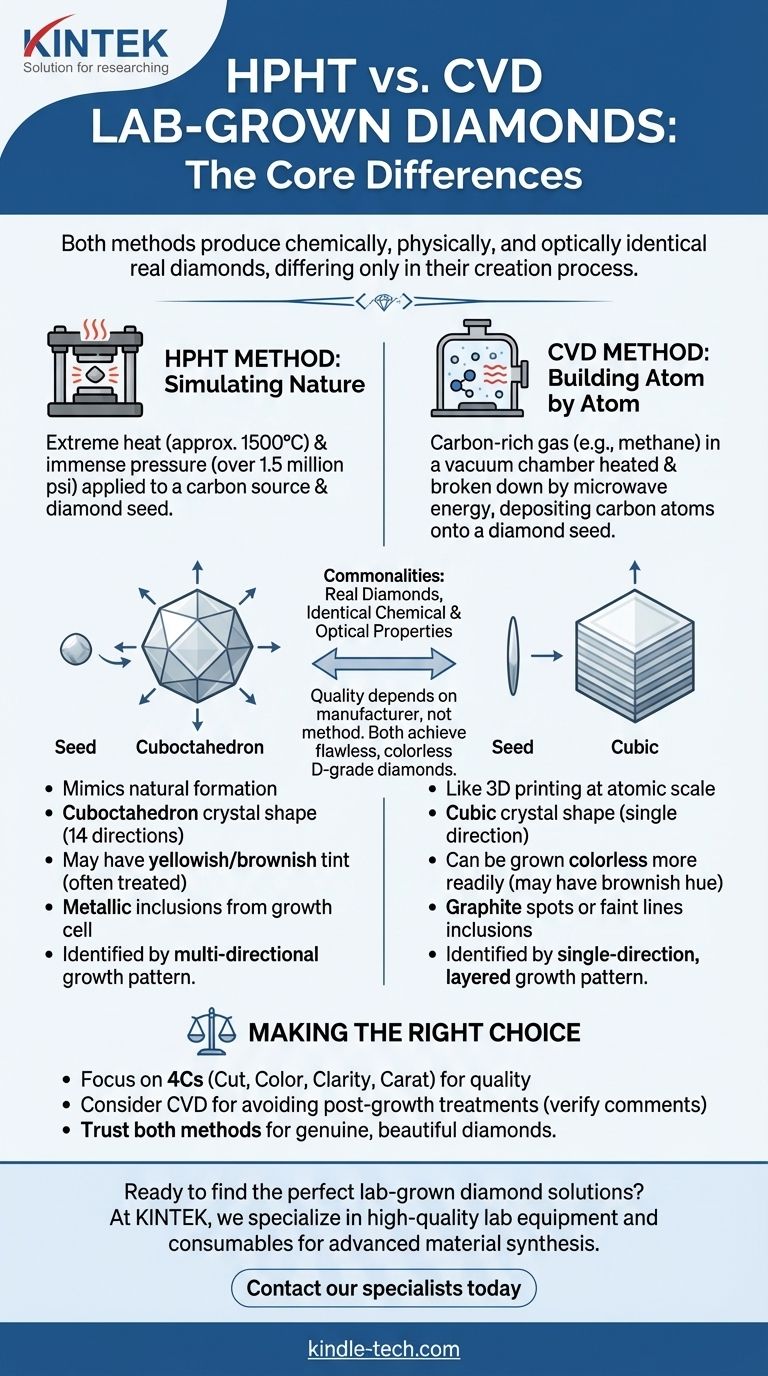
The primary difference between HPHT and CVD lab-grown diamonds lies in their creation process. High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT) diamonds are formed by subjecting a carbon source to intense heat and pressure, mimicking the natural conditions deep within the Earth. In contrast, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) diamonds are "grown" layer by layer in a vacuum chamber by depositing carbon atoms from a gas onto a diamond seed.
While the manufacturing methods are fundamentally different, the final output of both processes is a real diamond. For the consumer, the distinction is almost entirely academic, as both HPHT and CVD produce diamonds that are chemically, physically, and optically identical to natural ones.

The Core Difference: How They Are Made
The growth method is the defining characteristic that separates HPHT and CVD diamonds. Each technique leaves behind subtle atomic-level signatures that a gemologist can identify, but these do not affect the diamond's beauty or durability.
The HPHT Method: Simulating Nature
The HPHT process uses large, complex machines to replicate the extreme environment where diamonds form naturally.
A small diamond seed is placed in a growth cell along with a carbon source, like graphite. The cell is heated to approximately 1500°C and subjected to immense pressure—over 1.5 million pounds per square inch. This forces the carbon atoms to melt and crystallize onto the diamond seed, growing a larger rough diamond.
This process results in a characteristic crystal shape known as a cuboctahedron, which features 14 different growth directions.
The CVD Method: Building Atom by Atom
The CVD process is more akin to advanced 3D printing at an atomic scale.
A thin diamond seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber. The chamber is filled with carbon-rich gases (like methane) and heated. Microwave energy is then introduced to break the gas molecules apart, allowing carbon atoms to "rain" down and deposit onto the diamond seed.
This method builds the diamond in vertical layers, resulting in a cubic crystal shape with a single growth direction.
How This Affects the Final Diamond
While both methods produce genuine diamonds, the different growth environments can influence the final characteristics of the stone, such as its color and the types of inclusions it may contain.
Impact on Color
Historically, HPHT diamonds were more likely to have a slight yellowish or brownish tint due to nitrogen exposure during growth. Many undergo a post-growth treatment process to permanently improve their color and achieve a colorless state.
CVD diamonds can be grown colorless more readily. However, depending on the precision of the process, they can sometimes exhibit a subtle brownish hue, which may also be corrected with treatment.
Impact on Clarity and Inclusions
Both HPHT and CVD diamonds can be grown with exceptional clarity, rivaling the finest natural diamonds.
When inclusions are present, their type can be a clue to the growth method. HPHT diamonds may contain tiny metallic inclusions from the molten flux used in the growth cell. CVD diamonds, due to their layered growth, may exhibit dark graphite spots or faint lines visible only under magnification.
Identification for Gemologists
For a trained gemologist with advanced equipment, telling the two apart is straightforward. The primary indicator is the crystal growth pattern. The multi-directional growth of HPHT diamonds looks different under magnification than the single-direction, layered growth of CVD diamonds.
Understanding the Trade-offs
It is a common misconception that one method is inherently superior to the other. The quality of a lab-grown diamond depends on the skill and technology of the manufacturer, not the method itself.
The Myth of "Better"
Neither HPHT nor CVD is universally "better." Both methods are capable of producing flawless, colorless (D-grade) diamonds. The final quality is a direct result of the manufacturer's investment in technology and quality control.
The Role of Post-Growth Treatments
Many lab-grown diamonds, particularly HPHT stones, undergo a one-time, permanent treatment to improve color. This is a standard and fully disclosed part of the manufacturing process that perfects the diamond's final appearance. It is not an indicator of lower quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a lab-grown diamond, the growth method is far less important than the stone's certified quality.
- If your primary focus is the best quality for value: Ignore the growth method and focus entirely on the diamond's 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, Carat) as detailed in its GIA or IGI grading report.
- If your primary focus is avoiding post-growth treatments: You may lean toward high-quality CVD diamonds, but you must always verify this by checking the "Comments" section of the grading report.
- If your primary focus is simply owning a real, beautiful diamond: Trust that both HPHT and CVD produce chemically and optically identical diamonds that are indistinguishable from natural diamonds to the naked eye.
Ultimately, the best choice is the certified diamond that meets your standards for beauty and budget, as both HPHT and CVD deliver a genuine and brilliant result.
Summary Table:
| Feature | HPHT (High Pressure/High Temperature) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Mimics natural Earth conditions with high heat & pressure | Builds diamond layer-by-layer from carbon gas in a vacuum chamber |
| Crystal Shape | Cuboctahedron (14 growth directions) | Cubic (single growth direction) |
| Typical Color | May have yellowish/brownish tint (often treated) | Can be grown colorless (may have brownish hue) |
| Common Inclusions | Metallic inclusions from growth cell | Graphite spots or faint lines |
| Identification | Multi-directional growth pattern under magnification | Single-direction, layered growth pattern |
Ready to find the perfect lab-grown diamond for your needs? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced material synthesis, including diamond growth technologies. Whether you're a researcher, manufacturer, or jeweler, our expertise can help you achieve superior results. Contact our specialists today to discuss how our solutions can support your laboratory's diamond production and analysis needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of graphene nanocomposites? From Aerospace to Biomedicine
- What is chemical vapor deposition in semiconductors? The Atomic-Scale Engine of Modern Electronics
- What are the chemical Vapour deposition process parameters? Master CVD for Superior Thin Films
- What is the metal organic chemical vapor deposition method? The Key to High-Purity Semiconductor Films
- What is the process of deposition in semiconductors? Build Precise Thin Films for Your ICs
- Which deposition technique allows deposition of ultra-thin layers with atomic layer precision? Achieve Perfect Conformity with ALD
- Why is carbon coating important? Boost Battery Performance and Longevity
- What is the core function of the CVD deposition furnace? Master Bulk ZnS Production with Precision Control



















