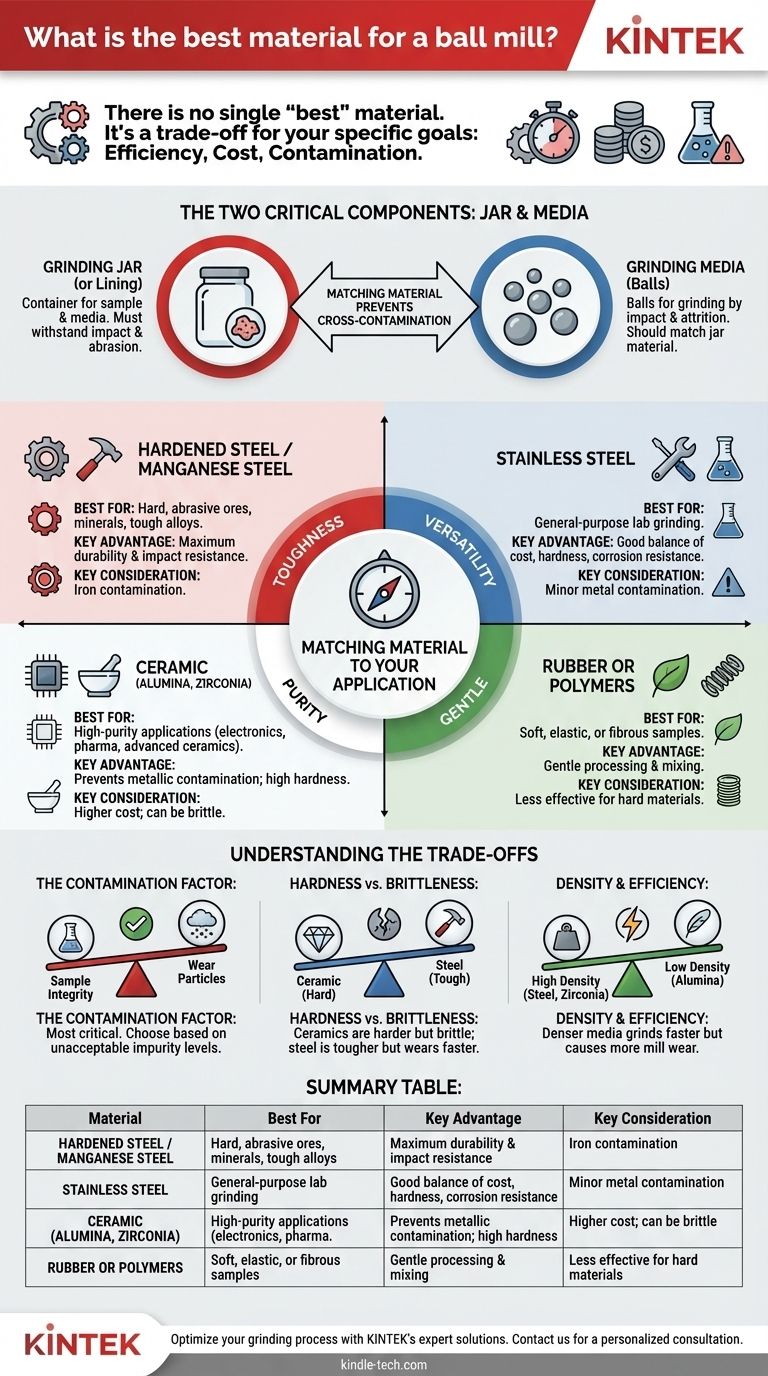
There is no single "best" material for a ball mill. The ideal choice is entirely dependent on the material you are grinding and your specific goals. The key principle is that the grinding media and jar must be harder than the sample material and chemically inert to avoid contamination.
The core decision in selecting a ball mill material is a trade-off between grinding efficiency, cost, and potential sample contamination. You must match the material of the mill's components—the jar and the grinding balls—to the specific physical and chemical properties of the sample you are processing.
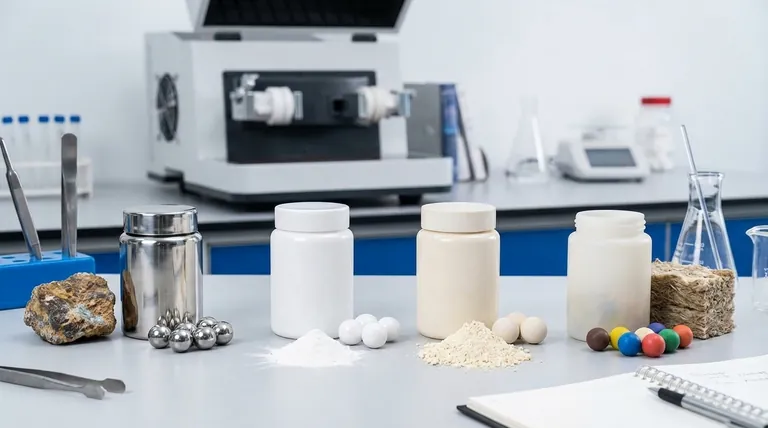

The Two Critical Components: Jar and Media
A ball mill has two parts where material choice is critical: the grinding jar (the shell) and the grinding media (the balls).
The Grinding Jar (or Lining)
The jar is the container that holds the sample and the grinding media. For large mills, this is a shell with an inner lining. Its material must withstand constant impact and abrasion from the grinding media.
The Grinding Media (Balls)
These are the balls that do the actual work of grinding through impact and attrition. As a rule, the material for the jar and the media should be the same to prevent cross-contamination from two different sources.
Matching Material to Your Application
The right choice depends on whether your priority is grinding speed, preventing contamination, or handling a specific type of sample.
Hardened Steel / Manganese Steel
These materials offer maximum toughness and high impact resistance. They are the go-to choice for grinding very hard, brittle, or abrasive materials like ores, minerals, and tough alloys. Their primary drawback is sample contamination with iron and other alloying elements.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a versatile, cost-effective choice for general-purpose grinding. It offers good hardness and corrosion resistance. It is suitable for a wide range of materials where minor iron or chromium contamination is not a critical issue for the final application.
Ceramic (Alumina, Zirconia)
Ceramic jars and media are essential for applications where metal contamination must be avoided. They are extremely hard and wear-resistant, making them ideal for grinding glass, other ceramics, and high-purity chemicals for biomedical or electronic use. Zirconia is harder and denser than alumina, providing more efficient grinding, but at a higher cost.
Rubber or Polymers
For samples that are soft, elastic, or fibrous, a hard grinding action can be ineffective or damaging. Rubber linings and media are used for gentle size reduction or mixing applications, where the goal is to process the material without the high-impact fracturing caused by metal or ceramic media.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every material choice involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these compromises is key to making an informed decision.
The Contamination Factor
This is the most critical trade-off. During milling, microscopic particles of the jar and balls will wear off and mix with your sample. If you are grinding an ore for metal extraction, steel contamination is irrelevant. If you are preparing a high-purity ceramic for a medical implant, it is unacceptable.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
There is a direct relationship between a material's hardness and its brittleness. Ceramics are extremely hard, leading to efficient grinding, but they can chip or crack under severe impact. Steel is tougher and more forgiving, but it wears more quickly, leading to higher contamination rates.
Density and Efficiency
The density of the grinding media directly impacts the energy of each collision. Denser media, like steel or zirconia, will grind materials faster and to a finer size than less dense media like alumina. However, higher density also means more wear and tear on the mill itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your material based on the most important outcome for your specific process.
- If your primary focus is heavy-duty grinding of hard, abrasive materials (e.g., minerals, alloys) where iron contamination is acceptable: Choose hardened steel or manganese steel for maximum durability.
- If your primary focus is preventing all metallic contamination for sensitive or high-purity applications (e.g., electronics, pharmaceuticals, advanced ceramics): Choose a ceramic like zirconia or alumina.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose laboratory grinding with a good balance of cost and performance: Stainless steel is the most common and versatile starting point.
- If your primary focus is gentle processing or mixing of soft, elastic, or fibrous samples: Rubber or specialized polymer media is the correct choice.
Ultimately, the right material is the one that protects your sample's integrity while efficiently achieving your desired particle size.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardened Steel | Hard, abrasive materials (ores, alloys) | Maximum durability and impact resistance | Iron contamination |
| Stainless Steel | General-purpose laboratory grinding | Good balance of cost, hardness, and corrosion resistance | Minor metal contamination |
| Ceramic (Alumina/Zirconia) | High-purity applications (electronics, pharmaceuticals) | Prevents metallic contamination; high hardness | Higher cost; can be brittle |
| Rubber/Polymers | Soft, elastic, or fibrous samples | Gentle processing and mixing | Less effective for hard, brittle materials |
Optimize your grinding process with KINTEK's expert solutions. Selecting the right ball mill material is critical to achieving your desired particle size without compromising sample integrity. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of ball mills and grinding media tailored to your specific application—whether you're in mining, pharmaceuticals, ceramics, or advanced materials research.
Let our specialists help you avoid costly contamination and inefficiency. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover the perfect grinding solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is grinder in chemistry? A Guide to Precision Sample Preparation
- What are the five methods of synthesis of nanoparticles? A Guide to Top-Down & Bottom-Up Approaches
- Why is grinding important in sample preparation? Ensure Accurate & Reliable Analytical Results
- How full should a ball mill be? Achieve Peak Grinding Efficiency with the 50% Rule
- What are the different types of grinding mills? Match the Mechanism to Your Material for Optimal Size Reduction



















