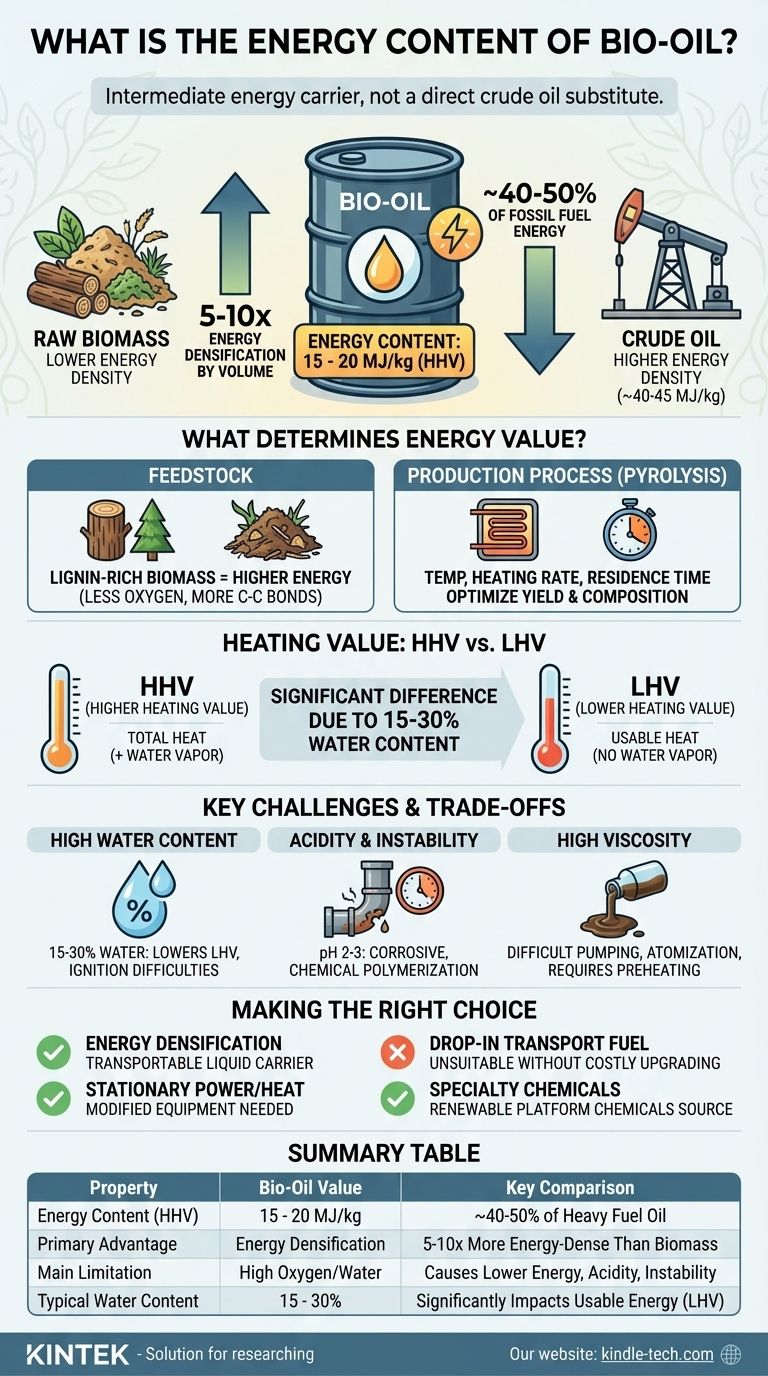
In short, the energy content of bio-oil typically ranges from 15 to 20 Megajoules per kilogram (MJ/kg). This value, known as the Higher Heating Value (HHV), is significantly lower than that of conventional crude oil but represents a substantial energy densification compared to the original raw biomass from which it is derived. The exact energy content varies based on the type of biomass used and the specific production process.
Bio-oil should be viewed as an intermediate energy carrier, not a direct substitute for crude oil. While it successfully concentrates the energy from bulky biomass into a transportable liquid, its high oxygen and water content fundamentally limit its energy value and create significant challenges for storage and use without further upgrading.

What Determines Bio-Oil's Energy Content?
The final energy value of bio-oil is not a fixed number. It is the direct result of its complex chemical composition, which is determined by the feedstock and the production method.
The Role of Feedstock
The source material is the primary factor. Different types of biomass contain varying ratios of three key polymers: cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
Biomass rich in lignin, such as softwood or certain forestry residues, tends to produce bio-oil with a higher energy content. Lignin's complex aromatic structure contains less oxygen and more carbon-carbon bonds compared to cellulose and hemicellulose, translating to more energy upon combustion.
The Impact of the Production Process
Bio-oil is typically produced through a process called fast pyrolysis, where biomass is rapidly heated in the absence of oxygen.
Key process parameters like temperature, heating rate, and vapor residence time directly influence the chemical reactions that break down the biomass. Fine-tuning these conditions can optimize the yield and alter the composition of the resulting oil, thereby affecting its final energy content.
Understanding Heating Value (HHV vs. LHV)
When discussing fuel energy, it's critical to distinguish between Higher Heating Value (HHV) and Lower Heating Value (LHV).
HHV is the total heat released during combustion, assuming the water vapor produced condenses back into liquid. LHV excludes this latent heat of vaporization. Because bio-oil contains a significant amount of water (15-30%), the difference between its HHV and LHV is much larger than for dry fossil fuels. LHV is often a more realistic measure of the usable energy in practical applications like engines or turbines.
How Bio-Oil Compares to Other Fuels
Placing the energy content of bio-oil in context reveals its unique position as a fuel.
Bio-Oil vs. Raw Biomass
The primary advantage of converting biomass to bio-oil is energy densification. Raw biomass is bulky, difficult to transport, and has a low energy density (especially when wet).
Pyrolysis converts this solid into a liquid that is roughly 5-10 times more energy-dense by volume. This transformation makes the energy from distributed biomass sources far easier to store and transport to a point of use.
Bio-Oil vs. Fossil Fuels
This is where the limitations become clear. The energy content of bio-oil (15-20 MJ/kg) is only about 40-50% of that of conventional fossil fuels like heavy fuel oil or crude oil, which are typically in the 40-45 MJ/kg range.
The reason for this large gap is bio-oil's high oxygen content (35-40% by weight). Oxygen atoms do not contribute to the energy released during combustion; they essentially add dead weight. In contrast, crude oil has a negligible oxygen content.
Understanding the Trade-offs: More Than Just Energy
A fuel's usefulness is determined by more than just its heating value. Bio-oil has several properties that present significant practical challenges.
The Challenge of High Water Content
Bio-oil contains a substantial amount of water (15-30%), which is intimately mixed in the organic matrix. This water comes from moisture in the original feedstock and from chemical reactions during pyrolysis.
This water content lowers the heating value, can make ignition difficult, and reduces the flame temperature during combustion.
Acidity and Chemical Instability
Bio-oil is highly acidic, with a pH typically between 2 and 3. This makes it corrosive to common construction materials like carbon steel, requiring more expensive stainless steel for tanks, pumps, and pipes.
Furthermore, it is chemically unstable. Over time, components within the oil can react with each other (polymerize), increasing its viscosity and eventually forming solid sludge. This limits its long-term storage viability.
High Viscosity
Compared to petroleum distillates like diesel, raw bio-oil is quite viscous. This property, which worsens with age, makes it difficult to pump and atomize in standard fuel injectors, often requiring preheating or specialized equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use bio-oil depends entirely on your objective. It is a flexible intermediate, but it is not a universal solution.
- If your primary focus is energy densification: Bio-oil is an excellent pathway to convert low-value, dispersed biomass into a transportable liquid energy carrier for subsequent use or upgrading.
- If your primary focus is a drop-in transportation fuel: Raw bio-oil is unsuitable. It requires significant and costly upgrading (e.g., hydrotreating) to remove oxygen, which increases its energy content and stability to resemble conventional fuels.
- If your primary focus is stationary power or heat: Bio-oil can be burned in modified industrial boilers, furnaces, and certain turbines, but equipment must be designed to handle its acidity, viscosity, and lower energy content.
- If your primary focus is producing specialty chemicals: The value of bio-oil may lie not in its energy but in its unique composition, which can be a source for renewable phenols, aldehydes, and other platform chemicals.
Ultimately, understanding these distinct properties is the first step toward effectively harnessing bio-oil as a renewable resource.
Summary Table:
| Property | Bio-Oil Value | Key Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Content (HHV) | 15 - 20 MJ/kg | ~40-50% of heavy fuel oil (40-45 MJ/kg) |
| Primary Advantage | Energy densification | 5-10x more energy-dense by volume than raw biomass |
| Main Limitation | High oxygen/water content | Causes lower energy, acidity, and instability vs. fossil fuels |
| Typical Water Content | 15 - 30% | Significantly impacts usable energy (LHV) and stability |
Ready to explore bio-oil applications or need reliable lab equipment for your biomass research?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your biomass conversion and analysis needs. Whether you are optimizing pyrolysis processes or analyzing fuel properties, our products support accurate and efficient research.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can equip your laboratory for success in renewable energy innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
People Also Ask
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products



