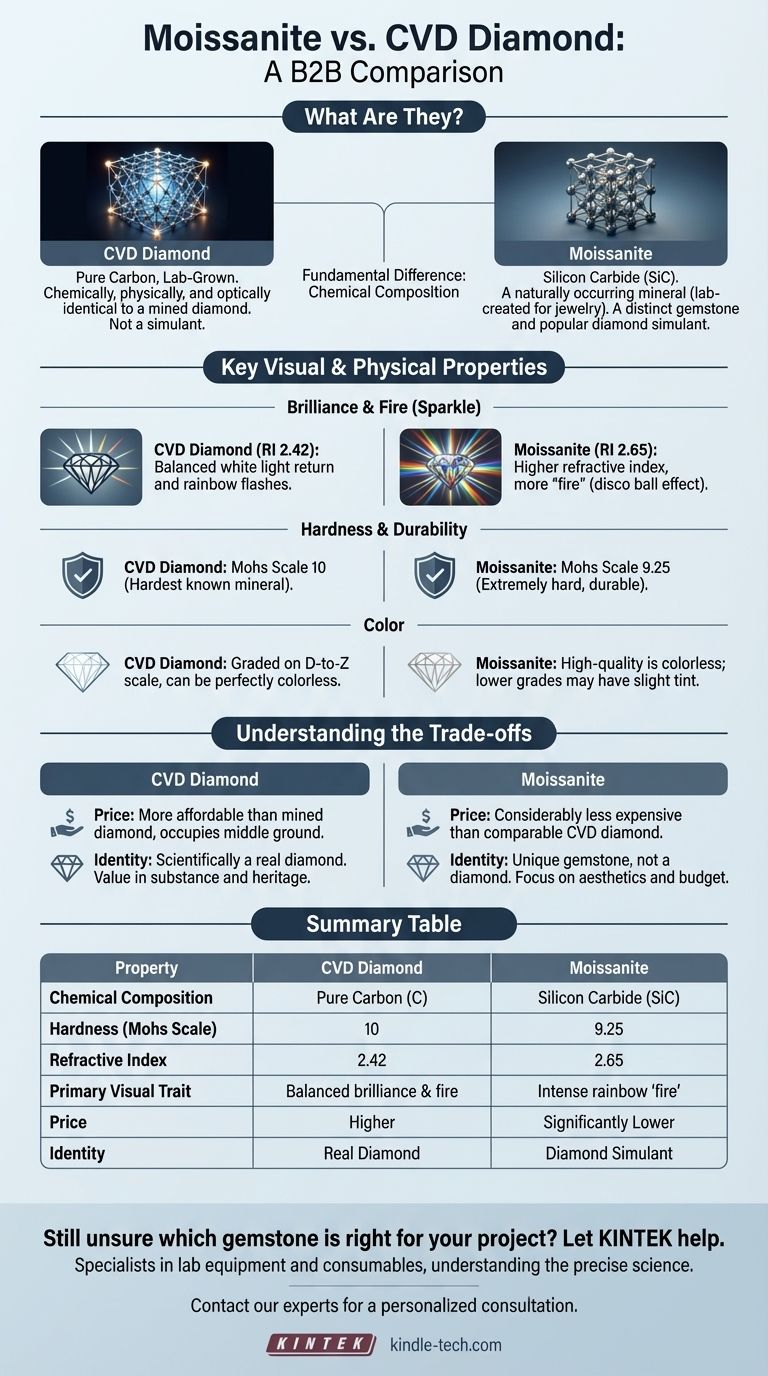
The fundamental difference is their chemical composition. A CVD diamond is a true diamond made of pure carbon, identical to a mined diamond in every way except its origin. Moissanite is a completely different gemstone made of silicon carbide; it is a popular diamond simulant, not a synthetic diamond.
The choice between Moissanite and a CVD diamond is not a matter of which is "better," but a decision based on your priorities. A CVD diamond offers the genuine chemical and physical properties of a diamond, while Moissanite provides exceptional brilliance at a much lower price point.

What Are These Materials, Fundamentally?
To understand the differences, we must first look at what each stone is made of at an atomic level. Their origin and composition dictate all of their other properties.
CVD Diamond: Pure Carbon, Lab-Grown
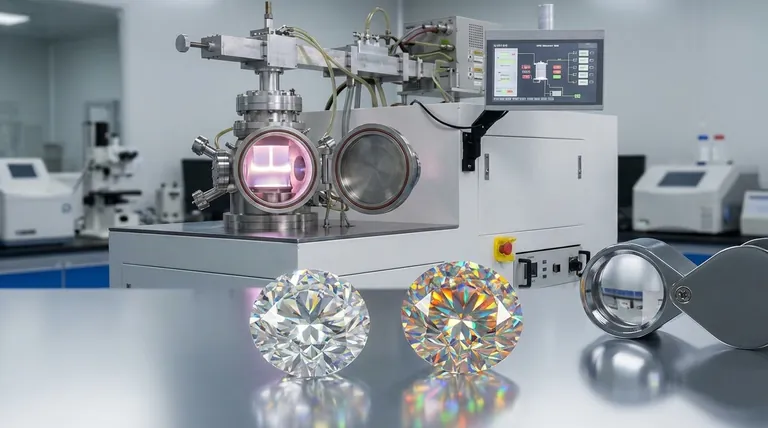
A CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) diamond is not a simulant or a "fake" diamond. It is a real diamond.
It is created in a lab by placing a small diamond "seed" in a chamber and introducing carbon-rich gases. Under specific conditions, these gases break down, and carbon atoms attach to the seed, growing a larger, pure diamond layer by layer.
The resulting stone is chemically, physically, and optically identical to a diamond mined from the earth. The only difference is its origin.
Moissanite: A Different Compound Entirely
Moissanite is a naturally occurring mineral called silicon carbide (SiC), originally discovered in a meteorite crater.
The moissanite used in jewelry is lab-created, as the natural mineral is incredibly rare. Because it is not made of carbon, it is not a diamond. It is a distinct gemstone in its own right that has become a popular diamond alternative due to its durability and intense sparkle.
Comparing Key Visual and Physical Properties
While they may look similar at a glance, their different chemical makeups result in distinct characteristics that a discerning eye can see.
Brilliance and Fire (The "Sparkle")
This is the most noticeable visual difference. Moissanite has a higher refractive index than a diamond (2.65 vs. 2.42).
This means Moissanite bends light more, resulting in more "fire"—the colorful, rainbow-like flashes of light you see when the stone moves. This intense, fiery sparkle is often described as a "disco ball effect."
A CVD diamond will have the exact same level of brilliance and fire as a high-quality natural diamond, which is known for its balance of white light return (brilliance) and rainbow flashes (fire).
Hardness and Durability
Both stones are exceptionally hard, making them perfect for daily wear in jewelry like engagement rings.
On the Mohs scale of hardness, a diamond (both mined and CVD) is a perfect 10, the hardest known mineral on earth.
Moissanite is a 9.25 on the Mohs scale. While technically less hard than a diamond, it is harder than any other gemstone besides diamond and is extremely resistant to scratching and damage.
Color
Both CVD diamonds and modern moissanite can be produced to be completely colorless.
CVD diamonds are graded on the same D-to-Z color scale as mined diamonds, allowing you to choose a perfectly colorless stone (D, E, or F grades).
High-quality moissanite is also colorless. However, some lower-quality or older versions can exhibit a slight yellow or grayish tint, which may become more noticeable in larger sizes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Your decision will ultimately come down to balancing price against the material's inherent identity.
The Price Difference
This is a significant factor. Moissanite is considerably less expensive than a CVD diamond of a comparable size and apparent quality.
A CVD diamond is, in turn, significantly more affordable than a mined diamond with the same specifications. It occupies a middle ground in price between moissanite and a mined stone.
The Question of "Realness"
This is a personal, psychological consideration. A CVD diamond is scientifically a real diamond. For many, the value lies in owning a stone with the same heritage, substance, and properties as the classic mined version.
Moissanite makes no claim to be a diamond. It is its own unique gemstone. For buyers focused purely on aesthetics, durability, and budget, the "simulant" label is irrelevant.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your stone based on what you value most. There is no universally "correct" answer.
- If your primary focus is authenticity and owning a real diamond: Choose a CVD diamond. It is physically and chemically a diamond in every sense, offering identical performance to a mined stone at a lower cost.
- If your primary focus is maximizing sparkle and budget: Choose Moissanite. It delivers more rainbow "fire" than a diamond for a fraction of the price, without sacrificing durability for everyday wear.
- If your primary focus is durability above all else: Both are excellent choices, but a CVD diamond has the slight technical edge as the hardest material available.
Understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to choose the stone that perfectly aligns with your values, budget, and desired aesthetic.
Summary Table:
| Property | CVD Diamond | Moissanite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon (C) | Silicon Carbide (SiC) |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 10 | 9.25 |
| Refractive Index | 2.42 | 2.65 |
| Primary Visual Trait | Balanced brilliance & fire | Intense rainbow 'fire' |
| Price | Higher | Significantly Lower |
| Identity | Real Diamond | Diamond Simulant |
Still unsure which gemstone is right for your project? Let KINTEK help you make the perfect choice. As specialists in lab equipment and consumables, we understand the precise science behind these materials. Whether you're a jeweler, researcher, or enthusiast, our expertise can guide you to the ideal solution for your specific needs.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory and gemological requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary advantages of the CVD method for growing diamonds? Engineering High-Purity Gems and Components
- How do lab-grown diamonds compare to natural diamonds? Uncover the Truth About Origin, Price, and Value
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection
- What is the difference between MPCVD and HFCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
















