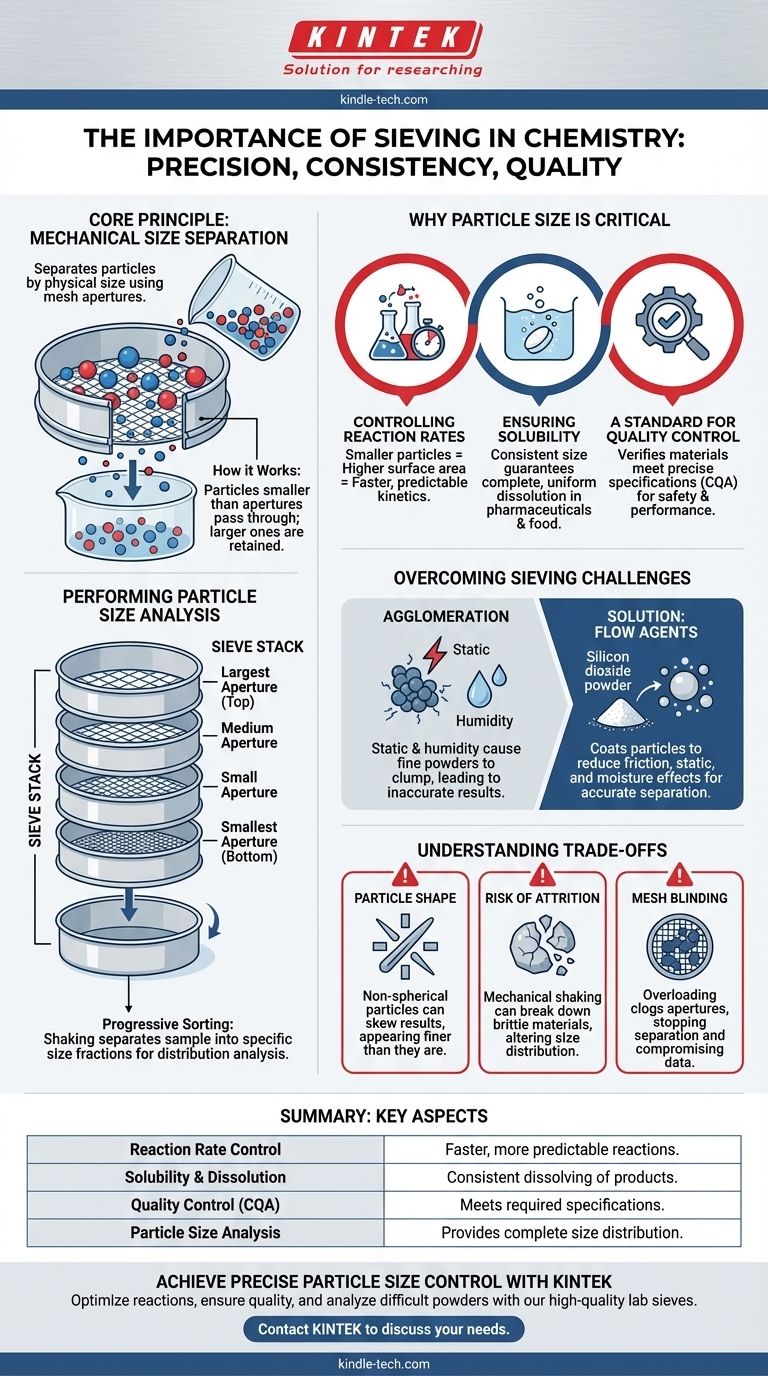
In chemistry, sieving is a fundamental mechanical process used to separate particles based on their physical size. By passing a sample through a mesh or screen with specific-sized openings, it allows chemists to isolate desired particle size ranges, analyze the distribution of sizes within a sample, and ensure the material uniformity critical for countless applications.
Sieving is more than just sorting; it's a critical quality control method that directly influences a material's physical and chemical properties, such as its reaction rate, solubility, and flowability.

The Core Principle: Mechanical Size Separation
How Sieving Works
Sieving operates on a simple, direct principle. A woven mesh screen contains apertures (openings) of a precise, uniform size.
When a granular or powdered sample is placed on the sieve and agitated, particles smaller than the apertures fall through, while particles larger than the apertures are retained on the mesh surface.
Performing Particle Size Analysis
For detailed analysis, multiple sieves are stacked in descending order of aperture size, with the largest openings at the top and the smallest at the bottom.
As the entire sieve stack is shaken, the sample is progressively sorted. The material retained on each sieve represents a specific particle size fraction, allowing for a complete particle size distribution analysis.
Why Particle Size is Critical in Chemistry
Controlling Reaction Rates
The rate of a chemical reaction often depends on the surface area of the reactants. Smaller particles have a much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio than larger particles.
By using sieving to ensure a uniform and fine particle size, chemists can guarantee faster and more predictable reaction kinetics, a crucial factor in both industrial production and laboratory research.
Ensuring Solubility and Predictable Dissolution
Similar to reaction rates, the speed at which a substance dissolves is highly dependent on its surface area.
In applications like pharmaceuticals or food science, sieving is used to control particle size, ensuring that products like medications or drink mixes dissolve consistently and completely for the end-user.
A Standard for Quality Control
In manufacturing, particle size is often a Critical Quality Attribute (CQA). Sieving provides a reliable and straightforward method to verify that raw materials and finished products meet required specifications for safety, efficacy, and performance.
Overcoming Common Sieving Challenges
The Problem of Agglomeration
Fine powders are often difficult to sieve accurately due to external factors. Static electricity can cause particles to repel each other or cling to the sieve frame, while humidity can cause them to clump together (agglomerate).
This agglomeration effectively creates larger particles, preventing them from passing through the appropriate mesh and leading to highly inaccurate results.
The Solution: Sieving Flow Agents
To counteract these issues, a sieving flow agent, such as a lightweight silicon dioxide powder, is sometimes added to the sample.
These agents work by coating the individual particles of the sample. This coating reduces inter-particle friction and mitigates the effects of static and moisture.
The result is a free-flowing powder that separates much more accurately and efficiently, with a minimal impact on the final weight of each separated fraction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Limitation by Particle Shape
Sieving assumes particles are roughly spherical. Long, needle-like or flat, flaky particles can pass through the mesh end-on or diagonally, skewing the results to appear finer than they actually are.
Risk of Attrition
The mechanical shaking required for sieving can be destructive. Brittle materials may break down during the process, an effect known as attrition. This alters the particle size distribution while it is being measured.
Mesh Blinding and Overloading
If too much sample is loaded onto a sieve, it can lead to blinding, where the apertures become clogged and blocked. This prevents any further particles from passing through, stopping the separation process and compromising the data.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sieving is an essential tool for controlling the physical properties of materials. The key is to apply it with a clear understanding of your objective.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Use sieving with certified test sieves to verify that your materials meet precise particle size specifications.
- If your primary focus is optimizing reaction kinetics: Employ sieving to create reactant batches with a consistent and fine particle size, ensuring repeatable and efficient reactions.
- If your primary focus is accurate analysis of difficult powders: Consider using a sieving flow agent to counteract static or humidity that may be causing particle agglomeration.
Ultimately, mastering the technique of sieving gives you direct control over the physical form of a substance, which is often just as important as its chemical composition.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Importance in Chemistry |
|---|---|
| Reaction Rate Control | Smaller particles increase surface area, leading to faster and more predictable reactions. |
| Solubility & Dissolution | Ensures consistent and complete dissolution of materials like pharmaceuticals. |
| Quality Control (CQA) | Verifies raw materials and finished products meet required size specifications. |
| Particle Size Analysis | Provides a complete size distribution by separating a sample into specific fractions. |
Achieve precise particle size control in your lab.
Accurate sieving is fundamental to consistent results in chemical reactions, quality assurance, and material analysis. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves and equipment designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern chemistry.
Whether you are optimizing a reaction, ensuring product quality, or analyzing difficult powders, the right tools are essential. Let our experts help you select the perfect sieving solution for your specific application.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how our reliable equipment can enhance your processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials



















