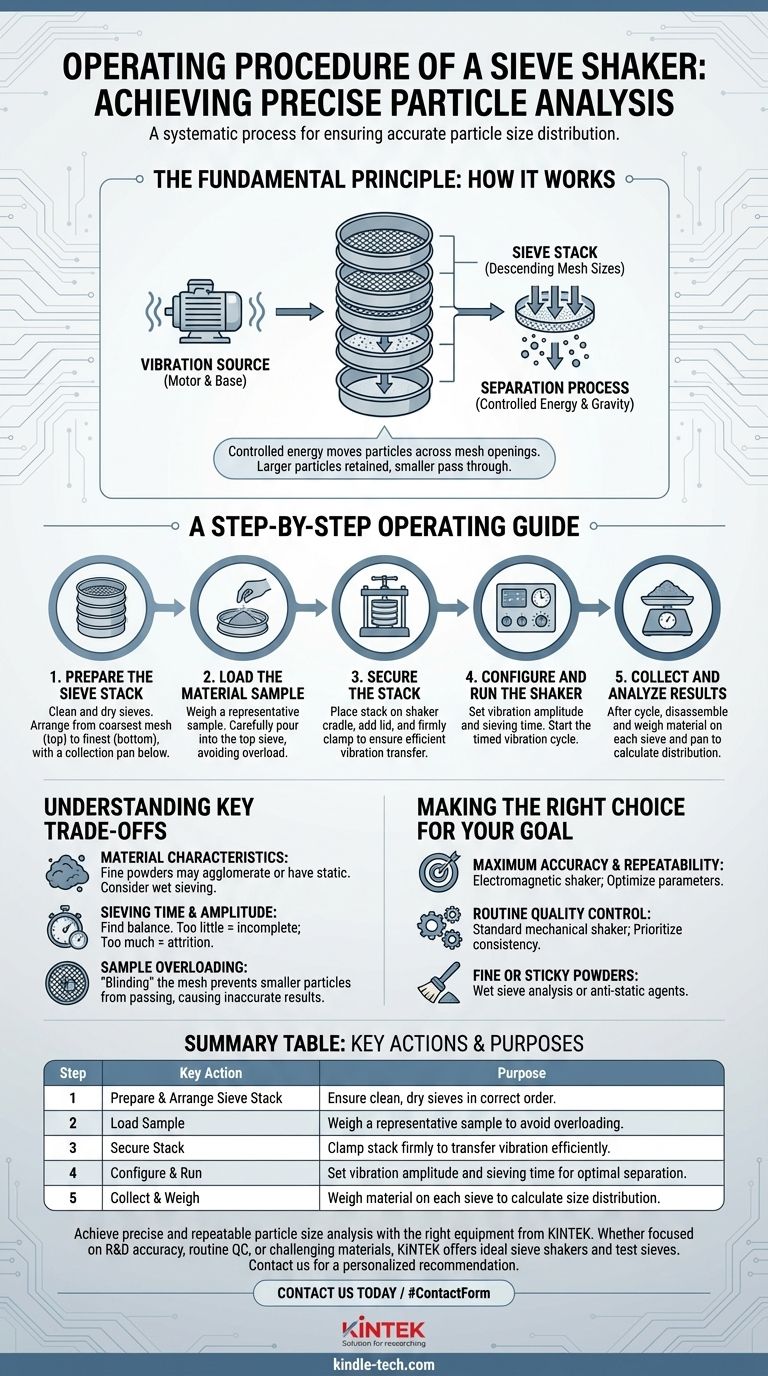
At its core, operating a sieve shaker is a systematic process for ensuring accurate particle size analysis. You begin by arranging a stack of test sieves in order of decreasing mesh size, placing your material sample in the top sieve, securing the stack in the shaker, and then running a timed vibration cycle to allow the particles to segregate themselves by size.
A sieve shaker automates and standardizes particle separation. It replaces subjective manual sieving with a controlled, repeatable mechanical process, ensuring that the results of your particle size analysis are both accurate and reliable.

The Fundamental Principle: How a Sieve Shaker Works
To operate a sieve shaker correctly, you must first understand its mechanics. The goal is to use controlled energy to give every particle an opportunity to pass through the mesh openings.
The Vibration Source
A motor, either mechanical or electromagnetic, serves as the heart of the shaker. This motor drives the machine's base, creating a consistent vibrating motion that is transferred directly to the stack of sieves.
Electromagnetic shakers often produce a three-dimensional elliptical motion, which is highly efficient for moving particles across the sieve mesh and is generally quieter.
The Sieve Stack
The analysis is performed using a sieve stack (or nest). This is a series of test sieves stacked vertically.
Sieves are arranged in descending order of opening size, with the sieve having the largest openings on top. A solid collection pan is always placed at the very bottom to catch the finest particles.
The Separation Process
When the shaker is activated, the vibration agitates the material sample. Larger particles are retained by the top sieves, while smaller particles pass through the mesh to the levels below until they reach a sieve they cannot pass through. This effectively separates the original sample into different size fractions.
A Step-by-Step Operating Guide
Following a precise procedure is critical for obtaining repeatable results.
Step 1: Prepare the Sieve Stack
First, ensure all sieves and the collection pan are clean and dry. Arrange them in a stack with the coarsest mesh size on top and the finest on the bottom, just above the collection pan.
Step 2: Load the Material Sample
Weigh a representative sample of your material. The amount is important; too much material can overload the mesh and lead to inaccurate results. Carefully pour the sample into the top sieve.
Step 3: Secure the Stack
Place the entire sieve stack onto the shaker's cradle or base. Put the lid on top of the stack. Use the shaker's clamping system—typically a retaining bar and locking nuts—to secure the stack firmly in place. This ensures the vibration is transferred efficiently.
Step 4: Configure and Run the Shaker
Set the analysis parameters on the control panel. The two most important settings are vibration amplitude (intensity) and sieving time. Once set, begin the shaking cycle.
Step 5: Collect and Analyze Results
After the cycle is complete, turn off the machine and carefully disassemble the stack. Weigh the material retained on each individual sieve and in the bottom collection pan. This data is then used to calculate the particle size distribution of your sample.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The quality of your results depends on more than just following the steps. Several factors can influence the outcome.
Material Characteristics
The nature of your material is critical. Some fine powders are prone to agglomeration (clumping) or static electricity, which prevents particles from separating properly. For these materials, wet sieving may be required.
Sieving Time and Amplitude
Finding the right balance of time and intensity is crucial. Insufficient time or amplitude will result in incomplete separation. However, excessive time or intensity can cause particle attrition—where particles break down—skewing your results toward a finer distribution.
Sample Overloading
"Blinding" the sieve mesh is a common error. If too much material is loaded into the stack, it can clog the openings and prevent smaller particles from passing through, leading to a falsely coarse measurement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective should guide your operational focus.
- If your primary focus is maximum accuracy and repeatability: Opt for an electromagnetic shaker and perform tests to optimize the sieving time and amplitude for your specific material.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control for coarse materials: A standard mechanical shaker is typically sufficient. Prioritize consistency by using the same sample weight and sieving time for every test.
- If your primary focus is analyzing fine, sticky, or static-prone powders: Consider wet sieve analysis or using anti-static agents to ensure particles can move freely and separate correctly.
By mastering its principles and procedure, the sieve shaker becomes an indispensable tool for understanding your material.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Prepare & Arrange Sieve Stack | Ensure clean, dry sieves in correct order (coarsest to finest). |
| 2 | Load Sample | Weigh a representative sample to avoid overloading the mesh. |
| 3 | Secure Stack | Clamp the stack firmly to transfer vibration efficiently. |
| 4 | Configure & Run | Set vibration amplitude and sieving time for optimal separation. |
| 5 | Collect & Weigh | Weigh material on each sieve to calculate size distribution. |
Achieve precise and repeatable particle size analysis with the right equipment from KINTEK.
Whether you are focused on maximum accuracy for R&D, efficient routine quality control, or handling challenging materials like fine powders, KINTEK has the ideal sieve shaker and test sieves for your laboratory's specific needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution to enhance your workflow and ensure reliable results.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation. Let KINTEK be your partner in precision.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis



















