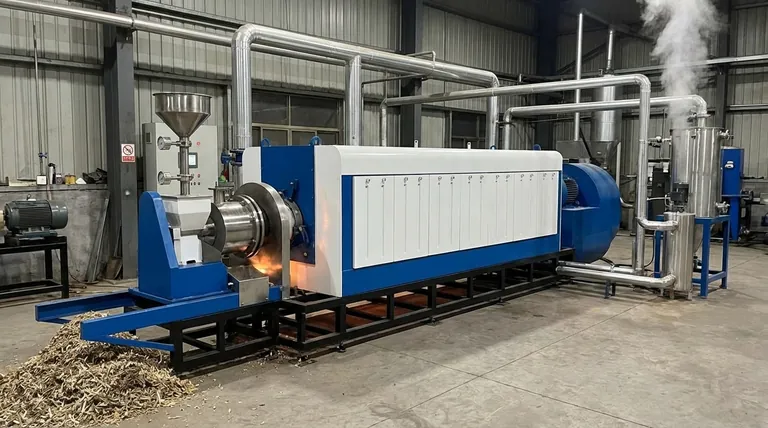
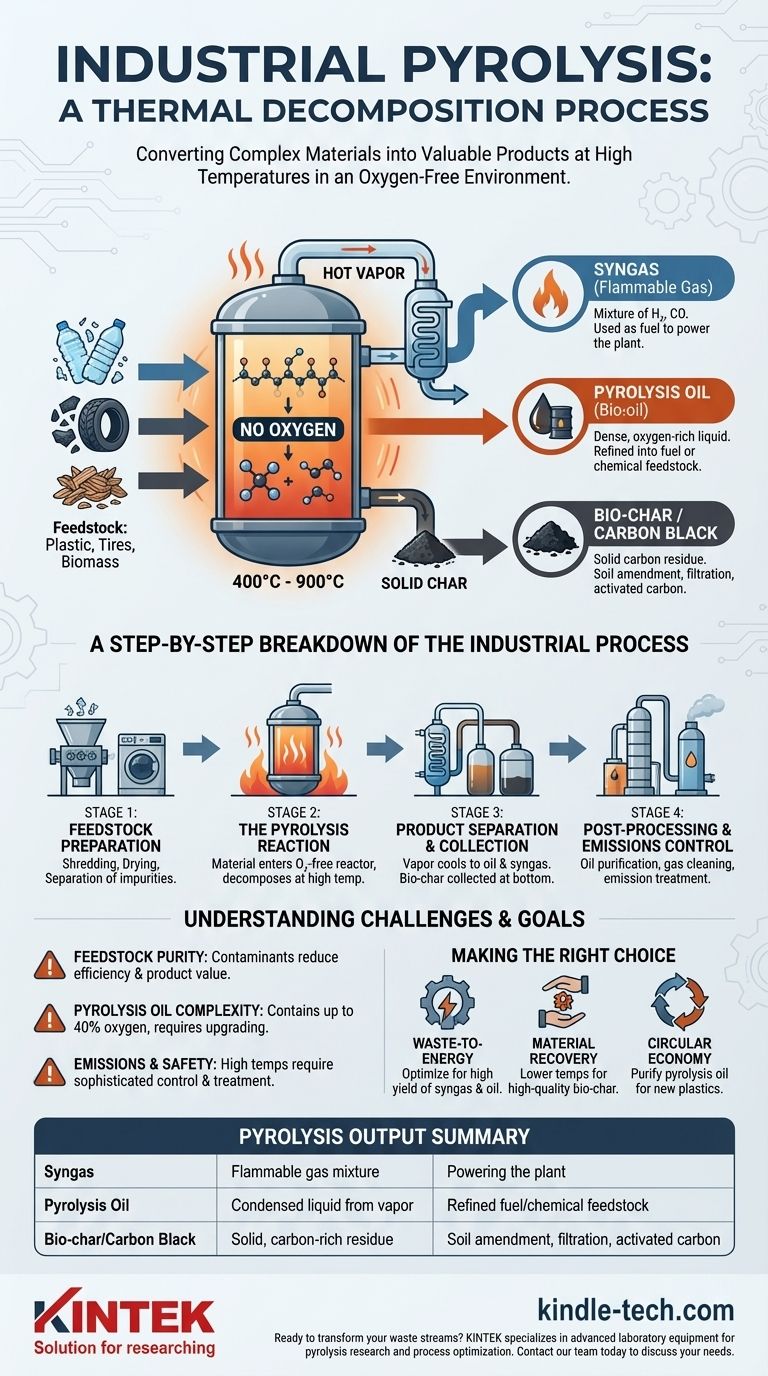
At its core, industrial pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition. It uses high temperatures, typically between 400°C and 900°C, to break down complex materials like plastic, tires, or biomass inside a reactor that has no oxygen. This isn't burning; it's a controlled chemical transformation that deconstructs the feedstock into simpler, more valuable products.
The key distinction to grasp is that pyrolysis is not incineration. By heating materials in an oxygen-free environment, it avoids combustion and instead chemically converts waste streams into three distinct outputs: a combustible gas (syngas), a liquid (pyrolysis oil), and a solid carbon-rich residue (bio-char).

The Core Principle: How Pyrolysis Works
To understand the industrial application of pyrolysis, it's essential to grasp the fundamental science that drives the process. The entire system is engineered around creating and controlling a specific chemical environment.
High Temperature, No Oxygen
The process relies on a simple principle: intense heat breaks chemical bonds. By doing this in a sealed, oxygen-free reactor, the material cannot combust. Instead of turning into ash and smoke, the long molecular chains in materials like plastics or biomass break apart into smaller, more volatile molecules.
The Three Primary Outputs
This decomposition reliably sorts the original material into three distinct forms:
- Syngas: A mixture of flammable gases (like hydrogen and carbon monoxide) that can be captured and used as fuel to help power the pyrolysis plant itself.
- Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil): A complex liquid emulsion created when the hot vapor is rapidly cooled and condensed. It is a dense, oxygen-rich oil that can be refined into fuel or chemical feedstocks.
- Bio-char (or Carbon Black): The solid, stable, carbon-rich material left behind. It can be used as a soil amendment, for filtration, or as a feedstock for producing activated carbon.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Industrial Process
An industrial pyrolysis plant is a highly integrated system. While specifics vary based on the feedstock, the operational flow generally follows four key stages.
Step 1: Feedstock Preparation
The process begins long before the reactor. Raw materials like plastic waste or biomass are first shredded into smaller, more uniform pieces to ensure even heating. They are then dried to reduce moisture content and often passed through systems to separate non-target materials and impurities.
Step 2: The Pyrolysis Reaction
The prepared feedstock is fed into the pyrolysis reactor. Inside, it is heated to the target temperature in the absence of oxygen. The material decomposes, generating a mixture of hot vapor and solid char.
Step 3: Product Separation and Collection
The hot vapor is piped out of the reactor and into a condensing system, where it rapidly cools and transforms into liquid pyrolysis oil. The non-condensable gases (syngas) are separated and collected. Simultaneously, the solid bio-char is discharged from the bottom of the reactor through an air-tight mechanism.
Step 4: Post-Processing and Emissions Control
The raw outputs are rarely ready for immediate end-use. The pyrolysis oil often requires distillation and purification to be used as fuel. The syngas may be cleaned before use, and a dedicated emission cleaning line is crucial for treating any exhaust to meet environmental regulations.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, industrial pyrolysis is not without its complexities. A realistic assessment requires understanding its operational challenges.
Feedstock Purity is Critical
The quality of the outputs is directly tied to the purity of the inputs. Contaminants in the feedstock can disrupt the chemical reactions, reduce efficiency, and degrade the value of the final products.
The Complexity of Pyrolysis Oil
Pyrolysis oil is not a direct substitute for crude oil. It is a complex mixture of water, oxygenated organic compounds, and polymers, containing up to 40% oxygen by weight. This composition makes it acidic and less stable, requiring significant upgrading before it can be used in traditional refineries.
Managing Emissions and Safety
Heating complex materials to high temperatures creates inherent risks. Industrial plants require sophisticated safety controls and robust emission cleaning systems to operate efficiently and in compliance with environmental standards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" pyrolysis setup depends entirely on the desired outcome. The process can be tuned to favor one output over another based on the end goal.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy: You will optimize temperature and residence time to maximize the yield of syngas and pyrolysis oil for their high fuel value.
- If your primary focus is material recovery: You might use lower temperatures and slower processing to produce a high-quality, stable bio-char for agricultural use or as a feedstock for activated carbon.
- If your primary focus is a circular economy for plastics: You will concentrate on purifying the pyrolysis oil to a grade suitable for use as a feedstock to create new plastics, closing the loop.
Ultimately, industrial pyrolysis is a versatile thermochemical tool that transforms low-value materials into a portfolio of valuable resources.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Output | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Syngas | Flammable gas mixture (e.g., hydrogen, CO) | Fuel to power the pyrolysis plant |
| Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil) | Condensed liquid from vapor | Refined into fuel or chemical feedstocks |
| Bio-char / Carbon Black | Solid, carbon-rich residue | Soil amendment, filtration, activated carbon feedstock |
Ready to transform your waste streams into valuable products? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and process optimization. Whether you're developing waste-to-energy solutions, exploring material recovery, or creating a circular economy for plastics, our expertise and reliable products can help you achieve your goals. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's pyrolysis needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success



















