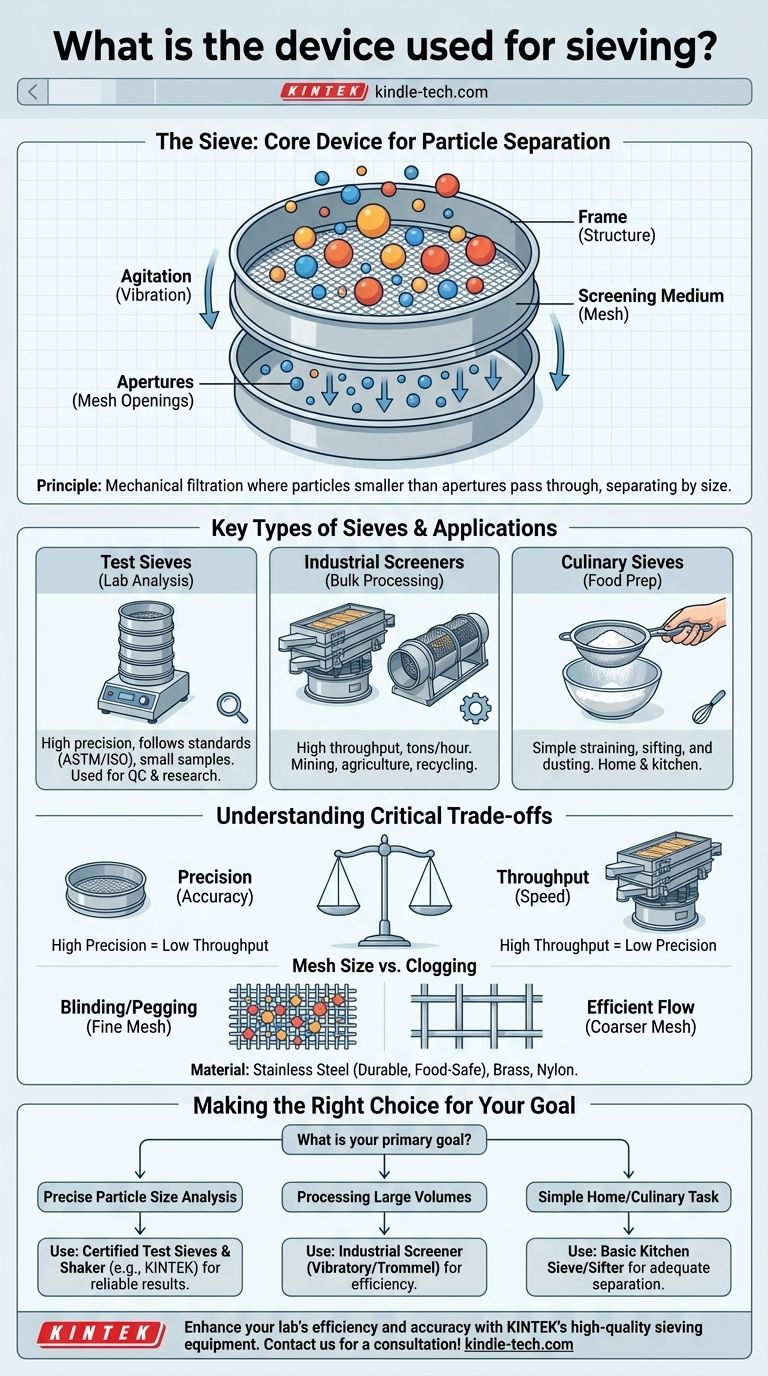
The primary device used for sieving is called a sieve. It is a tool featuring a mesh, screen, or perforated surface designed to separate particles of different sizes. Its fundamental purpose is to either retain larger, desired elements while allowing smaller ones to pass through, or to analyze the particle size distribution of a sample.
A sieve is more than a simple screen; it is a precision instrument for separation. The key to effective sieving is not just the device itself, but understanding how the mesh size, particle characteristics, and method of agitation work in concert to achieve a specific separation goal.
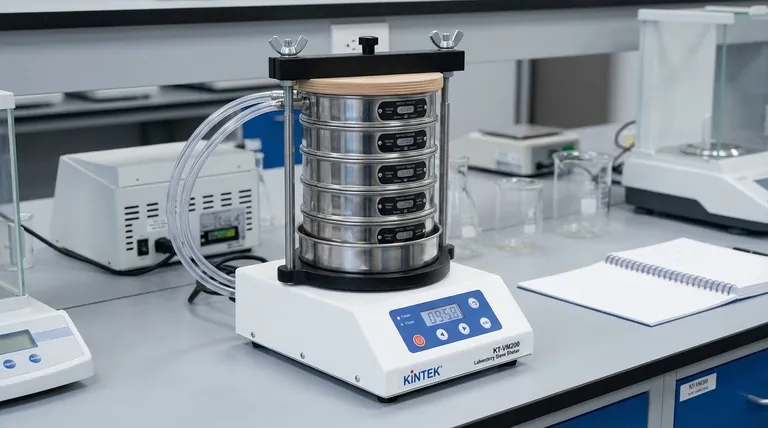

The Fundamental Principle: How a Sieve Works
A sieve operates on the straightforward mechanical principle of filtration based on size. Particles are introduced to a screening medium, and only those smaller than the openings in the medium can pass through.
The Core Components
A standard sieve consists of two main parts. The frame provides a rigid structure, typically circular, and the screening medium (the mesh or perforated plate) is stretched across it and sealed to the frame.
The Mechanism of Separation
When a sample containing a mix of particle sizes is placed on the sieve, the particles rest on the screening medium. The openings in the mesh are referred to as apertures. Particles with a diameter smaller than the aperture size can fall through, while larger particles are retained on top.
The Critical Role of Agitation
For efficient and accurate separation, the sieve must be agitated. A mechanical sieve shaker is used in laboratory settings to provide consistent vibration or tapping. This movement ensures that all particles are presented to the apertures multiple times and in different orientations, preventing clogging and guaranteeing a true separation based on size.
Key Types of Sieves for Different Applications
The design and construction of a sieve vary dramatically depending on its intended use, from precise laboratory analysis to heavy industrial processing.
Test Sieves for Laboratory Analysis
These are high-precision instruments used for particle size analysis in quality control and research. They are manufactured to meet strict standards (like ASTM E11 or ISO 3310-1) that define the exact wire diameter and aperture size. Test sieves are often stacked in a column from coarsest to finest and placed in a sieve shaker for analysis.
Industrial Screeners for Bulk Processing
In industries like mining, agriculture, and recycling, large-scale devices called industrial screeners or grizzlies are used. These are designed for high throughput to process tons of material per hour. Examples include vibratory screeners, which use powerful motors to separate materials, and trommel screens, which are large rotating cylindrical drums.
Culinary Sieves for Food Preparation
The most common type of sieve is the one found in the kitchen, often called a sifter or strainer. These are used for less precise tasks like removing lumps from flour to aerate it, dusting surfaces with powdered sugar, or straining liquids from solids.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing the right sieving method involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for achieving a successful outcome.
Precision vs. Throughput
There is an inherent conflict between the speed of processing and the accuracy of the separation. Test sieves offer extremely high precision but can only handle small sample sizes. Industrial screeners prioritize high throughput at the expense of precise particle-size cutoffs.
Mesh Size vs. Clogging
Finer meshes with smaller apertures are necessary for separating very small particles. However, they are highly susceptible to blinding (when particles block the apertures) and pegging (when a particle becomes wedged in an aperture), which drastically reduces the sieve's efficiency.
Material and Durability
Sieve mesh is commonly made from woven stainless steel wire for its durability, resistance to corrosion, and minimal reactivity, making it ideal for food and pharmaceutical applications. Other materials like brass or synthetic polymers (nylon) may be used for specific chemical compatibility or cost considerations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective dictates the type of sieving device and process required.
- If your primary focus is precise particle size analysis: You must use certified test sieves with a mechanical sieve shaker to ensure repeatable and accurate results for quality control or research.
- If your primary focus is processing large volumes of material: An industrial screener, such as a vibratory or trommel screen, is the correct choice to handle high throughput efficiently.
- If your primary focus is a simple home or culinary task: A basic, handheld kitchen sieve or sifter is perfectly adequate for removing lumps or straining liquids.
Ultimately, the right sieving device is the one that correctly balances the required precision with the scale of your operation.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Type | Primary Use | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Test Sieves | Laboratory Analysis | High precision, follows standards (ASTM/ISO), small sample sizes |
| Industrial Screeners | Bulk Processing | High throughput, handles large volumes (tons/hour) |
| Culinary Sieves | Food Preparation | Simple straining, sifting, and dusting for home/kitchen use |
Need the Right Sieving Equipment for Your Lab?
Choosing the correct sieve is critical for accurate results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including precision test sieves and mechanical sieve shakers designed for reliable particle size analysis. Our experts can help you select the perfect tool to meet your quality control and research standards.
Enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy — Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity



















