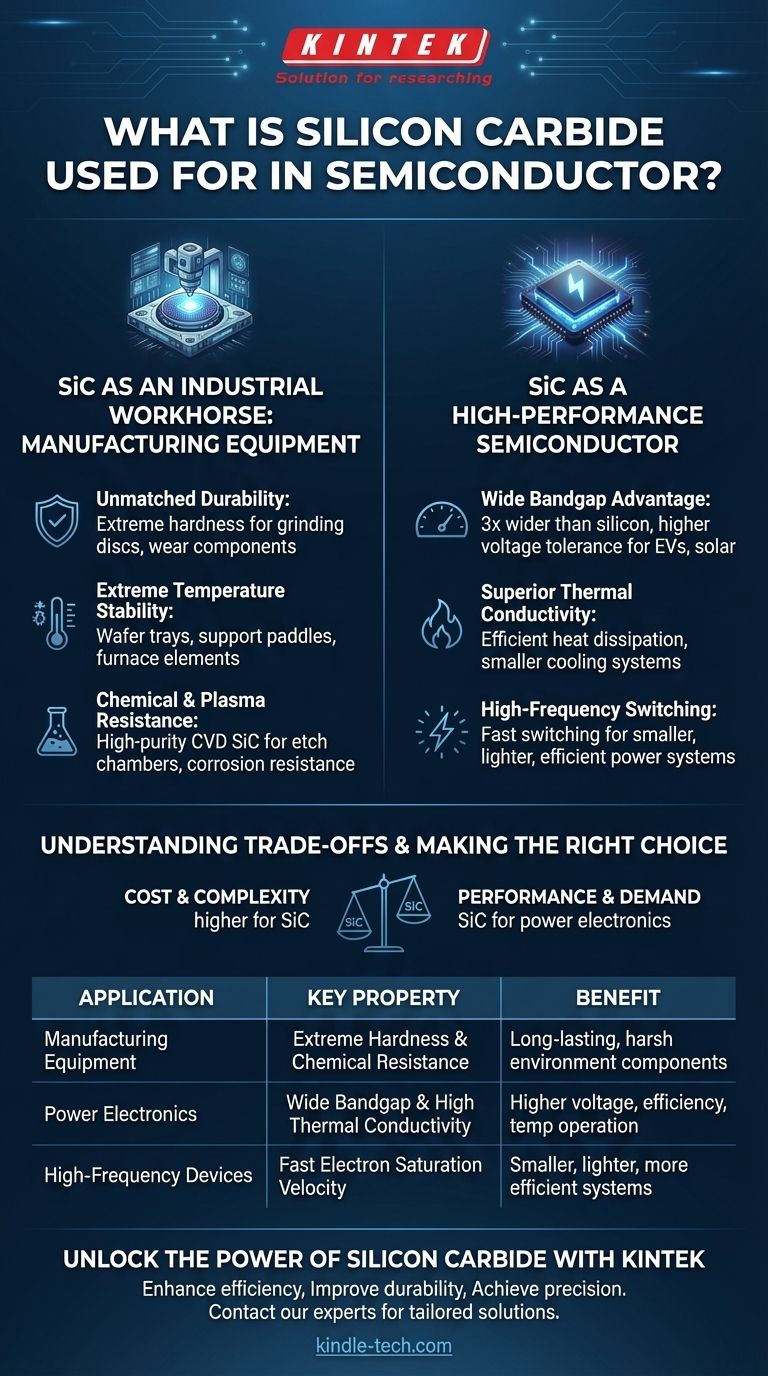
In the semiconductor industry, silicon carbide (SiC) serves two distinct and critical functions. It is used both as an ultra-durable support material for manufacturing equipment and as a high-performance semiconductor material itself, enabling devices that operate at higher powers, temperatures, and frequencies than traditional silicon.
The core reason for silicon carbide's adoption is its exceptional resilience. Its unique combination of hardness, thermal stability, and electrical properties allows it to both withstand the brutal conditions of chip manufacturing and outperform silicon in demanding power electronics applications.

The Dual Roles of Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide is not just one thing in the world of semiconductors. Its application is best understood by separating its use into two primary categories: as a structural material for building the tools that make chips, and as the active material from which high-performance chips are made.
SiC as an Industrial Workhorse: Manufacturing Equipment
Long before it was widely used for chips, SiC was valued for its physical toughness. This has made it an indispensable material for constructing the sophisticated machinery used in semiconductor fabrication.
Unmatched Durability in Harsh Environments
Silicon carbide possesses extreme hardness, second only to diamond. This makes it ideal for components that experience significant physical wear.
It is used for grinding discs and fixtures during wafer production, where its hardness ensures precision and a long operational life. Its resistance to erosion is also critical in modern fabrication plants.
Stability at Extreme Temperatures
Semiconductor manufacturing involves incredibly high temperatures. SiC maintains its structural integrity and strength when other materials would fail.
Because of this, it is frequently used for wafer trays, support paddles, and even heating elements inside high-temperature industrial furnaces for processing silicon wafers.
Resistance to Chemical and Plasma Attack
Modern chipmaking relies on aggressive processes like plasma etching to carve intricate circuits. These processes create highly corrosive environments that can destroy lesser materials.
High-purity CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) silicon carbide is used for critical components inside etch chambers because it resists erosion from high-energy plasmas and harsh chemicals, ensuring process stability and reducing contamination.
SiC as a High-Performance Semiconductor
Beyond its role in manufacturing, SiC is a "wide bandgap" semiconductor material. This allows it to create electronic devices that can operate far beyond the physical limits of conventional silicon.
The "Wide Bandgap" Advantage
The bandgap of a semiconductor determines the voltage it can withstand. SiC has a bandgap roughly three times wider than silicon's.
This fundamental difference means SiC devices can block significantly higher voltages, making them ideal for high-power applications like electric vehicles, solar inverters, and industrial motor drives.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
Power electronics generate a lot of heat, which is a primary cause of failure. SiC is exceptionally good at conducting heat away from the active parts of a device.
This high thermal conductivity allows SiC-based electronics to run cooler, operate at higher temperatures, and require smaller, less complex cooling systems.
Enabling High-Frequency Switching
SiC also possesses a high electron saturation velocity. In practical terms, this allows devices to be switched on and off much faster than silicon-based equivalents.
Faster switching leads to higher efficiency and allows for smaller supporting components (like capacitors and inductors), resulting in power systems that are lighter, smaller, and more energy-efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, SiC is not a universal replacement for silicon. Its adoption involves specific considerations and is concentrated where its benefits are most needed.
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Producing high-quality, defect-free SiC crystals is significantly more difficult and expensive than producing silicon wafers. This cost difference is a primary reason why silicon remains the dominant material for the vast majority of electronics.
A Material for Specific Demands
SiC does not compete with silicon in applications like computer processors or memory chips. Its strengths are specifically in power electronics. For low-power or cost-sensitive applications, silicon remains the undisputed and more practical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use silicon carbide is driven entirely by the performance demands of the end product or manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is building durable semiconductor manufacturing equipment: Use high-purity CVD SiC for components exposed to high temperatures, corrosive plasma, and physical wear.
- If your primary focus is designing high-efficiency power electronics: Use SiC as the semiconductor material to manage higher voltages, operate at higher temperatures, and achieve faster switching speeds.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose computing or low-power devices: Traditional silicon remains the more established and cost-effective solution for these applications.
Ultimately, silicon carbide empowers the next generation of high-performance electronics by pushing the boundaries where traditional silicon cannot go.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Property | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Equipment | Extreme Hardness & Chemical Resistance | Long-lasting components for harsh environments like plasma etching |
| Power Electronics | Wide Bandgap & High Thermal Conductivity | Higher voltage tolerance, efficiency, and temperature operation than silicon |
| High-Frequency Devices | Fast Electron Saturation Velocity | Enables smaller, lighter, and more efficient power systems |
Unlock the Power of Silicon Carbide with KINTEK
Whether you are developing next-generation power electronics or require ultra-durable components for your semiconductor manufacturing equipment, KINTEK has the expertise and solutions to meet your needs. We specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including SiC-based products designed for extreme conditions.
Let us help you:
- Enhance efficiency with SiC's superior thermal and electrical properties.
- Improve durability in harsh manufacturing environments.
- Achieve precision with reliable, high-purity materials.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory and semiconductor projects. Reach out via our contact form for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Versatile PTFE Solutions for Semiconductor and Medical Wafer Processing
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer CaF2 Substrate Window Lens
People Also Ask
- What are the recommended and prohibited cleaning methods for the PTFE electrode stand? Protect Your Lab Equipment
- Why is high-purity PTFE selected as the sample holder for zirconium alloy corrosion tests? Gain Unmatched Data Accuracy
- How should the PTFE electrode stand and its components be cleaned after use? A Step-by-Step Guide to Prevent Contamination
- How can corrosion of the sample holder be prevented when using corrosive chemicals? Protect Your Lab's Integrity
- What materials are the sample holders made of? Engineered with PTFE and PEEK for Purity



















