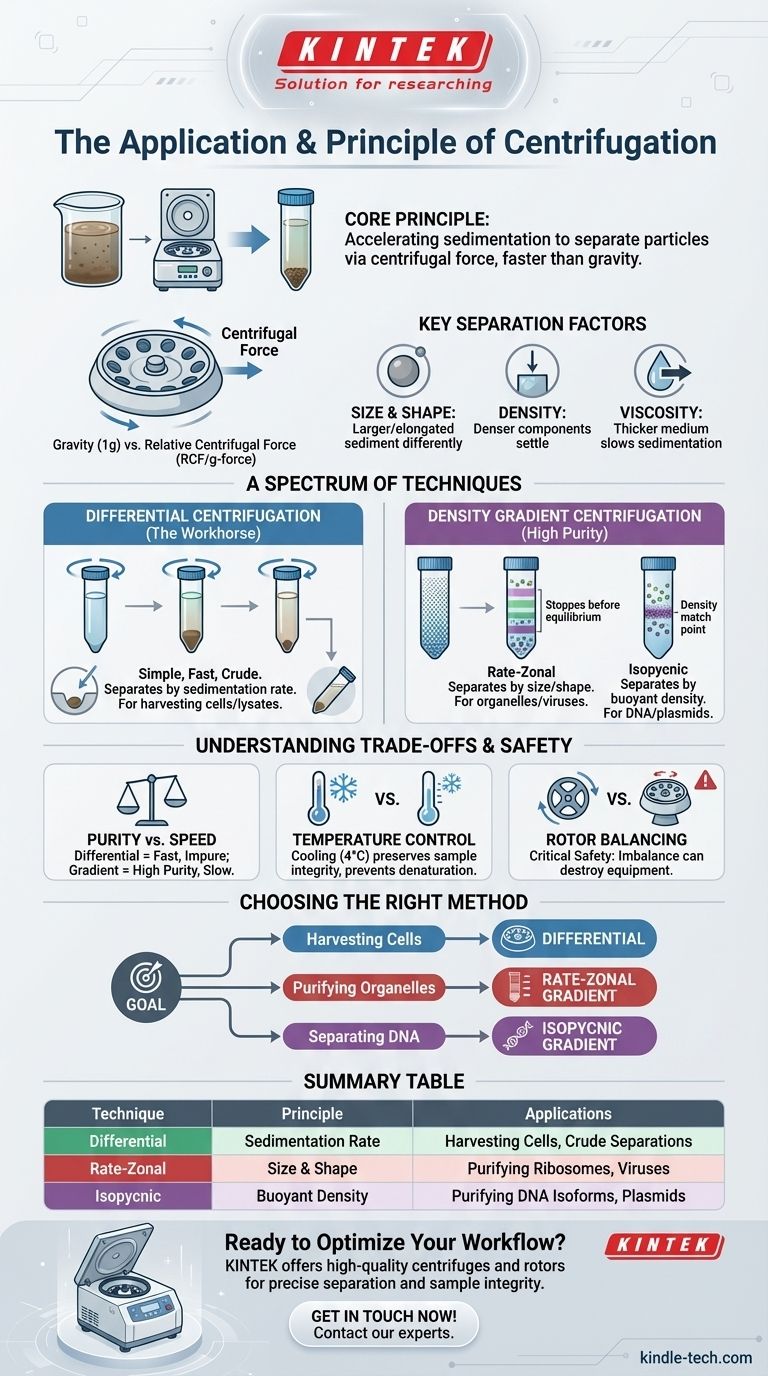
At its core, centrifugation is a technique that uses centrifugal force to separate particles from a solution. The fundamental principle is to accelerate the natural process of sedimentation, where denser components settle out of a mixture over time. By spinning samples at high speed, a centrifuge generates a powerful force that can separate components based on their size, shape, and density in a fraction of the time gravity would require.
The true power of centrifugation lies not in simply spinning samples, but in the precise application of force to exploit subtle physical differences between particles, enabling their selective isolation from a complex mixture.
The Fundamental Principle: Harnessing Sedimentation
Centrifugation is a cornerstone of modern biology, chemistry, and medicine because it provides a reliable way to purify and concentrate components from a liquid sample. Understanding the physics behind it is key to using it effectively.
From Gravity to G-Force
Imagine a glass of muddy water. Over time, the denser sand and silt particles will slowly settle to the bottom due to gravity. A centrifuge radically accelerates this process.
By spinning samples in a rotor, the machine creates a centrifugal force that acts outward, away from the center of rotation. This force pushes denser and larger particles toward the bottom of the tube much faster than gravity alone, forming a compact pellet.
What is Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF)?
The speed of the rotor is often described in revolutions per minute (RPM), but this metric is incomplete. The actual separating force depends on the radius of the centrifuge rotor.
The true measure of the force applied is Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF), also known as g-force. RCF standardizes the force across different machines and rotors, making it the critical parameter for any centrifugation protocol. It represents how many times stronger the centrifugal force is than Earth's gravitational force.
The Key Factors Influencing Separation
A particle's movement in a centrifugal field is determined by four main properties:
- Size and Shape: Larger or more elongated particles experience more drag and sediment differently than small, spherical ones.
- Density: A particle denser than the surrounding liquid (the medium) will sediment and move toward the bottom of the tube. A particle less dense will float.
- Viscosity of the Medium: A thicker, more viscous liquid will create more friction, slowing down the rate of sedimentation for all particles.
A Spectrum of Techniques for Diverse Applications
Not all centrifugation is the same. The method is chosen based on the components to be separated and the required level of purity.
Differential Centrifugation: The Workhorse Method
This is the simplest and most common technique. It involves subjecting a sample to a series of centrifugation cycles at progressively higher speeds.
After each spin, the settled material (pellet) is separated from the remaining liquid (supernatant). The supernatant is then spun again at a higher RCF to pellet out the next smallest and less dense components. This is often used for crude separations, like isolating intact cells from culture medium or separating major cell organelles.
Density Gradient Centrifugation: For High-Purity Separations
For more refined separations where components have similar sizes, a density gradient is used. This involves creating a solution in the centrifuge tube that gradually increases in density from top to bottom, often using sucrose or caesium chloride (CsCl).
When the sample is spun through this gradient, particles migrate until they reach a point where their density matches the surrounding medium, or they are separated into distinct bands based on their sedimentation rate.
Rate-Zonal vs. Isopycnic Separation
Density gradient centrifugation has two primary modes:
- Rate-Zonal: Particles are separated primarily based on their size and shape (their sedimentation rate). The run is stopped before particles reach their density equilibrium point. This is ideal for separating particles of similar density but different sizes, like ribosomes and polysomes.
- Isopycnic: Particles are separated purely based on their buoyant density. The centrifugation run is long enough for each particle to migrate to a point in the gradient where its density is equal to the density of the gradient medium. At this point, it stops moving. This powerful method can separate macromolecules like different isoforms of DNA.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a centrifugation method requires balancing speed, purity, and sample integrity.
Purity vs. Contamination
Differential centrifugation is fast and simple but often results in impure pellets. Because the only factor is sedimentation, smaller particles that start near the bottom of the tube can be co-pelleted with larger particles, leading to cross-contamination.
Density gradient centrifugation provides much higher purity by separating particles into distinct bands. However, it is significantly more time-consuming and technically complex to prepare and run the gradients.
The Critical Role of Temperature Control
The friction of a rotor spinning at high speeds generates significant heat. For biological samples like proteins or nucleic acids, this heat can cause denaturation, destroying their structure and function.
Therefore, most high-speed centrifuges (ultracentrifuges) are refrigerated to maintain a constant, cool temperature (typically 4°C) throughout the run, preserving sample integrity.
The Most Common Pitfall: An Unbalanced Rotor
The single most critical safety practice is balancing the centrifuge. The tubes placed in the rotor must be balanced with another tube of identical mass directly opposite.
An imbalanced load at high speeds creates immense vibration and torque that can destroy the rotor and the centrifuge itself, posing a severe safety hazard. Even a slight imbalance can cause damage over time and lead to suboptimal separation.
Choosing the Right Centrifugation Method
Your choice of technique should be dictated by your ultimate analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is harvesting cells or collecting a crude lysate: Differential centrifugation is the fastest and most efficient method.
- If your primary focus is purifying specific organelles or viruses: Rate-zonal density gradient centrifugation will provide the necessary resolution to separate components by size.
- If your primary focus is separating molecules with different buoyant densities, like plasmids from chromosomal DNA: Isopycnic density gradient centrifugation is the gold standard for achieving the highest purity.
By understanding these principles, you transform the centrifuge from a simple spinner into a precise and powerful tool for purification and analysis.
Summary Table:
| Centrifugation Technique | Primary Principle | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Differential Centrifugation | Sedimentation rate at increasing speeds | Harvesting cells, crude organelle separation |
| Rate-Zonal (Density Gradient) | Separation by size and shape | Purifying ribosomes, viruses, organelles |
| Isopycnic (Density Gradient) | Separation by buoyant density | Purifying DNA isoforms, plasmids |
Ready to Optimize Your Lab's Centrifugation Workflow?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable centrifuges and rotors designed for precise separation and sample integrity. Whether you need equipment for differential centrifugation or high-purity density gradient separations, our solutions are built to meet the demanding needs of modern laboratories.
Contact us today to discuss how our centrifugation equipment can enhance your research and purification processes. Let our experts help you select the perfect tool for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the speed of a sieving machine? Optimize Vibration for Maximum Efficiency and Accuracy
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- What are the different types of sieving machines? Choose the Right Motion for Your Material
- What are the applications of sieving machine? From Mining to Pharmaceuticals
- What does a vibrating sieve do? Automate Particle Size Analysis for Accurate Results



















