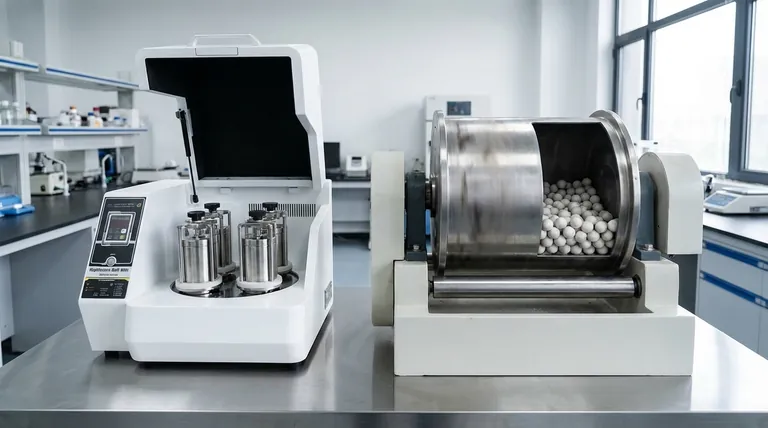
In short, a planetary ball mill is a specific, high-energy type of ball mill. While the term "ball mill" describes a general class of grinder that uses media to crush material, a "planetary ball mill" refers to a device with a distinct mechanism where jars spin on their own axes while also orbiting a central point, generating significantly higher forces.
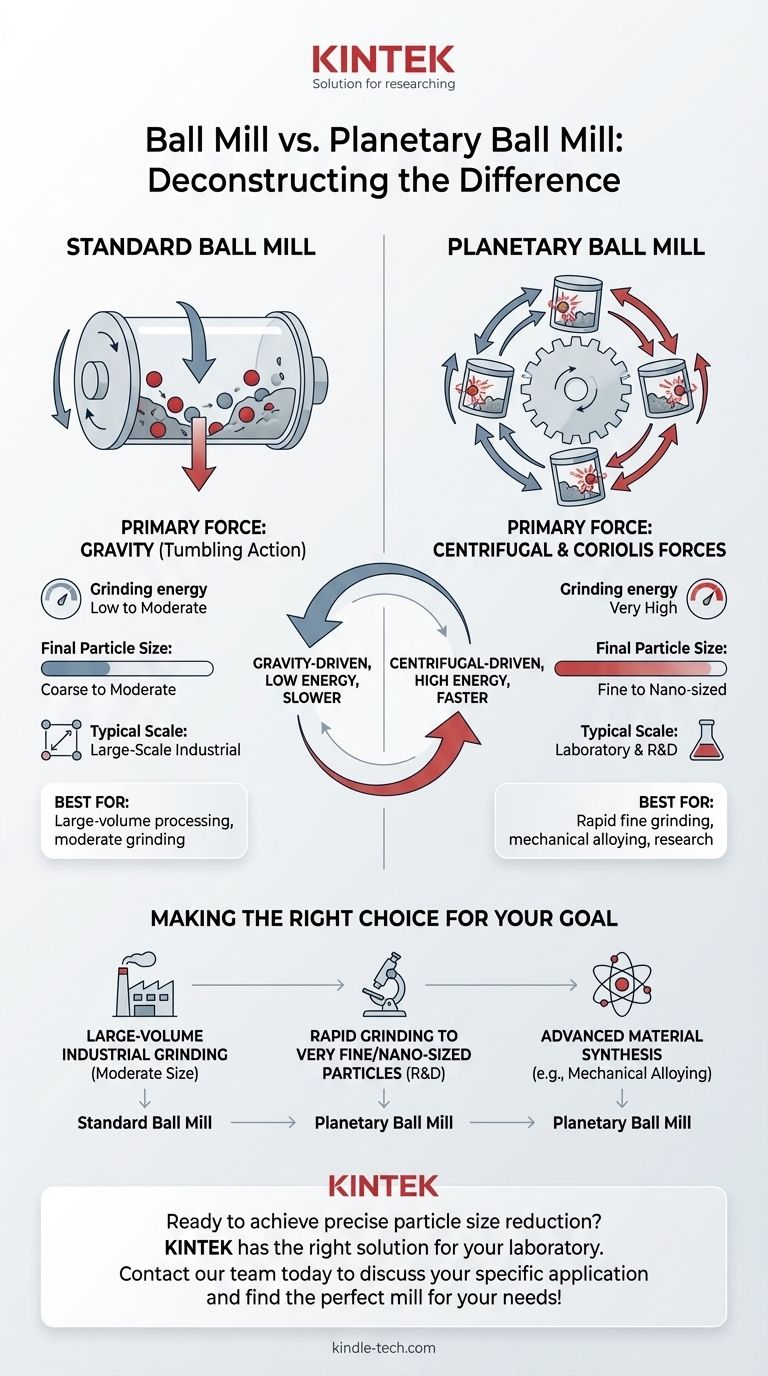
The fundamental difference is the source of the grinding force. A standard ball mill primarily uses gravity to tumble grinding media, while a planetary ball mill uses intense centrifugal and Coriolis forces to achieve much faster and finer grinding.

Deconstructing the "Standard" Ball Mill
A standard or "rolling" ball mill is the simplest form of this technology. Its operation is straightforward and has been a workhorse in industries for decades.
The Core Mechanism: Gravity and Tumbling
A standard ball mill consists of a large hollow cylinder that rotates on a horizontal axis. The cylinder is partially filled with the material to be ground, along with the grinding media—typically steel or ceramic balls.
As the cylinder rotates, the media and material are lifted up one side. Once they reach a certain height, gravity causes them to cascade and tumble back down, crushing and grinding the material through impact and abrasion.
Energy and Action
The grinding action in a standard mill is entirely dependent on gravity and the drum's rotational speed. The energy is relatively low and is applied through two primary actions: impact (balls falling on the material) and attrition (material rubbing between the rolling balls).
Understanding the Planetary Ball Mill
A planetary ball mill is a more complex and powerful instrument, typically used in laboratory and R&D settings for achieving very fine particle sizes.
The Sun-and-Planet Motion
This design features one large rotating disc, often called the "sun wheel." Mounted on this disc are several smaller grinding jars, the "planets."
Crucially, as the sun wheel turns in one direction, the planetary jars rotate on their own axes in the opposite direction. This compound motion is the key to its effectiveness.
The Force Multiplier: High-Energy Impact
The counter-rotating motion generates extremely powerful centrifugal and Coriolis forces. These forces press the grinding balls and sample material against the inner walls of the jars with tremendous energy.
This action results in much higher-energy impacts compared to a standard mill. The balls don't just tumble; they are propelled across the jar, leading to rapid and efficient particle size reduction through high-frequency, high-energy collisions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these mill types involves a clear set of trade-offs related to your specific grinding objectives.
Speed and Final Particle Size
A planetary ball mill is significantly faster. Due to the high-energy impacts, it can reduce materials to very fine or even nano-sized particles in a fraction of the time it would take a standard mill.
Capacity and Scale
Standard rolling ball mills excel at large-scale production. They can be built to handle several hundred liters or even tons of material at once, making them ideal for industrial processing.
Planetary ball mills typically have a much smaller capacity, ranging from a few milliliters to several liters, making them suited for laboratory research, quality control, and pilot-scale work.
Applications and Complexity
The intense forces of a planetary ball mill enable advanced applications like mechanical alloying and mechanochemistry, which are impossible with a standard mill. However, this performance comes with greater mechanical complexity and higher energy consumption relative to its size.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements for scale, speed, and final particle size will dictate the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is large-volume industrial grinding with moderate size reduction: A standard horizontal rolling mill is the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is rapid grinding to achieve very fine or nano-sized particles for research and development: A planetary ball mill is the superior and necessary instrument.
- If your primary focus is advanced material synthesis like mechanical alloying: The high-impact energy of a planetary ball mill is essential for your work.
Ultimately, understanding that a planetary mill uses centrifugal force while a standard mill uses gravity is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Ball Mill | Planetary Ball Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Grinding Force | Gravity (Tumbling Action) | Centrifugal & Coriolis Forces |
| Grinding Energy | Low to Moderate | Very High |
| Final Particle Size | Coarse to Moderate | Fine to Nano-sized |
| Typical Scale | Large-Scale Industrial | Laboratory & R&D |
| Best For | Large-volume processing, moderate grinding | Rapid fine grinding, mechanical alloying, research |
Ready to achieve precise particle size reduction?
Whether your project requires the large-scale capabilities of a standard ball mill or the high-energy, fine-grinding performance of a planetary ball mill, KINTEK has the right solution for your laboratory. Our experts can help you select the ideal equipment to enhance your research, quality control, or material synthesis workflows.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect mill for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a planetary high-energy ball mill? Master Mechanical Alloying for Nickel Nanoparticles
- Why are high-intensity planetary ball mills preferred for reducing the crystallinity of lignocellulose?
- What role does a high-energy planetary ball mill play in Mo-La2O3 alloying? Achieve Superior Microstructure Control
- What is the primary function of a planetary ball mill for LLZTO targets? Achieving High-Energy Pulverization
- What is the function of a planetary high-energy ball mill? Master Mechanical Alloying for Ni-Co-Al Superalloy Powders



















