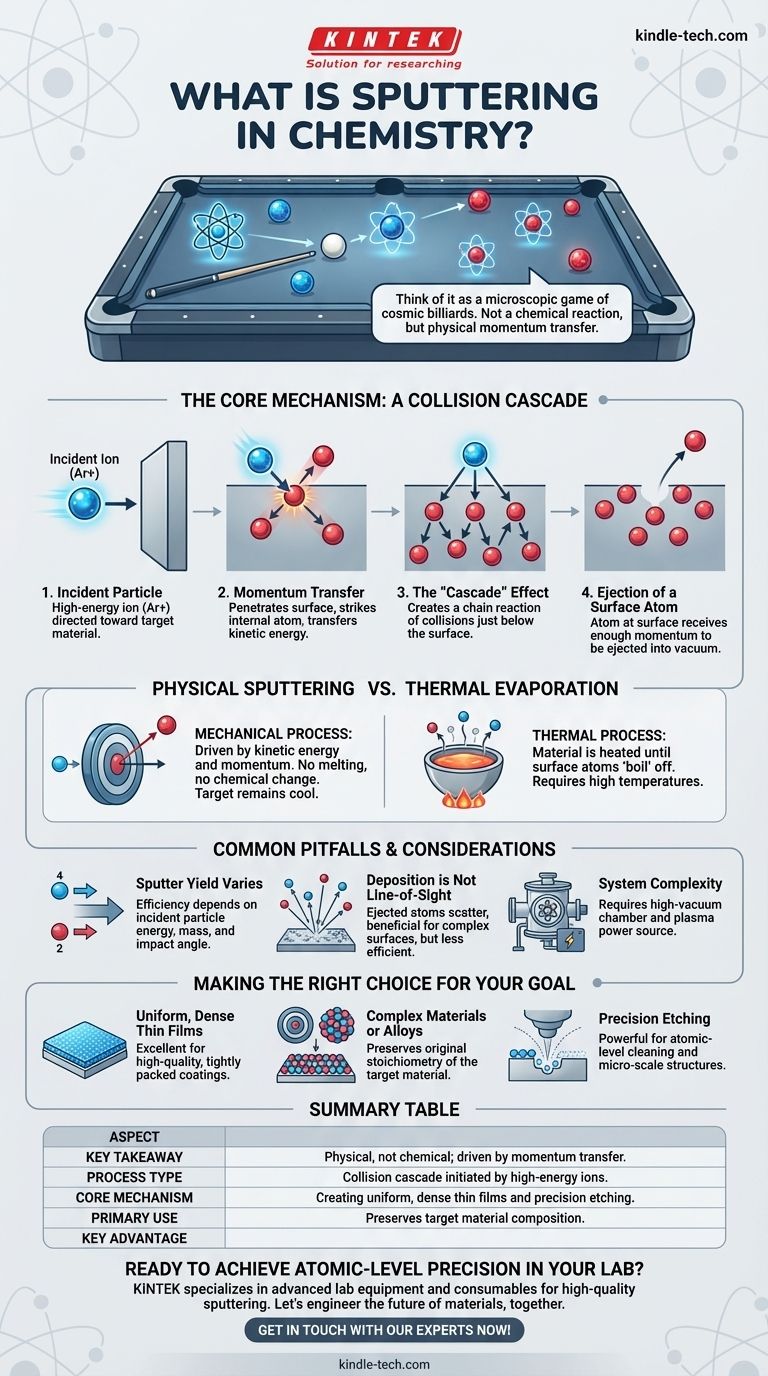
In the simplest terms, sputtering is a physical process where atoms are ejected from a solid material's surface when that surface is bombarded by energetic particles. This process is a direct consequence of momentum transfer, where the incoming particle initiates a chain reaction of collisions within the material, ultimately knocking a surface atom loose.
Think of sputtering not as a chemical reaction, but as a microscopic game of cosmic billiards. An incoming particle acts as the cue ball, striking atoms within a target material. This sets off a chain reaction that transfers energy and momentum until a surface atom is ejected, much like a ball being knocked out of the rack.
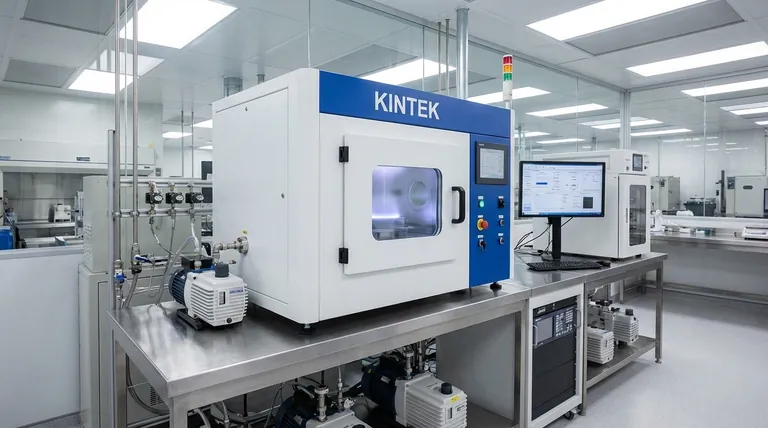

The Core Mechanism: A Collision Cascade
The term "sputtering" describes the outcome, but the process that enables it is known as a collision cascade. Understanding this chain reaction is key to understanding the entire phenomenon.
The Incident Particle
The process begins when a high-energy particle, typically an ion from a plasma (like Argon, Ar+), is accelerated and directed toward a target material. This is the "incident radiation" that initiates the action.
Momentum Transfer
Unlike chipping away at a surface, the incident particle usually penetrates a few atomic layers deep into the target. It then collides with an atom inside the material, transferring its kinetic energy and momentum, similar to one billiard ball striking another.
The "Cascade" Effect
The atom that was struck now has enough energy to move and collide with its neighbors. Each of those neighbors, in turn, collides with others. This creates an expanding, branching series of atomic collisions just below the surface—the collision cascade.
Ejection of a Surface Atom
For sputtering to occur, this cascade of collisions must work its way back toward the surface. When an atom at the surface receives enough momentum from a collision below it to overcome the forces holding it to the material, it is ejected into the vacuum. This ejected atom is the "sputtered" particle.
Physical Sputtering vs. Other Processes
The reference specifically identifies this process as physical sputtering. This distinction is critical because it separates it from other methods of material removal or deposition.
The Defining Factor: Kinetic Energy
Physical sputtering is a purely mechanical process driven by kinetic energy and momentum. It does not rely on heat to melt or evaporate the material, nor does it involve chemical reactions to change the material's composition before removal.
How It Differs from Evaporation
In thermal evaporation, a material is heated in a vacuum until its surface atoms "boil" off. This is a thermal process. Sputtering, by contrast, is a kinetic process that can occur with a target that remains relatively cool.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, sputtering is a complex process with important variables that must be controlled for it to be effective and repeatable.
Sputter Yield is Not Universal
The efficiency of the process, known as sputter yield, is the number of atoms ejected for each incoming ion. This yield varies significantly depending on the energy of the incident particle, the mass of the ion and target atoms, and the angle of impact.
Deposition is Not Line-of-Sight
Sputtered atoms are ejected from the target in many directions. While this can be advantageous for coating complex, non-flat surfaces, it also means that the process can be less efficient than highly directional line-of-sight techniques like evaporation.
System Complexity
Practical sputtering requires a significant investment in equipment. It must be performed in a high-vacuum chamber to ensure the sputtered atoms can travel without colliding with air molecules, and it requires a power source to generate the plasma of incident ions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sputtering is chosen for its unique advantages in precision and material control. It is a cornerstone of modern materials science, particularly in semiconductor fabrication and optics.
- If your primary focus is creating highly uniform, dense thin films: Sputtering is an excellent choice because the high kinetic energy of the sputtered atoms helps them form a tightly packed, high-quality coating on a substrate.
- If your primary focus is depositing complex materials or alloys: Sputtering excels because it generally preserves the original composition (stoichiometry) of the target material in the resulting film.
- If your primary focus is atomic-level surface cleaning or precision etching: The controlled, physical removal of atoms makes sputtering a powerful tool for preparing substrates or fabricating micro-scale structures.
Understanding sputtering as a controlled collision process unlocks its potential as a foundational tool for engineering materials at the atomic scale.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical, not chemical; driven by momentum transfer. |
| Core Mechanism | Collision cascade initiated by high-energy ions (e.g., Ar+). |
| Primary Use | Creating uniform, dense thin films and precision etching. |
| Key Advantage | Preserves target material composition in the deposited film. |
Ready to achieve atomic-level precision in your lab?
Sputtering is a cornerstone technique for creating high-quality thin films and surface modifications. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables you need to implement sputtering effectively. Our solutions are designed to help you achieve superior results in semiconductor fabrication, optics, and materials science research.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can support your specific laboratory goals. Let's engineer the future of materials, together.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















