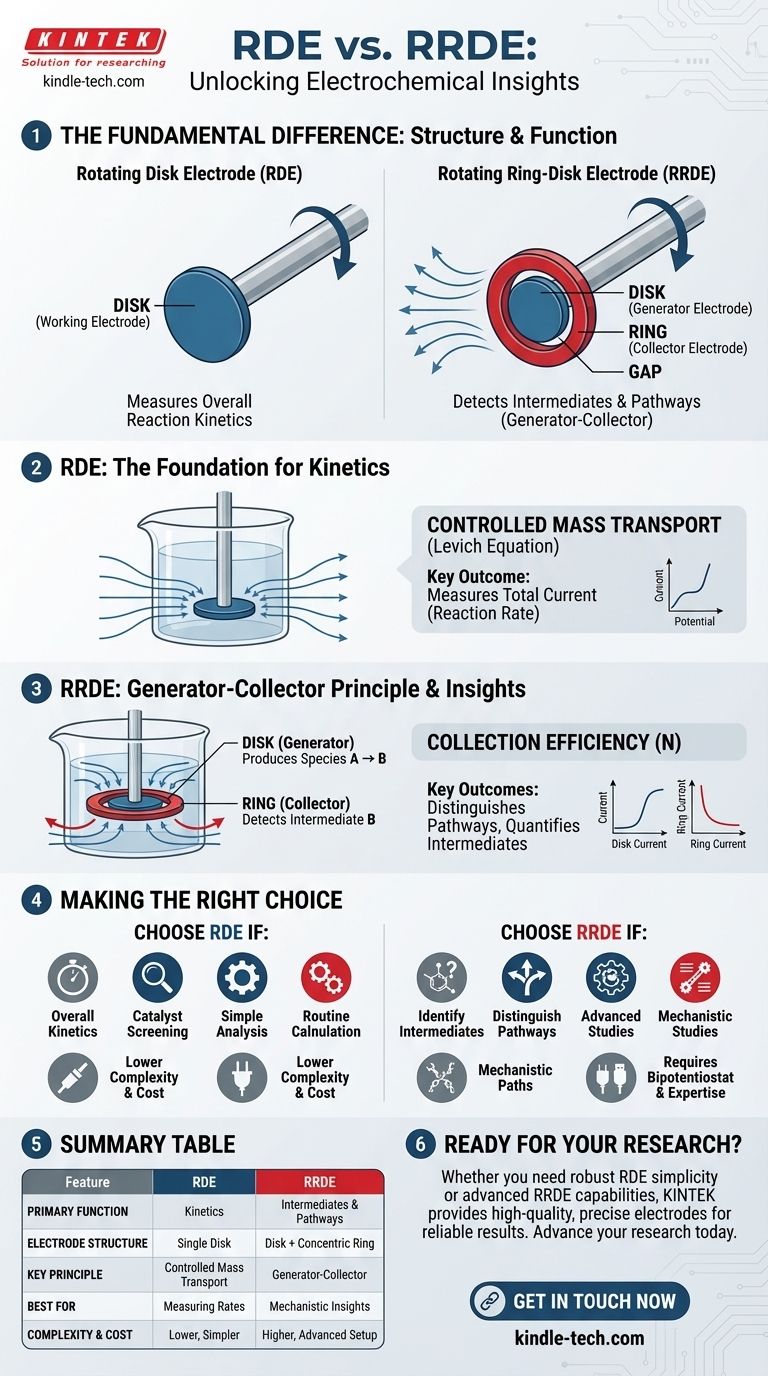
The fundamental difference between a rotating ring-disk electrode (RRDE) and a rotating disk electrode (RDE) is structural. An RRDE features a second, independent working electrode—the ring—that concentrically surrounds the central disk. This addition transforms the electrode from a simple tool for studying overall reaction rates into a sophisticated system for detecting reaction products and intermediates in real-time.
While both electrodes use rotation to precisely control the flow of reactants to their surface, the RRDE's ring acts as a downstream detector. This allows you to actively "collect" and identify the chemical species being generated at the central disk, providing a level of mechanistic insight that is impossible to achieve with an RDE alone.

The Foundation: The Rotating Disk Electrode (RDE)
An RDE is a powerful tool used to study electrochemical reactions under highly controlled and reproducible conditions. Its design overcomes the limitations of a stationary electrode.
Why Rotate the Electrode?
At a stationary electrode, reactants in the solution are consumed, creating a depletion zone that grows over time and complicates analysis.
By spinning the electrode at a constant, known rate, a thin, well-defined layer of solution is forced toward the surface and then thrown outwards. This creates a stable and predictable flow of fresh reactants to the electrode.
This process ensures the measured current is not limited by random diffusion but by a controlled rate of mass transport, allowing for the precise measurement of reaction kinetics. The resulting stable, plateau-like current is described by the Levich equation.
What an RDE Measures
The RDE provides a single output: the total current flowing at the disk for a given electrochemical potential.
This makes it excellent for measuring the overall rate of a reaction, determining kinetic parameters, and comparing the performance of different catalysts under identical hydrodynamic conditions.
The Advancement: The Rotating Ring-Disk Electrode (RRDE)
The RRDE builds directly upon the RDE's foundation by adding the ring electrode, introducing a powerful new capability.
The "Generator-Collector" Principle
In an RRDE experiment, the two working electrodes are controlled independently. The central disk acts as the "generator," where the primary electrochemical reaction of interest occurs, producing products or intermediates.
As these newly generated chemical species are swept outward by the electrode's rotation, a fraction of them pass over the ring, which acts as the "collector." The ring's potential is set specifically to detect these species by either oxidizing or reducing them.
Unlocking Deeper Mechanistic Insights
This generator-collector setup allows you to answer questions an RDE cannot. For example, in the study of the oxygen reduction reaction, an RDE can only measure the total current produced.
An RRDE, however, can distinguish between a direct four-electron pathway to water and an indirect two-electron pathway that produces hydrogen peroxide as an intermediate. By setting the ring potential to detect hydrogen peroxide, you can quantify which reaction pathway is dominant.
Quantifying with Collection Efficiency
Each RRDE has a known geometric constant called the collection efficiency (N). This value represents the calculated fraction of stable species generated at the disk that will be intercepted by the ring.
By comparing the measured ring current to the disk current, you can determine if your intermediates are stable or if they are participating in further chemical reactions before reaching the ring.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While more powerful, the RRDE introduces additional complexity that is not always necessary.
Increased Complexity and Cost
An RRDE system requires a bipotentiostat, an instrument capable of controlling the potential of two working electrodes simultaneously. The electrodes themselves are also more expensive and delicate than standard RDEs.
More Demanding Experimental Design
Designing an RRDE experiment requires careful thought. You must select a ring potential that is selective for the intermediate you want to detect without causing other interfering reactions to occur.
When an RDE Is Sufficient
If your goal is simply to measure the overall kinetic current of a well-understood reaction or to screen catalysts for general activity, an RDE is often the simpler, more cost-effective, and perfectly adequate choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct electrode is a matter of matching the tool to the scientific question you need to answer.
- If your primary focus is measuring overall reaction kinetics: The RDE is your standard, robust tool for analysis under controlled mass transport.
- If your primary focus is identifying reaction intermediates: The RRDE is essential, as its collector ring is specifically designed to detect species generated at the disk.
- If your primary focus is distinguishing between competing reaction pathways: The RRDE's generator-collector capability is the only way to quantify the products of different pathways.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis with maximum simplicity: The RDE provides the core functionality you need without the added complexity of the ring.
Ultimately, your choice depends on whether you need to know only that a reaction is happening or precisely how it is happening.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rotating Disk Electrode (RDE) | Rotating Ring-Disk Electrode (RRDE) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Measures overall reaction kinetics | Detects reaction intermediates & pathways |
| Electrode Structure | Single disk electrode | Central disk surrounded by a concentric ring |
| Key Principle | Controlled mass transport (Levich equation) | Generator-Collector principle |
| Best For | Measuring reaction rates, catalyst screening | Identifying intermediates, mechanistic studies |
| Complexity | Lower cost & simpler setup | Higher cost, requires bipotentiostat |
Ready to choose the right electrode for your electrochemical research?
Whether you need the robust simplicity of an RDE for kinetic studies or the advanced capabilities of an RRDE for mechanistic insights, KINTEK has the high-quality lab equipment you need. Our electrodes are designed for precision and reliability, helping you achieve accurate and reproducible results.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your specific application. Our experts will help you select the perfect tool to advance your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is the rotating ring disk electrode method? Unlock Real-Time Reaction Analysis
- What is the application of RRDE? Unlock Quantitative Catalyst and Reaction Insights
- What is the common role of a platinum disk electrode? A Guide to Its Primary Use as a Working Electrode
- What is the difference between RDE and RRDE? Unlock Advanced Electrochemical Reaction Analysis
- What is the RRDE in electrochemistry? Unlock Detailed Reaction Pathways with Dual-Electrode Analysis



















