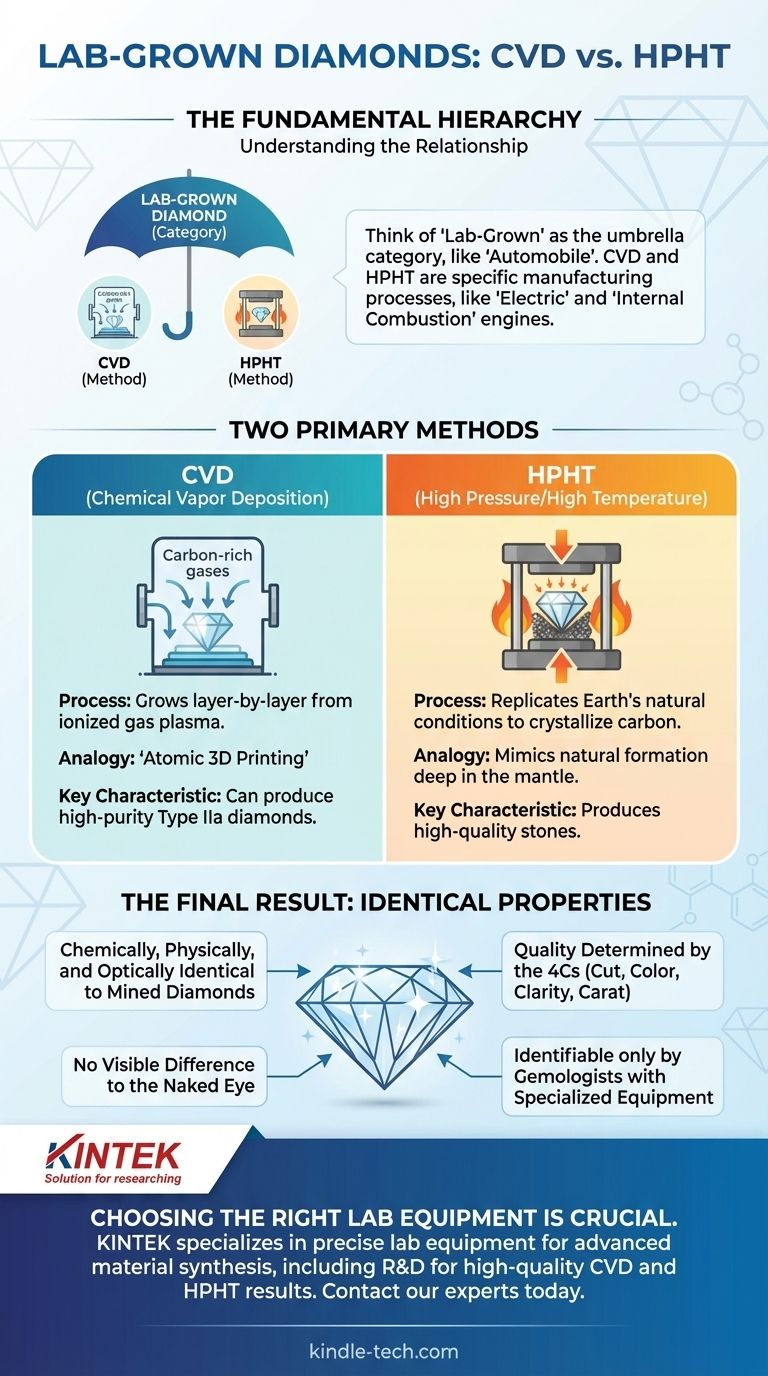
The fundamental difference is not between "lab-grown" and "CVD" diamonds, but rather in understanding that CVD is one of the two primary methods used to create a lab-grown diamond. The term "lab-grown diamond" is a broad category, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a specific manufacturing process that falls under that umbrella. The other major process is known as High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT).
Your question reveals a common point of confusion in the market. The choice isn't between a lab-grown diamond and a CVD diamond; it's that a CVD diamond is a lab-grown diamond. The real distinction lies in the two creation methods: CVD and HPHT.

Understanding the Terminology
The terms can be confusing, but the hierarchy is simple. Think of "lab-grown diamond" as the general category, like "automobile," while CVD and HPHT are the specific engine types, like "electric" or "internal combustion."
"Lab-Grown" Is the Umbrella Term
Any diamond created by humans in a controlled environment is a lab-grown diamond. These are not simulants like cubic zirconia; they are physically, chemically, and optically identical to diamonds mined from the Earth. They are real diamonds, simply with a different origin story.
CVD and HPHT Are the Two Primary Methods
Nearly all lab-grown diamonds on the market today are created using one of two technologies:
- CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition)
- HPHT (High Pressure/High Temperature)
The difference in name refers entirely to how the diamond crystal is grown.
How Each Method Works
Both processes start with a "seed," which is a minuscule slice of a pre-existing diamond. The goal is to make carbon atoms attach to this seed and crystallize, growing a new, larger diamond. The methods for achieving this are distinct.
The CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) Process
The CVD method is often compared to 3D printing on an atomic level. A diamond seed is placed in a vacuum chamber, which is then filled with carbon-rich gases (like methane).
These gases are heated to extreme temperatures until they ionize into a plasma. This process breaks the gas molecules apart, and the pure carbon atoms "rain down" and bond to the diamond seed, building the diamond layer by layer.
The HPHT (High Pressure/High Temperature) Process
The HPHT method seeks to replicate the natural conditions deep within the Earth's mantle where diamonds form. A diamond seed is placed in a chamber with a source of solid carbon (like graphite).
This chamber is subjected to immense pressure (over 870,000 pounds per square inch) and extreme heat. Under these conditions, the carbon source melts and crystallizes around the seed, forming a new diamond.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Do These Differences Matter?
While the science is different, the practical implications for you as a buyer are subtle. The end product from either method, if grown well, is a genuine diamond.
Final Properties Are Identical
A finished and polished diamond from a CVD or HPHT process is chemically identical to a natural diamond. All are made of carbon atoms arranged in the same crystal lattice structure. To the naked eye, there is no visible difference between a high-quality CVD, HPHT, or natural diamond.
The Impact on Quality and Color
Historically, each method had certain tendencies. HPHT diamonds sometimes had a slight yellow or brown tint due to nitrogen exposure, while early CVD diamonds could have brown undertones.
However, modern refinement techniques have largely overcome these issues. Both methods can now produce the highest-purity, colorless diamonds (Type IIa), which are actually rarer in nature. The final quality of the stone is determined by its grading (the 4Cs), not its origin method.
Identification by Gemologists
While you cannot see a difference, a trained gemologist with specialized equipment can identify the origin. The different growth patterns leave behind subtle markers.
HPHT diamonds may have trace metallic inclusions from the growth chamber, while CVD diamonds can exhibit specific layered patterns. Reputable manufacturers often laser-inscribe a serial number and "Lab Grown" on the diamond's girdle for full transparency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The debate between CVD and HPHT is mostly academic. Your focus should be on the final quality and beauty of the individual stone.
- If your primary focus is obtaining the highest quality for your budget: Ignore the manufacturing method and concentrate on the diamond's official grading report (the 4Cs: Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat).
- If you are concerned about color or purity: Both CVD and HPHT can produce flawless, colorless diamonds, so let the grading certificate be your guide, not the growth method.
- If you simply want a beautiful, ethical diamond: Rest assured that both methods produce real, conflict-free diamonds with a significantly smaller environmental footprint than mined diamonds.
Ultimately, your decision should be based on the certified quality and personal appeal of the diamond, not the technical label of its creation.
Summary Table:
| Method | Process Overview | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | Grows diamond layer-by-layer from carbon-rich gas in a vacuum chamber. | Often compared to 3D printing; can produce high-purity Type IIa diamonds. |
| HPHT (High Pressure/High Temperature) | Replicates Earth's natural conditions to crystallize carbon around a seed. | Mimics natural diamond formation; also produces high-quality stones. |
Choosing the right lab equipment is as crucial as understanding diamond creation methods. KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced material synthesis, including R&D for high-quality results. Whether your focus is on CVD, HPHT, or other laboratory processes, we provide the reliable tools to support your innovation. Let's discuss your specific lab requirements — contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance



















