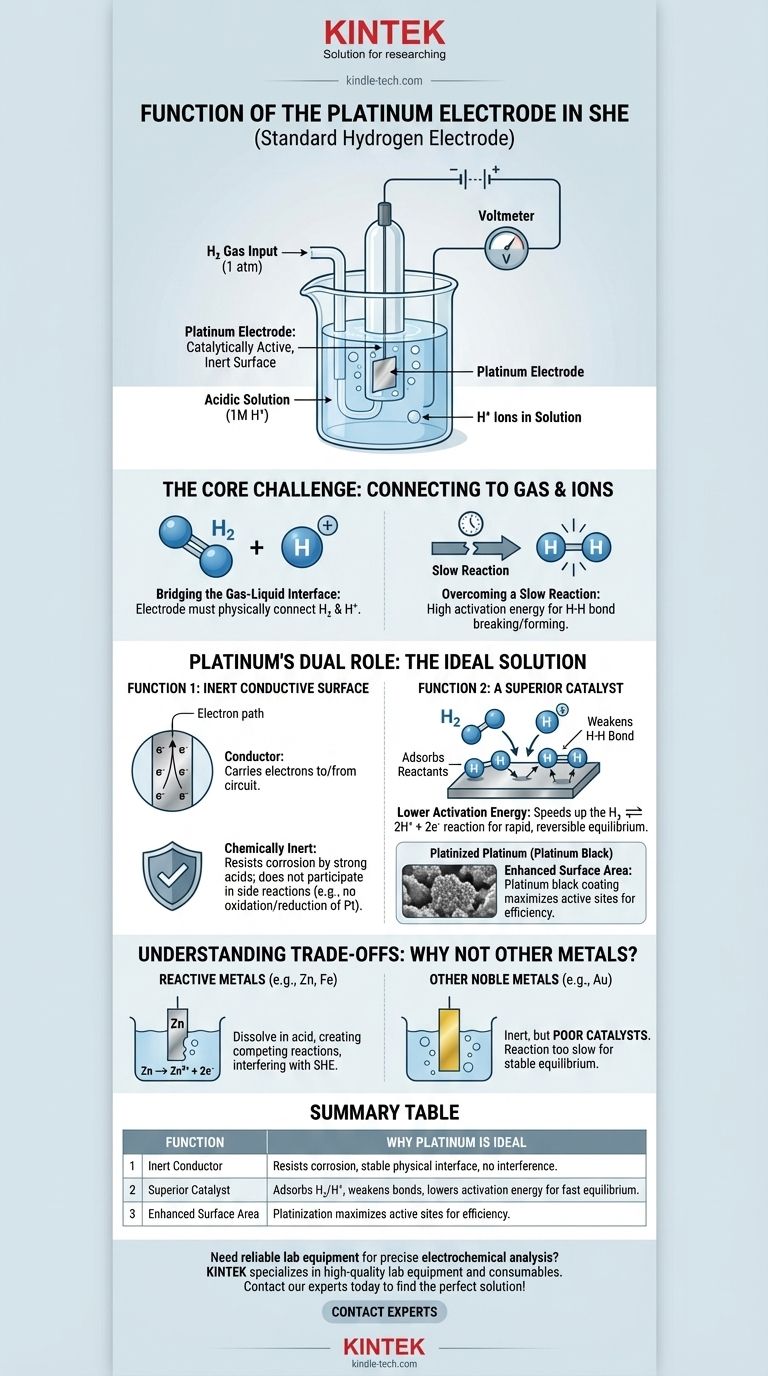
In short, the platinum electrode in a Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) functions as a catalytically active, inert surface. It provides the physical site where the hydrogen reaction can occur and lowers the activation energy required, allowing the cell to reach a stable, measurable equilibrium without the electrode itself being consumed.
The core challenge of the SHE is creating a reliable electrical connection to a reaction involving a gas (H₂) and an ion (H⁺). Platinum is uniquely suited for this role because it is both an excellent catalyst for the hydrogen reaction and a chemically inert conductor, ensuring it facilitates the reaction without interfering with it.
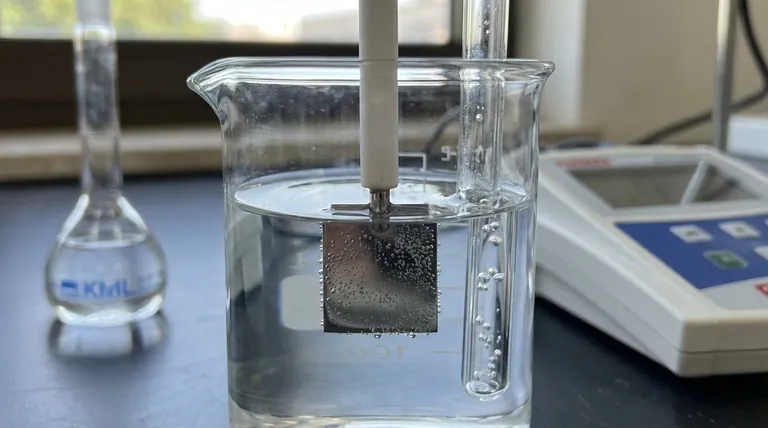

The Core Challenge: Connecting a Circuit to a Gas
To understand platinum's function, we must first recognize the fundamental problem in constructing a Standard Hydrogen Electrode. The goal is to measure the potential of the hydrogen redox reaction: 2H⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ H₂(g).
Bridging the Gas-Liquid Interface
The reaction involves hydrogen ions dissolved in an acidic solution and hydrogen gas bubbled over the electrode. An electrode must physically exist in this environment to either supply or accept electrons from an external circuit.
Overcoming a Slow Reaction
This hydrogen reaction does not happen quickly or efficiently on its own. The energy required to break the H-H bond in a hydrogen molecule or to combine two hydrogen ions is high. Without help, the system would not reach a rapid and reversible equilibrium, making it useless as a standard reference.
Platinum's Dual Role: The Ideal Solution
Platinum is chosen because it solves both of these problems simultaneously. It acts as both an inert physical conductor and an active chemical catalyst.
Function 1: An Inert Conductive Surface
First, the electrode must be a conductor to carry electrons to or from the external circuit. Crucially, it must also be chemically inert.
It cannot react with the strong acid (typically 1M HCl) or be oxidized or reduced itself. Platinum is a noble metal, meaning it is extremely resistant to corrosion and dissolution, making it the perfect stable, physical foundation for the electrode.
Function 2: A Superior Catalyst
This is platinum's most critical function. It dramatically speeds up the hydrogen redox reaction.
The surface of the platinum adsorbs both the hydrogen gas molecules (H₂) and the hydrogen ions (H⁺). Think of the platinum surface as a workbench that holds the reactants in place, making it easier for them to interact.
By adsorbing hydrogen gas, the platinum surface weakens the strong covalent H-H bond, making it much easier to split the molecule into individual atoms that can then be oxidized to H⁺ ions. This catalytic action is what allows the reaction to proceed quickly and reversibly.
The Role of "Platinized Platinum"
To maximize this effect, the electrode is often coated with a layer of finely divided platinum powder, known as platinum black. This process, called platinization, dramatically increases the effective surface area of the electrode, providing many more active sites for catalysis and ensuring the electrode performs efficiently.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Not Other Metals?
Examining why other metals fail helps clarify why platinum is the definitive choice.
The Problem with Reactive Metals
Metals like zinc, iron, or aluminum are highly reactive. If placed in the acidic solution of the SHE, they would simply dissolve (Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻). This creates a competing electrochemical reaction that would completely interfere with the hydrogen electrode's function.
The Problem with Other Noble Metals
Other inert metals, like gold, could serve as the inert conductor. However, gold is a significantly poorer catalyst for the hydrogen reaction compared to platinum. While a gold electrode would not corrode, the reaction would be too slow to establish a reliable and reproducible equilibrium potential, defeating the purpose of a "standard" electrode.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the dual function of platinum is key to grasping the fundamental principles of electrochemistry and reference standards.
- If your primary focus is on reaction kinetics: Remember that platinum's main purpose is to act as a heterogeneous catalyst, lowering the activation energy for both the forward and reverse hydrogen reactions.
- If your primary focus is on cell design: Remember that the electrode material must be an inert conductor that provides a stable physical interface without participating in any interfering side reactions.
The selection of platinum is a deliberate engineering choice that enables the hydrogen electrode to serve as the universal zero point for all electrochemical measurements.
Summary Table:
| Function | Why Platinum is Ideal |
|---|---|
| Inert Conductor | Resists corrosion in acid, provides a stable physical interface without interfering reactions. |
| Superior Catalyst | Adsorbs H₂ and H⁺, weakens H-H bonds, and lowers activation energy for fast, reversible equilibrium. |
| Enhanced Surface Area | Platinization (platinum black coating) maximizes active sites for efficient performance. |
Need reliable lab equipment for precise electrochemical analysis? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, ensuring your laboratory achieves accurate and consistent results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your research needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Gold Disc Electrode
People Also Ask
- How should a platinum sheet electrode be operated during an experiment? Ensure Accurate and Reproducible Results
- What precautions should be taken when using a platinum sheet electrode? Ensure Accurate & Reproducible Electrochemical Data
- What are the performance characteristics of platinum sheet electrodes? Unlock Superior Electrochemical Performance
- What are the available specifications for platinum sheet electrodes? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Electrochemical Needs
- What is the most critical guideline for immersing a platinum sheet electrode in an electrolyte? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements



















