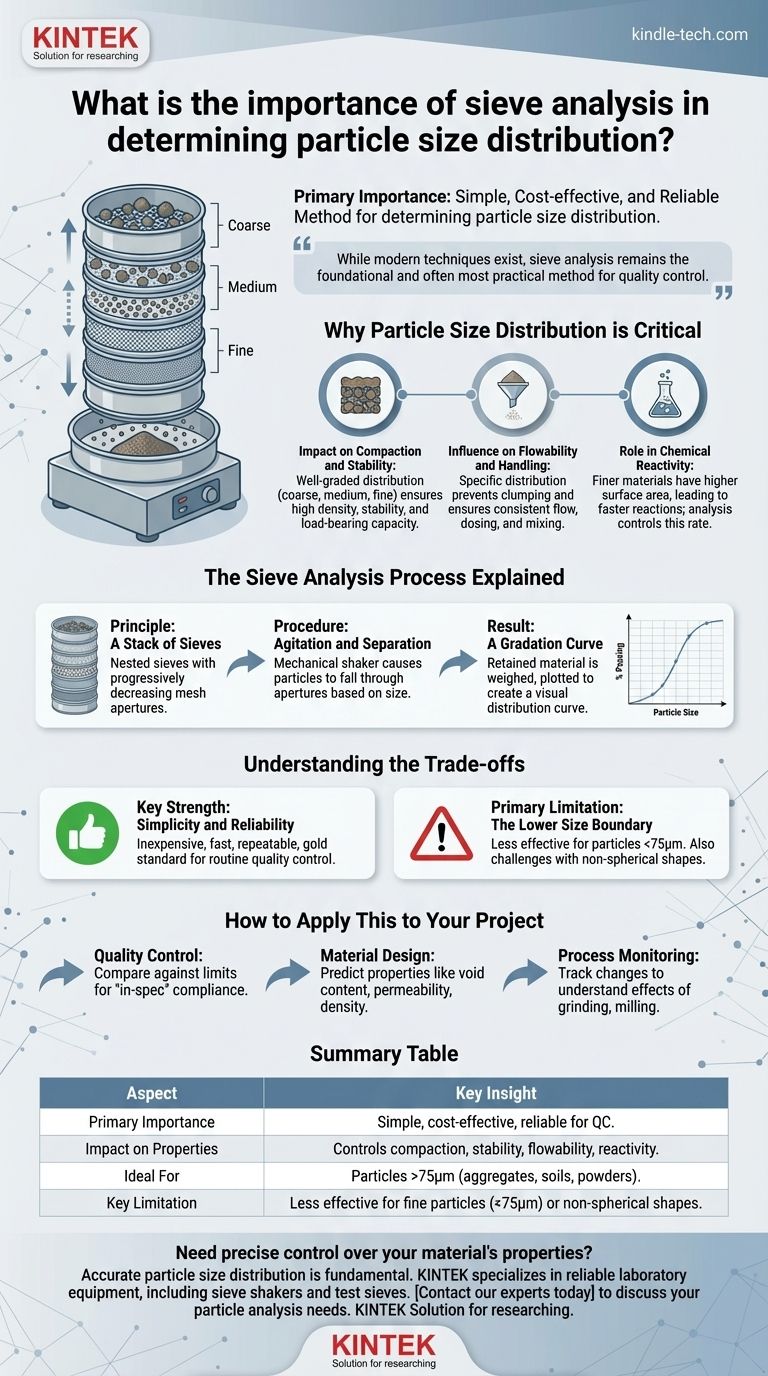
The primary importance of sieve analysis is its role as a simple, cost-effective, and highly reliable method for determining the particle size distribution of granular materials. By mechanically separating a sample into distinct size fractions, this technique provides the essential data needed to ensure a material meets required quality specifications, predict its physical behavior, and control its performance in a final application.
While modern techniques exist for particle analysis, sieve analysis remains the foundational and often most practical method for quality control. Understanding a material's particle size distribution is not just about measurement; it's about controlling its fundamental properties like strength, density, and reactivity.

Why Particle Size Distribution is Critical
The arrangement of different particle sizes within a bulk material, known as its gradation, directly dictates its physical and chemical properties. This is why measuring it is not an academic exercise but a practical necessity.
The Impact on Compaction and Stability
For materials like soil, sand, and gravel used in construction, a well-graded distribution (a good mix of coarse, medium, and fine particles) is crucial. Smaller particles fill the voids between larger ones, leading to higher density, greater stability, and improved load-bearing capacity.
The Influence on Flowability and Handling
In industries that handle powders, such as pharmaceuticals and food production, particle size distribution affects how a material flows. Uniformly sized particles may flow poorly, whereas a specific distribution can prevent clumping and ensure consistent dosing and mixing.
The Role in Chemical Reactivity
Chemical reactions often occur at the surface of a particle. Finer materials have a much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, causing them to dissolve or react more quickly than coarser materials. Sieve analysis helps control this rate by managing the particle size.
The Sieve Analysis Process Explained
Sieve analysis is a straightforward method based on mechanical separation. Its simplicity is a key reason for its widespread and continued use across industries.
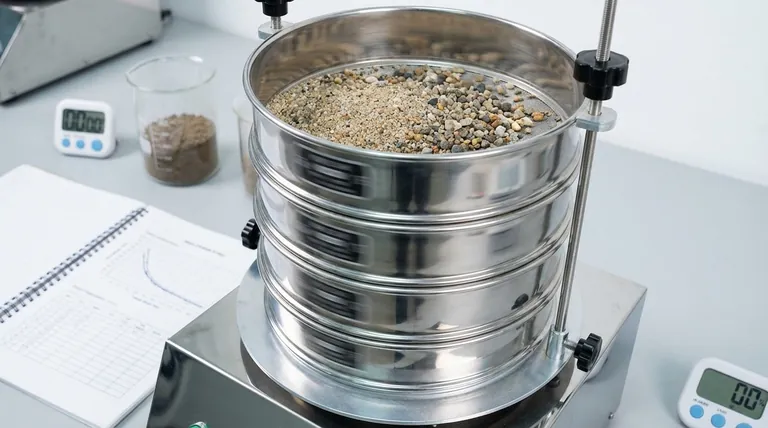
The Principle: A Stack of Sieves
The core of the process involves a sieve stack, which is a set of nested sieves with wire mesh screens. The mesh openings, or apertures, are largest at the top of the stack and progressively decrease in size toward the bottom, which ends in a solid collection pan.
The Procedure: Agitation and Separation
A carefully weighed sample of the dry material is placed in the top sieve. The entire stack is then agitated by a mechanical shaker, causing particles to fall through the apertures until they are retained by a sieve too small for them to pass.
The Result: A Gradation Curve
After agitation, the material retained on each sieve is weighed. This data is used to calculate the percentage of the total mass that falls within each size range. The results are typically plotted on a graph to create a particle size distribution curve, providing a clear visual representation of the material's gradation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sieve analysis is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively and knowing when to employ a different method.
Key Strength: Simplicity and Reliability
Sieve analysis is inexpensive, fast, and does not require highly specialized operators. Its results are highly repeatable, making it the gold standard for routine quality control in many industries, from aggregates to agriculture.
Primary Limitation: The Lower Size Boundary
The method is most effective for particles larger than approximately 75 micrometers (the opening of a standard 200-mesh sieve). For finer materials like clays or pigments, particles can agglomerate or even clog the mesh, making the results unreliable. In these cases, methods like laser diffraction or sedimentation are more appropriate.
The Challenge of Particle Shape
Sieve analysis inherently measures a particle's second-smallest dimension, as this determines whether it can pass through a square aperture. Long, needle-like, or flat particles can pass through openings that do not represent their true size, potentially skewing the distribution data.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your reason for performing a sieve analysis will dictate how you interpret the results.
- If your primary focus is quality control: You will compare your material's gradation curve against a specified upper and lower limit to determine if it is "in-spec."
- If your primary focus is material design: You will use the distribution data to predict physical properties like void content, permeability, and compaction density.
- If your primary focus is process monitoring: You will track changes in the particle size distribution to understand the effects of processes like grinding, milling, or screening.
Mastering this fundamental test gives you direct control over your material's behavior and final performance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Primary Importance | Simple, cost-effective, and reliable method for quality control. |
| Impact on Properties | Controls compaction, stability, flowability, and chemical reactivity. |
| Ideal For | Particles larger than 75 micrometers (e.g., aggregates, soils, powders). |
| Key Limitation | Less effective for fine particles (<75µm) or non-spherical shapes. |
Need precise control over your material's properties?
Accurate particle size distribution is fundamental to your product's quality and performance. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment, including high-quality sieve shakers and test sieves, to ensure your materials meet exact specifications.
Whether you're in construction, pharmaceuticals, or food production, our solutions help you achieve consistent results and optimize your processes.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific particle analysis needs and discover the right equipment for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution



















