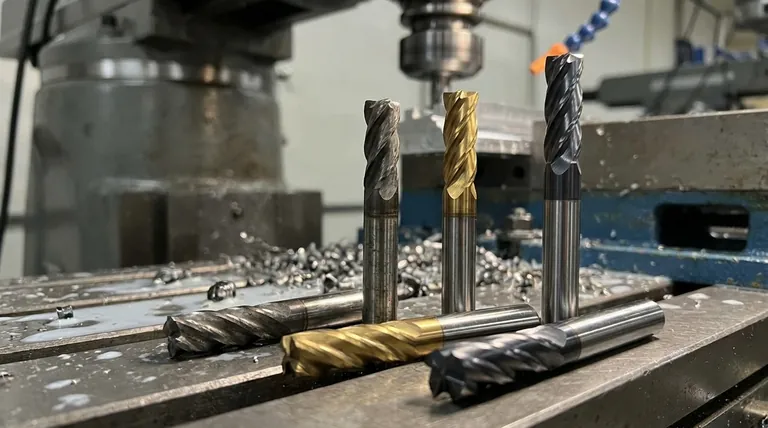
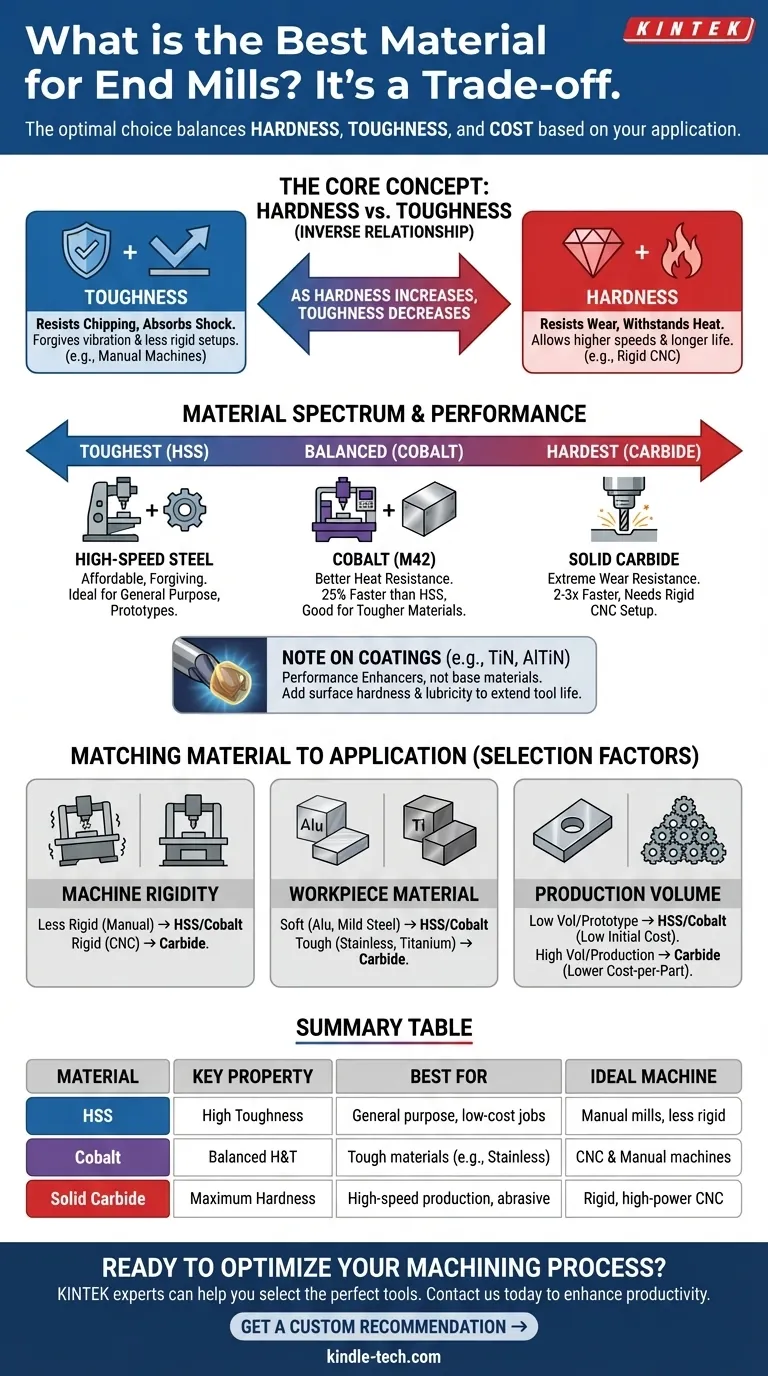
In machining, there is no single "best" material for an end mill. The optimal choice is always a trade-off determined by your specific application. The most common materials are High-Speed Steel (HSS), Cobalt, and Solid Carbide, each offering a different balance of hardness, toughness, and cost.
The core decision in selecting an end mill material is balancing hardness against toughness. Harder materials like carbide allow for higher speeds and longer life in stable conditions, while tougher materials like HSS resist chipping and breaking in less rigid setups.

The Core Material Properties: Hardness vs. Toughness
Understanding the interplay between hardness and toughness is the key to selecting the right tool for your job. These two properties exist in an inverse relationship.
What is Hardness?
Hardness is a material's ability to resist deformation and abrasion. In an end mill, this translates to wear resistance and heat resistance.
A harder tool material maintains a sharp cutting edge for longer, especially when cutting abrasive materials. It also retains its strength at the high temperatures generated by aggressive cutting speeds.
What is Toughness?
Toughness is a material's ability to absorb energy and resist fracturing or chipping under sudden loads. This is critical in setups with vibration, interrupted cuts, or less-than-perfect rigidity.
A tougher tool is more forgiving. It is less likely to shatter if it encounters unexpected forces, making it a safer choice for manual machines or less stable workholding.
The Inverse Relationship
Generally, as a material's hardness increases, its toughness decreases. A very hard material like carbide is also very brittle, similar to glass. A softer, tougher material like HSS behaves more like steel, bending or deforming before it breaks.
A Breakdown of Common End Mill Materials
Your choice of material will fall somewhere on the spectrum from the toughest (HSS) to the hardest (Carbide).
High-Speed Steel (HSS)
HSS is the baseline tool material. It is the toughest and most affordable option, making it an excellent choice for general-purpose milling.
Its high toughness makes it very forgiving of chatter, vibration, and less-than-rigid machine tools. This makes it ideal for manual milling machines, drill presses, and prototype work where cost and tool durability are primary concerns.
Cobalt (M42 / HSSE)
Cobalt end mills are essentially a premium version of HSS. They are HSS alloys with 5% to 8% cobalt added to the mix.
This addition significantly increases the material's hardness and heat resistance (hot hardness) compared to standard HSS. This allows them to be run about 25% faster and provides better performance in tougher materials like stainless steel. They represent a superb middle ground between the affordability of HSS and the performance of carbide.
Solid Carbide (Tungsten Carbide)
Solid carbide end mills are the hardest and most wear-resistant tools widely available. They can operate at speeds 2-3 times higher than HSS.
This extreme hardness allows for exceptional tool life and superior surface finishes in stable, high-speed applications. However, carbide is very brittle and requires a rigid, powerful CNC machine with minimal runout to prevent chatter and catastrophic tool failure.
A Note on Coatings
Coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) are micro-thin ceramic layers applied to an end mill's surface. They are not a base material, but a performance enhancer.
A coating adds surface hardness, heat resistance, and lubricity, which significantly extends the life and performance of the base tool (whether it's HSS, Cobalt, or Carbide).
Understanding the Trade-offs: Matching Material to Application
The "best" material is the one that best matches your machine, workpiece, and production goals.
Your Machine's Rigidity and Spindle Speed
A heavy, rigid CNC machine can leverage the speed and performance of solid carbide. Using a carbide end mill on a less rigid benchtop mill or manual machine is often a mistake, as any vibration will quickly chip the brittle cutting edges.
For less rigid setups, the toughness of HSS and Cobalt makes them a much more reliable and effective choice.
The Workpiece Material
For soft materials like aluminum, brass, and mild steel, HSS and Cobalt are perfectly adequate and cost-effective.
For tough or abrasive materials like stainless steel, titanium, or hardened tool steels, the superior hardness and heat resistance of a coated carbide end mill are almost always necessary for efficient machining.
Production Volume and Cost
For one-off parts or small batches, the low initial cost of HSS or Cobalt is often the most economical choice.
For high-volume production, the higher initial cost of a solid carbide end mill is easily justified. Its higher running speeds and significantly longer tool life lead to a lower cost-per-part and greater overall efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Consider your primary objective to make a definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and flexibility on manual machines: Start with HSS for general work and upgrade to Cobalt for tougher materials or longer tool life.
- If your primary focus is balanced performance on a mix of CNC and manual machines: Cobalt is the most versatile and cost-effective workhorse for most shops.
- If your primary focus is maximum speed, tool life, and finish quality in a rigid CNC environment: Solid carbide is the only choice for serious production and machining difficult materials.
Ultimately, selecting the right end mill material is about aligning the tool's properties with your specific operational and economic needs.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Property | Best For | Ideal Machine |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | High Toughness | General purpose, low-cost jobs, prototype work | Manual mills, less rigid setups |
| Cobalt (HSSE) | Balanced Hardness & Toughness | Tough materials like stainless steel, 25% faster than HSS | CNC and manual machines |
| Solid Carbide | Maximum Hardness | High-speed production, abrasive materials, superior finish | Rigid, high-power CNC machines |
Ready to Optimize Your Machining Process?
Choosing the right tooling is critical for efficiency, finish quality, and cost control. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving the exacting needs of modern laboratories and workshops.
Our experts can help you select the perfect tools for your specific materials and machines. Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how we can enhance your productivity and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Cabinet Planetary Ball Milling Machine
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the preparation of NiCr-Al2O3-SrCO3 composite powders? Enhanced Homogeneity
- Why are high-intensity planetary ball mills preferred for reducing the crystallinity of lignocellulose?
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a planetary mill? Choose the Right Grinding Tool for Your Lab
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a planetary ball mill? Unlock the Right Grinding Technology for Your Lab
- What is the working principle of planetary ball mill? Unlock High-Energy Grinding for Nanoscale Results













