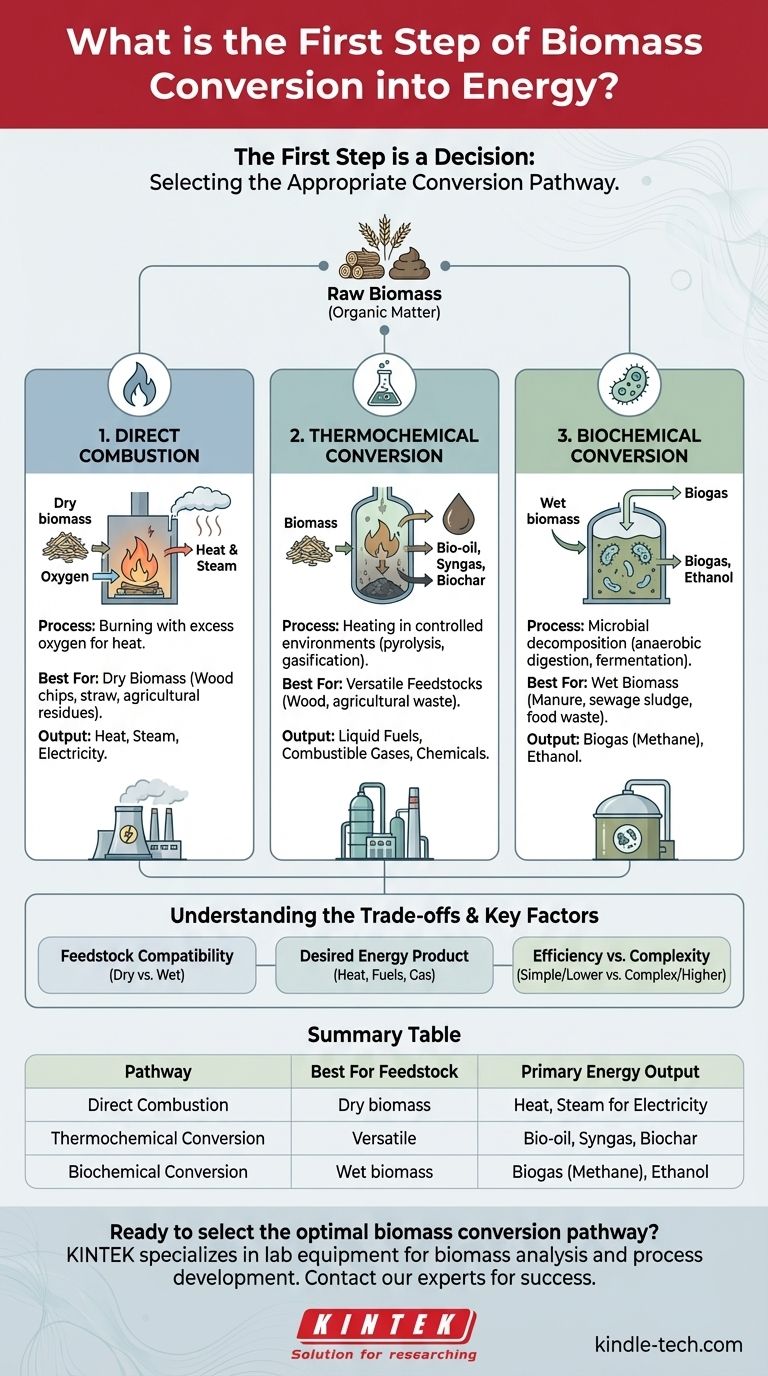
The first step in converting biomass to energy is not a single physical action, but a critical decision: selecting the appropriate conversion pathway. This choice dictates the entire technological process, the type of energy produced, and the kind of biomass that can be used. The primary methods are direct combustion, thermochemical conversion, and biochemical conversion.
The true first step of any bioenergy process is choosing a conversion method. Your decision between burning the material directly (combustion), using heat to chemically alter it (thermochemical), or using microbes to break it down (biochemical) depends entirely on your raw material and your energy goal.
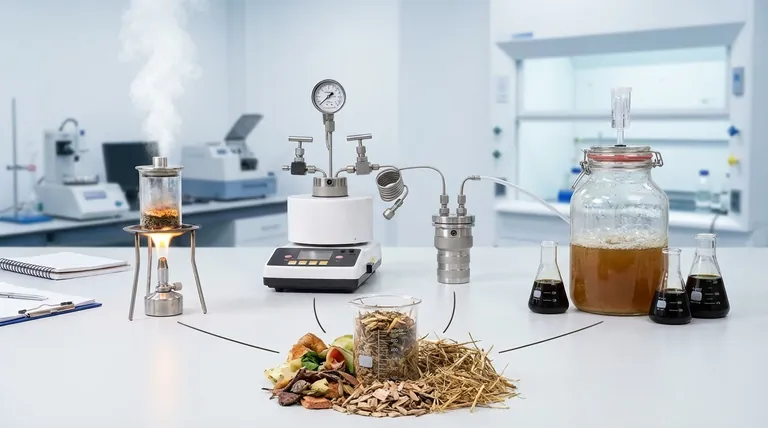

The Three Primary Conversion Pathways
Understanding the "first step" means understanding your options. The conversion of raw organic matter into usable energy begins by funneling it into one of three distinct technological routes. Each is designed for different types of biomass and produces different forms of energy.
Direct Combustion: The Simplest Path
Direct combustion is the most straightforward and common method. It is simply the process of burning biomass in the presence of excess oxygen to release heat.
This heat can be used directly for heating applications or to boil water, creating steam that drives a turbine to generate electricity.
This pathway is best suited for dry biomass with low moisture content, such as wood chips, straw, and other agricultural residues.
Thermochemical Conversion: Using Heat and Chemistry
Thermochemical conversion involves heating biomass in controlled environments, typically with limited or no oxygen. This process breaks down complex organic materials into simpler, more valuable products without fully burning them.
Key methods include pyrolysis (heating without oxygen to produce bio-oil, syngas, and biochar) and gasification (using limited oxygen to convert biomass into a combustible gas called syngas).
This approach is highly versatile and can process a wide range of feedstocks, producing liquid fuels, combustible gases, or valuable chemical feedstocks.
Biochemical Conversion: Leveraging Biology
Biochemical conversion uses microorganisms like bacteria and yeast to decompose wet organic matter. This process mimics natural decomposition but in a controlled environment to capture the energy released.
The two main processes are anaerobic digestion, where bacteria break down organic waste in an oxygen-free environment to produce biogas (mostly methane), and fermentation, which uses yeast to convert sugars into ethanol.
This pathway is ideal for wet biomass such as animal manure, sewage sludge, and food processing waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the correct initial pathway is a matter of balancing the feedstock, the desired energy product, and operational complexity. Selecting the wrong path leads to inefficiency and failure.
Feedstock Compatibility is Key
The most important factor is the nature of your biomass. Dry materials like wood and dry crops are incompatible with biochemical processes that require moisture for microbes to thrive.
Conversely, wet materials like manure or food waste are poor candidates for combustion, as significant energy is wasted just to boil off the excess water before any useful heat is generated.
Desired Energy Product Defines the Process
Your end goal dictates your choice. If you simply need heat or steam-generated electricity, direct combustion is the most established and direct route.
If you need to produce liquid fuels for transportation (like bio-oil or ethanol) or a combustible syngas for specialized engines, you must choose a thermochemical or biochemical pathway.
Efficiency and Complexity
Direct combustion is technologically simple but can have lower overall energy efficiency compared to more advanced methods. Poorly controlled combustion can also lead to significant air pollution.
Thermochemical and biochemical processes are more complex and require higher initial capital investment. However, they can convert biomass into higher-value, more versatile energy carriers with greater efficiency and often lower emissions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting your conversion pathway is the foundational decision for any bioenergy project. Your choice should be guided by your specific circumstances and objectives.
- If your primary focus is generating heat or electricity from dry waste (like wood chips): Direct combustion is the most straightforward and established method.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid fuels or chemical feedstocks from various organic materials: Thermochemical conversion offers a flexible and powerful route to produce higher-value products.
- If your primary focus is managing wet organic waste (like manure or food scraps) and producing fuel gas: Biochemical conversion is the ideal choice for its efficiency with high-moisture feedstocks.
Aligning your biomass source with the right conversion technology is the essential first step toward unlocking its energy potential.
Summary Table:
| Pathway | Best For Feedstock | Primary Energy Output |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Combustion | Dry biomass (wood chips, straw) | Heat, Steam for Electricity |
| Thermochemical Conversion | Versatile (wood, agricultural waste) | Bio-oil, Syngas, Biochar |
| Biochemical Conversion | Wet biomass (manure, food waste) | Biogas (Methane), Ethanol |
Ready to select the optimal biomass conversion pathway for your lab or facility? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for efficient biomass analysis and process development. Whether you're researching thermochemical processes or scaling up biochemical digestion, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for success. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific biomass conversion needs and how we can support your energy goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-pressure hydrothermal synthesis autoclave necessary for MnO2 nanowires? Precision Catalyst Growth
- What is the function of a PTFE-lined hydrothermal autoclave in cys-CDs synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Carbon Dots
- Why are high-strength alloy tube reactors critical for HHIP? Ensuring Safety and Purity in High-Pressure Environments
- What is the advantage of using high-pressure hydrothermal reactors to treat biomass waste? Efficient Resource Recovery
- Why use high-pressure reactors for food waste pretreatment? Boost Hydrogen Production Efficiency Today!



















