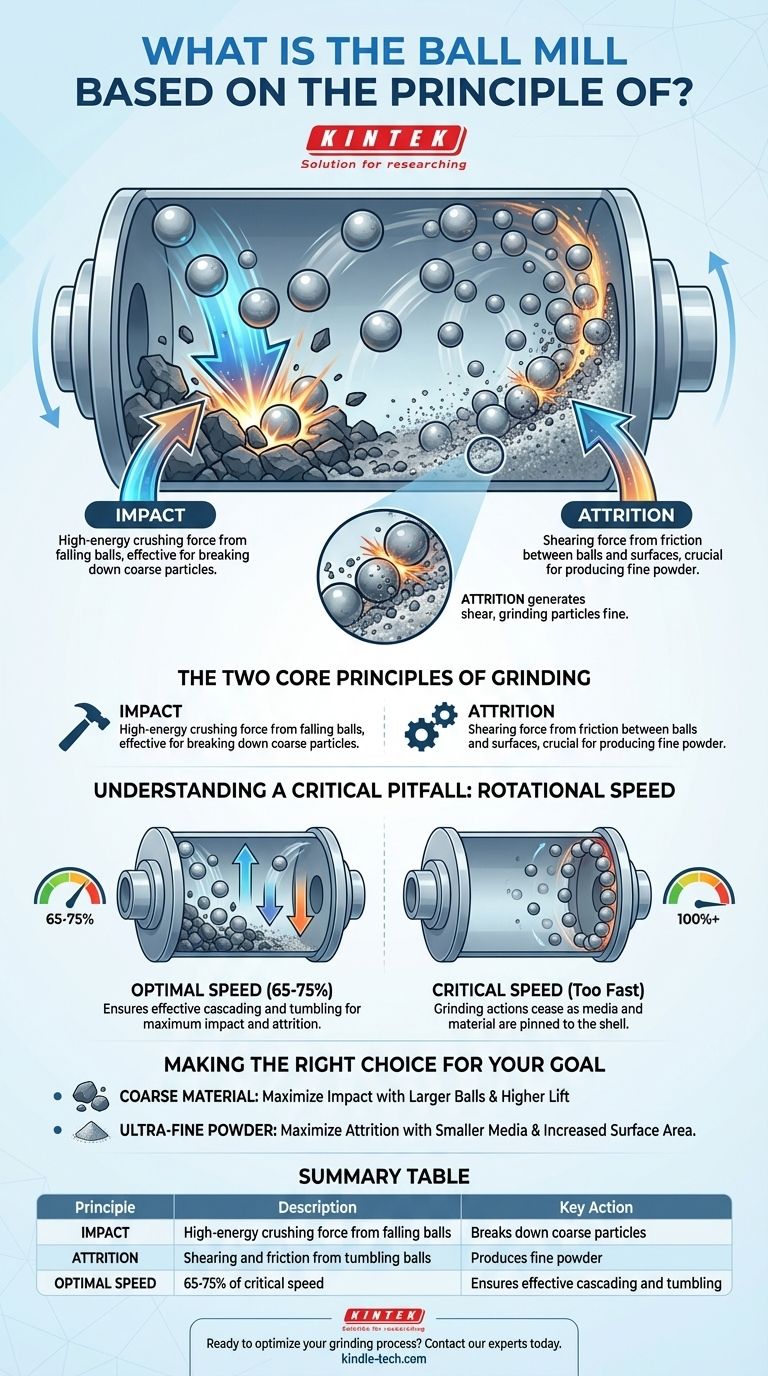
At its core, a ball mill operates on the combined principles of impact and attrition. Inside a rotating cylinder, heavy grinding media (like steel balls) are lifted and then fall, creating a powerful impact that smashes the material. Simultaneously, as these balls tumble and rub against each other and the material, they generate attrition, a shearing force that grinds the particles into a fine powder.
The essential function of a ball mill is to use the controlled, chaotic motion of tumbling media within a rotating drum to systematically crush and grind materials down to a desired particle size.

Deconstructing the Ball Mill's Operation
To grasp the principles, you must first visualize the machine's components and their coordinated movement. The design is mechanically simple but highly effective.
The Rotating Cylinder
A ball mill is fundamentally a hollow cylinder or shell that rotates on a horizontal axis. The material to be ground is fed into one end, and the finely ground product is discharged from the other.
The Grinding Media
The cylinder is partially filled, typically to about 30% of its volume, with grinding media. These are most often hard steel or ceramic balls, though rods or pebbles can also be used.
The Grinding Process in Motion
As the cylinder rotates, it carries the grinding media and the material up its inner wall. The effectiveness of the entire process depends on what happens next, which is dictated by the speed of this rotation.
The Two Core Principles of Grinding
The actual size reduction happens through two distinct but complementary actions occurring simultaneously inside the mill.
Principle 1: Impact
As the balls are lifted by the rotating wall, they reach a point where gravity overcomes the forces holding them to the shell. They then cascade and drop, falling onto the material at the bottom of the mill.
This fall creates a high-energy impact, a crushing force that is highly effective at breaking down larger, coarser particles into smaller pieces.
Principle 2: Attrition
Attrition is the grinding action that results from friction and shear. As the mass of balls tumbles, the individual balls rub and slide against one another and against the cylinder's inner surface.
Material caught between these moving surfaces is subjected to intense shearing forces, wearing it down into a very fine powder. This action is crucial for achieving the final desired fineness.
Understanding a Critical Pitfall: Rotational Speed
The efficiency of a ball mill is almost entirely dependent on operating it at the correct speed. The wrong speed can render the machine ineffective.
The Concept of "Critical Speed"
Critical speed is the specific rotational speed at which the centrifugal force is so great that it pins the grinding media and material against the inner wall of the cylinder.
When this happens, the balls no longer tumble or fall. They simply rotate with the shell, and the grinding actions of both impact and attrition cease completely.
The Importance of Optimal Speed
A ball mill must operate at a percentage below its critical speed, typically around 65-75%.
If the speed is too slow, the balls will just roll at the bottom of the mill, producing minimal impact. If it's too fast, it approaches critical speed and the grinding stops. The optimal speed ensures the balls are lifted high enough for a powerful impact while still allowing for a constant cascading and tumbling motion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the two core principles allows you to optimize the process for a specific outcome, as ball mills are used for everything from mineral processing to making paint pigments and ceramics.
- If your primary focus is breaking down coarse material: You want to maximize the impact force by using larger grinding balls and an operating speed that elevates them as high as possible before they fall.
- If your primary focus is producing an ultra-fine powder: You want to maximize the attrition force by using smaller media, which increases the total surface area and the number of contact points for grinding.
Ultimately, the ball mill's genius lies in its simplicity, using gravity and friction to transform coarse solids into fine powder through a controlled, continuous process.
Summary Table:
| Principle | Description | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| Impact | High-energy crushing force from falling balls | Breaks down coarse particles |
| Attrition | Shearing and friction from tumbling balls | Produces fine powder |
| Optimal Speed | 65-75% of critical speed | Ensures effective cascading and tumbling |
Ready to optimize your grinding process?
Whether your goal is coarse crushing or producing ultra-fine powders, the right ball mill is critical for your lab's efficiency and results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including ball mills tailored to your specific material and particle size requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior grinding performance and enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination
- Why is a ball mill jar lined with Y-ZrO2 required for Na3PS4 synthesis? Ensuring Purity in Sulfide Electrolytes
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results
- What is the benefit of using tungsten carbide (WC) milling jars and balls? Achieve High-Energy Milling Efficiency
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.



















