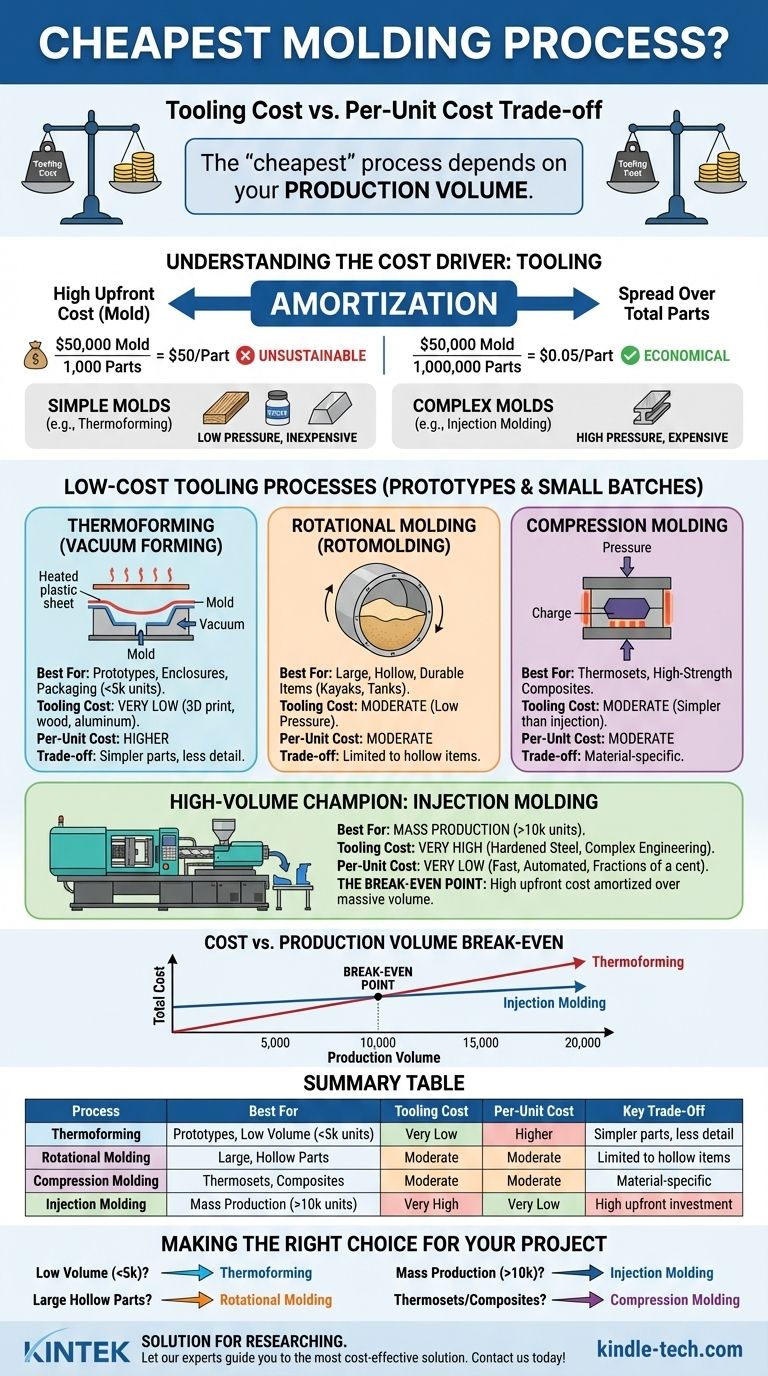
For projects with low to medium production volumes, the cheapest molding process is typically thermoforming, specifically vacuum forming. Its advantage comes from exceptionally low tooling costs, which can be thousands of dollars less than other methods. However, for mass production, injection molding becomes the cheapest on a per-part basis, despite its extremely high initial tooling investment.
The "cheapest" molding process is not a single answer but a calculation based on your specific needs. The core trade-off is between the low initial tooling cost of processes like thermoforming and the low per-unit cost of processes like injection molding at high volumes.

Why Tooling Is the Decisive Cost Factor
The primary cost driver in any molding process isn't the plastic or the machine time; it's the cost of the mold itself, also known as the "tool." Understanding this is crucial to making an economical choice.
The Concept of Amortization
The high upfront cost of creating a mold must be "amortized," or spread out, across the total number of parts you produce.
A $50,000 mold producing one million parts adds only $0.05 to each part. That same mold producing only 1,000 parts adds an unsustainable $50 to each part.
Simple vs. Complex Molds
Processes that use low pressure, like thermoforming, can use simple, inexpensive molds made from materials like epoxy, wood, or aluminum.
High-pressure processes like injection molding require highly engineered, multi-part molds made from hardened steel to withstand immense forces, making them exponentially more expensive.
A Breakdown of Low-Cost Molding Processes
These methods are defined by their relatively inexpensive tooling, making them ideal for prototypes, small batches, and projects where initial capital is a major constraint.
Thermoforming (Vacuum Forming)
Thermoforming involves heating a sheet of plastic until it's pliable, draping it over a single-sided mold, and using a vacuum to pull the sheet tight against the mold's surface.
It is exceptionally cheap to get started. Molds for prototyping can even be 3D printed or made of wood. This makes it ideal for trays, enclosures, and packaging.
Rotational Molding (Rotomolding)
In this process, plastic powder is placed inside a hollow mold which is then heated and rotated on two axes. The powder melts and coats the inside of the mold, creating a hollow part.
Tooling is cheaper than injection molding because it doesn't need to withstand high pressure. This method is the go-to for large, durable, hollow items like kayaks, water tanks, and large containers.
Compression Molding
This method involves placing a pre-measured amount of molding material (a "charge") into a heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed, and pressure is applied to force the material into the shape of the cavity.
Tooling is simpler and less expensive than for injection molding, and it is particularly well-suited for high-strength composite materials and thermoset plastics.
The High-Volume Champion: Injection Molding
While its entry cost is the highest, injection molding is the undisputed king of low-cost mass production.
The High Cost of Entry
An injection mold is a masterpiece of engineering, often made of hardened steel with complex cooling channels, slides, and ejector systems. These molds frequently cost tens of thousands, and sometimes hundreds of thousands, of dollars.
The Ultra-Low Per-Unit Cost
Once the mold is made and installed, the process is incredibly fast and automated. Parts can be produced in a matter of seconds for fractions of a cent in material and machine time.
The Break-Even Point
There is always a "break-even" volume where the high cost of the injection mold is fully amortized. Beyond this point, its low per-unit cost makes it vastly cheaper than any other process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a molding process is always a balancing act. The cheapest option is not always the best one for the final product's requirements.
Cost vs. Production Volume
This is the most critical trade-off. Thermoforming is cheapest for hundreds or a few thousand units. Injection molding is cheapest for tens of thousands to millions of units.
Part Complexity and Precision
Injection molding allows for incredibly complex geometries, including fine details, ribs, and screw bosses, with very high precision and tight tolerances.
Thermoforming is limited to simpler, drafted shapes and cannot produce the same level of detail or precision. Wall thickness can also be less consistent.
Material Selection
Your choice of material may limit your process options. While many thermoplastics can be used in both thermoforming and injection molding, other materials like thermosets or high-performance composites are better suited for compression molding.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
To determine the truly "cheapest" process, you must first define your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or low-volume production (under ~5,000 units): Thermoforming is almost certainly your most economical option due to its minimal tooling investment.
- If your primary focus is producing large, hollow, and durable parts: Rotational molding offers an unbeatable combination of tooling cost and part strength.
- If your primary focus is mass production for a proven design (over ~10,000 units): Injection molding will deliver the lowest possible per-unit cost, justifying the significant initial investment.
- If your primary focus is working with thermoset plastics or composites: Compression molding is often the most effective and affordable method.
By aligning your production volume and part requirements with the right process, you can ensure you are making the most cost-effective decision for your project.
Summary Table:
| Process | Best For | Tooling Cost | Per-Unit Cost | Key Trade-Off |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoforming (Vacuum Forming) | Prototypes, Low Volume (<5k units) | Very Low | Higher | Simpler parts, less detail |
| Rotational Molding | Large, Hollow Parts | Moderate | Moderate | Limited to hollow items |
| Compression Molding | Thermosets, Composites | Moderate | Moderate | Material-specific |
| Injection Molding | Mass Production (>10k units) | Very High | Very Low | High upfront investment |
Still Unsure Which Molding Process is Cheapest for Your Project?
Making the wrong choice can cost you thousands in unnecessary tooling or per-part expenses. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and R&D teams. Whether you're prototyping a new device enclosure or scaling up production for lab consumables, we can help you navigate the cost trade-offs between thermoforming, injection molding, and other processes.
Let our experts guide you to the most cost-effective solution for your specific volume and material requirements.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and ensure your project starts on the most economical footing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Lab Infrared Press Mold
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- Why is it necessary to use high-precision temperature-controlled heating furnaces? Secure Natural Fiber Integrity.
- What is the temperature range for compression molding? Optimize Your Process for Perfect Parts
- What role do molds play in the formation of Ruthenium sheets? Master High-Density Ruthenium Fabrication
- What role does a benchtop hot press play in densifying composite cathodes? Achieve <10% Porosity with Thermo-Mechanical Flow



















