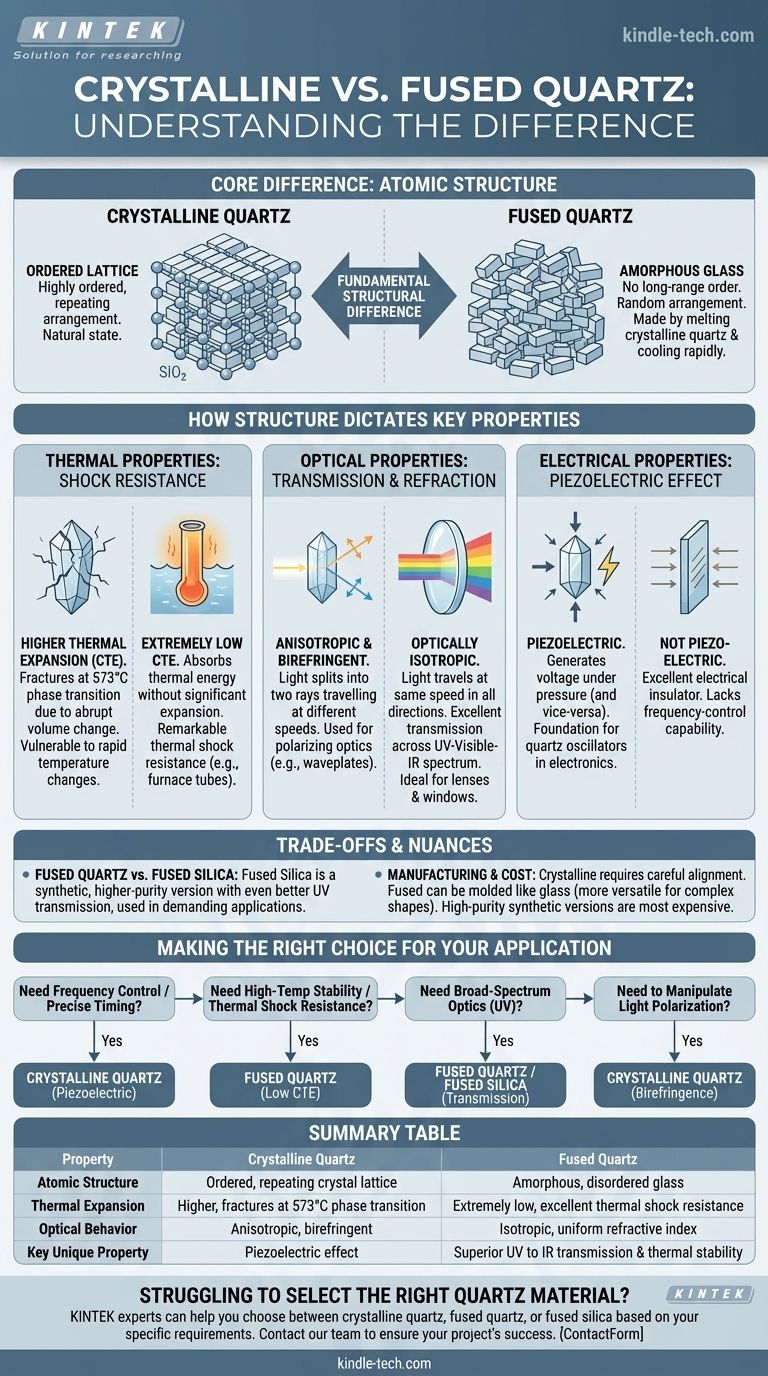
At their core, the difference between crystalline quartz and fused quartz comes down to atomic structure. Crystalline quartz has a highly ordered, repeating arrangement of silicon and oxygen atoms, which is its natural state. Fused quartz is a non-crystalline, amorphous glass made by melting crystalline quartz and cooling it rapidly, locking its atoms into a disordered, random state.
This fundamental structural difference—ordered versus disordered—is the source of all their distinct properties. Crystalline quartz’s order gives it unique electrical and optical effects, while fused quartz’s disorder gives it superior thermal stability and transparency.
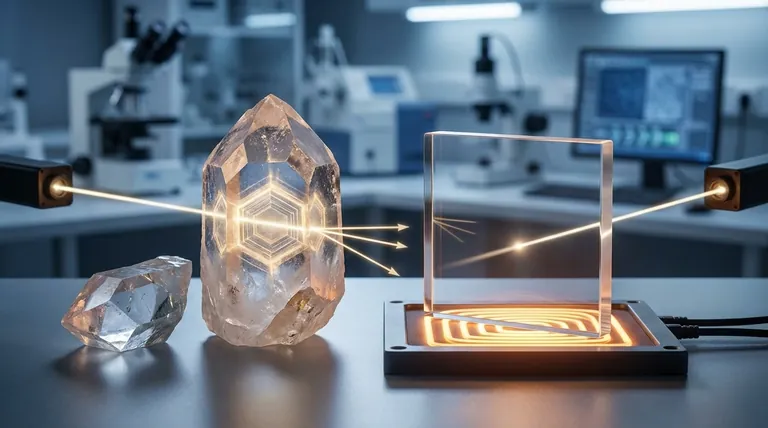

Understanding the Core Difference: Atomic Structure
The material in both cases is silicon dioxide (SiO₂). The distinction lies entirely in how the atoms are arranged.
Crystalline Quartz: The Ordered Lattice
Crystalline quartz features a repeating, predictable three-dimensional pattern known as a crystal lattice. Think of it as bricks stacked in a neat, orderly wall.
This precise structure is responsible for its unique properties, but also creates planes of weakness and directional dependencies.
Fused Quartz: The Amorphous Glass
Fused quartz is an amorphous solid, meaning its atoms have no long-range order. It's the same silicon and oxygen atoms, but they are frozen in a random arrangement, like a pile of bricks dumped on the ground.
This is achieved by melting high-purity crystalline quartz at approximately 2000°C and then cooling it down too quickly for the atoms to organize back into a crystal lattice.
How Structure Dictates Key Properties
The atomic arrangement directly impacts how each material behaves when exposed to heat, light, and mechanical stress. Understanding these differences is critical for selecting the right material for your application.
Thermal Properties: Shock Resistance
Fused quartz has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). Because of its disordered structure, it can absorb thermal energy without significant expansion or contraction.
This gives it remarkable thermal shock resistance. You can heat a fused quartz tube to red-hot and plunge it into cold water without it cracking. This makes it ideal for high-temperature applications like furnace tubes, crucibles, and semiconductor processing equipment.
Crystalline quartz, by contrast, has a higher CTE. More importantly, it undergoes a phase transition at 573°C, causing an abrupt change in volume that will fracture the material if the temperature change is too rapid.
Optical Properties: Transmission and Refraction
Fused quartz is optically isotropic, meaning light travels at the same speed in all directions. Its refractive index is uniform.
Crucially, it exhibits excellent optical transmission across a very wide spectrum, from the deep ultraviolet (UV) through the visible and into the infrared (IR) range. This makes it a go-to material for lenses, windows, and lamps used in UV sterilization and spectroscopy.
Crystalline quartz is anisotropic and birefringent. This means light entering the crystal is split into two rays that travel at different speeds and are polarized at right angles to each other. This property is a direct result of its ordered, asymmetrical crystal structure. While a disadvantage for simple lenses, this effect is purposefully used to create waveplates and other polarizing optics.
Electrical Properties: The Piezoelectric Effect
Crystalline quartz is piezoelectric. Due to its lack of structural symmetry, applying mechanical pressure to the crystal generates a measurable electric voltage.
Conversely, applying a voltage causes the crystal to deform at a precise frequency. This electromechanical property is the foundation for all modern quartz crystal oscillators used in clocks, radios, computers, and sensors.
Fused quartz, lacking a repeating crystal structure, is not piezoelectric. It is an excellent electrical insulator but does not possess this unique frequency-control capability.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Choosing between these materials also involves considering purity, manufacturing methods, and cost.
Fused Quartz vs. Fused Silica
While often used interchangeably, there is a technical distinction. Fused quartz is typically made by melting naturally mined, high-purity quartz sand or crystals.
Fused silica is a synthetic, higher-purity version made from chemical precursors like silicon tetrachloride (SiCl₄). It has even better UV transmission and fewer impurities, making it the material of choice for demanding semiconductor and optical applications.
Manufacturing and Cost
Natural and synthetic crystalline quartz is grown or selected for its specific crystallographic orientation, which is essential for piezoelectric applications. Machining it requires careful alignment with the crystal axes.
Fused quartz can be molded, blown, and worked like conventional glass, making it more versatile for producing complex shapes like laboratory glassware. Generally, high-purity fused silica and perfectly oriented synthetic crystalline quartz are the most expensive variants due to their complex and energy-intensive production processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice is dictated entirely by the physical properties required for your goal.
- If your primary focus is frequency control or precise timing: You must use crystalline quartz for its piezoelectric properties.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability or thermal shock resistance: You need the low thermal expansion of fused quartz.
- If your primary focus is broad-spectrum optics, especially in the UV: You need the superior transmission and isotropy of fused quartz or, for highest performance, fused silica.
- If your primary focus is manipulating the polarization of light: You must use the birefringence of crystalline quartz to create components like waveplates.
Ultimately, selecting the correct material depends on a clear understanding of how its atomic structure enables the performance you require.
Summary Table:
| Property | Crystalline Quartz | Fused Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Structure | Ordered, repeating crystal lattice | Amorphous, disordered glass |
| Thermal Expansion | Higher, fractures at 573°C phase transition | Extremely low, excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Optical Behavior | Anisotropic, birefringent | Isotropic, uniform refractive index |
| Key Unique Property | Piezoelectric effect | Superior UV to IR transmission & thermal stability |
Struggling to select the right quartz material for your lab equipment, semiconductor process, or optical application? KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you choose between crystalline quartz, fused quartz, or fused silica based on your specific requirements for thermal stability, optical transmission, or piezoelectric performance. Contact our team today to ensure your project's success with the perfect material solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature of quartz glass? Master Its High-Temp Limits & Applications
- How does quartz differ from glass? A Guide to Material Selection for Performance
- What are the thermal properties of quartz? Unlocking Extreme Temperature Stability for Your Lab
- What are the uses of quartz glass? Essential for Extreme-Temperature and UV Applications
- What is optical quartz? The Ultimate Material for UV and High-Temp Optics



















