At its core, X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) is a powerful method for atomic-level detective work. It uses a focused beam of X-rays to excite the atoms within a sample, causing them to emit a secondary set of X-rays in response. These secondary X-rays act as a unique "fingerprint" for each element, allowing the instrument to identify which elements are present and in what quantities, all without damaging the material.
XRF operates on a fundamental principle of atomic physics: when a high-energy X-ray dislodges an inner-shell electron, a higher-energy electron drops to fill the vacancy, releasing a secondary, "fluorescent" X-ray. The energy of this secondary X-ray is unique to the element it came from, while its intensity reveals the element's concentration.

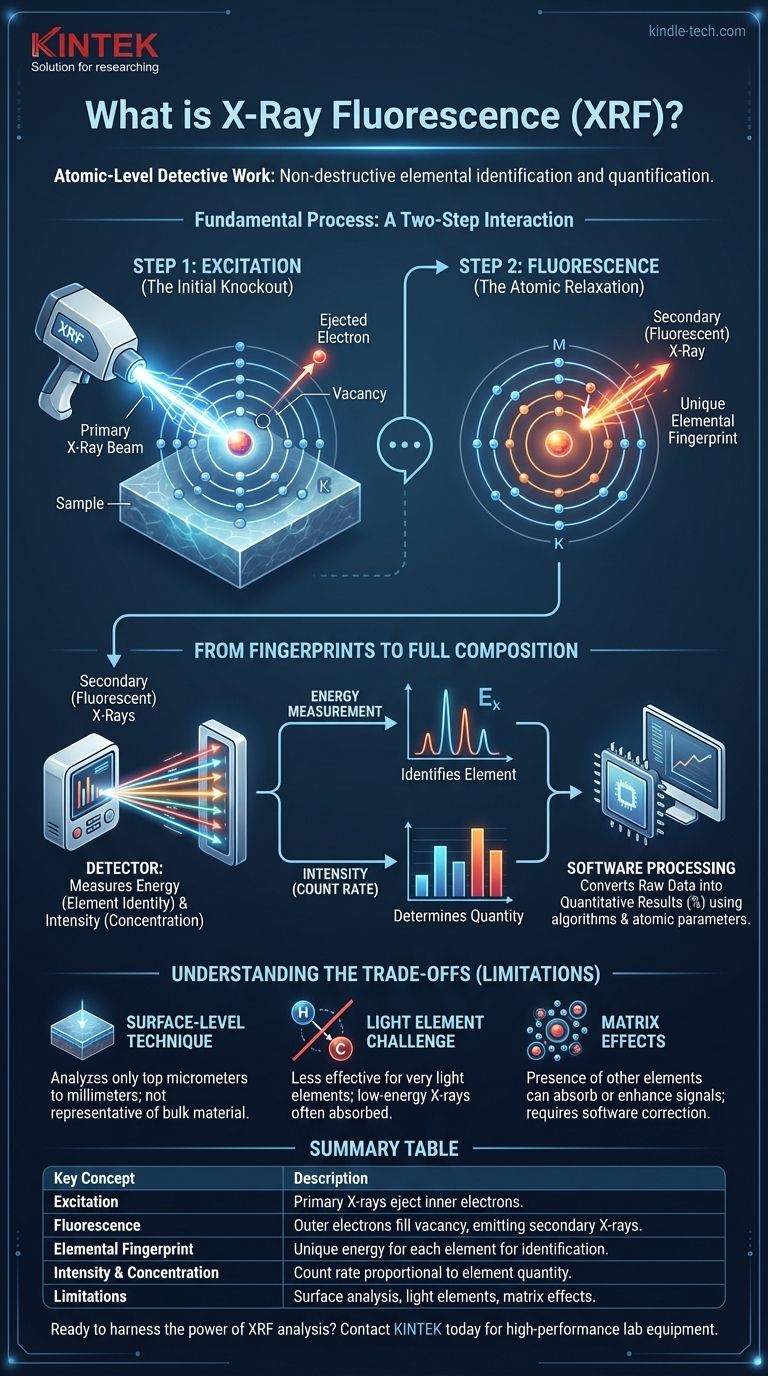
The Fundamental Process: A Two-Step Interaction
To understand XRF, you must visualize what happens to a single atom during analysis. The entire process unfolds in two distinct, near-instantaneous steps.
Step 1: Excitation - The Initial Knockout
An XRF analyzer first directs a beam of primary X-rays onto the surface of your sample. These high-energy X-rays penetrate the sample and collide with the atoms that compose it.
When a primary X-ray strikes an atom with sufficient force, it can knock an electron out of one of the atom's inner orbital shells (most commonly the "K" or "L" shell).
This event creates a vacancy, leaving the atom in an unstable, high-energy state.
Step 2: Fluorescence - The Atomic Relaxation
Nature abhors this kind of instability. To return to a stable, lower-energy state, the atom must fill the vacancy in its inner shell.
Almost immediately, an electron from a higher-energy outer shell (such as the "L" or "M" shell) drops down to fill the void left by the ejected electron.
The Result: An Elemental Fingerprint
This "drop" from a high-energy shell to a low-energy shell releases a specific amount of energy. This excess energy is emitted from the atom in the form of a secondary, or "fluorescent," X-ray.
Crucially, the energy difference between the outer and inner shells is unique and characteristic for every element. An iron atom will always release a fluorescent X-ray with a different energy signature than a nickel atom, a chromium atom, or a lead atom. This is the elemental fingerprint.
From Fingerprints to a Full Composition
The XRF analyzer is engineered to read these fingerprints and translate them into a complete elemental analysis.
The Role of the Detector
The detector is the heart of the analyzer. Its job is to capture the millions of secondary X-rays being emitted from the sample and precisely measure the energy of each one. By sorting these X-rays by their energy level, the instrument can definitively identify every element present.
The Importance of Intensity
Beyond just identifying elements, the detector also counts how many X-rays of each characteristic energy it receives per second. This count rate, or intensity, is directly proportional to the concentration of that element in the sample.
More fluorescent X-rays from iron means there is more iron in the sample. Fewer X-rays from copper means there is less copper.
The Final Calculation
This raw data—energy levels and their corresponding intensities—is fed into the instrument's processor. Using complex algorithms and a library of fundamental atomic parameters, the software corrects for various physical effects (like absorption and enhancement) to convert the raw counts into a quantitative result, typically displayed as a percentage or parts-per-million (PPM).
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the theory behind XRF also dictates its limitations. Understanding these is key to interpreting your data correctly.
It's a Surface-Level Technique
The primary X-rays can only penetrate a limited distance into a material. This means that XRF is inherently a surface analysis technique. The results you see represent the composition of the top micrometers to millimeters of your sample, which may not be representative of the bulk material if it is coated, corroded, or non-homogeneous.
The "Light Element" Challenge
XRF is less effective for very light elements (those with low atomic numbers, like Hydrogen, Carbon, or Sodium). The fluorescent X-rays emitted by these elements are very low-energy. They are often absorbed by the air path between the sample and the detector or by the detector window itself, preventing them from being measured accurately, if at all.
Matrix Effects
The cloud of atoms in a sample is a crowded environment. The fluorescent X-rays from one element can be absorbed or enhanced by the presence of other elements in the sample "matrix." Modern XRF software is designed to mathematically correct for these matrix effects, but they are a fundamental physical consideration in complex materials like alloys and minerals.
How This Theory Impacts Your Results
Understanding this atomic-level theory helps you interpret your results and use the technology more effectively.
- If your primary focus is material identification (PMI): The unique energy 'fingerprint' of each element is the key principle, allowing for rapid and accurate alloy grade verification.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis (e.g., compliance testing): The intensity of the fluorescent signal is critical, as its direct correlation to concentration is what allows you to measure how much of an element is present.
- If you are analyzing coated or non-homogeneous materials: Remember that XRF is a surface technique; your results represent the composition of the near-surface layer, not necessarily the bulk material.
By grasping this atomic-level interaction, you move from simply using a tool to truly understanding the data it provides.
Summary Table:
| Key Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Excitation | Primary X-rays knock inner-shell electrons out of atoms, creating instability. |
| Fluorescence | Outer-shell electrons drop to fill the vacancy, releasing secondary X-rays. |
| Elemental Fingerprint | The energy of emitted X-rays is unique to each element, enabling identification. |
| Intensity & Concentration | The count of X-rays for an element is proportional to its concentration in the sample. |
| Limitations | Surface-level analysis; less effective for light elements; matrix effects can influence results. |
Ready to harness the power of XRF analysis in your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including XRF analyzers, to help you achieve precise, non-destructive material identification and quantification. Whether you're involved in material verification, compliance testing, or research, our solutions are designed to deliver accurate results efficiently. Contact us today to explore how our expertise and products can enhance your analytical capabilities and drive your projects forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the minimum sample required for XRD analysis? Optimize Your Material Analysis
- What are the specific storage requirements for a sample holder? Protect Your Lab's Critical Assets
- What are the limitations of the IR spectroscopy? Understanding Its Boundaries for Accurate Analysis
- What are the factors that affect melting and boiling point? Unlock the Science of Phase Transitions
- Why is an airtight sample holder with a beryllium window required for XRD of sulfide solid electrolytes?



















