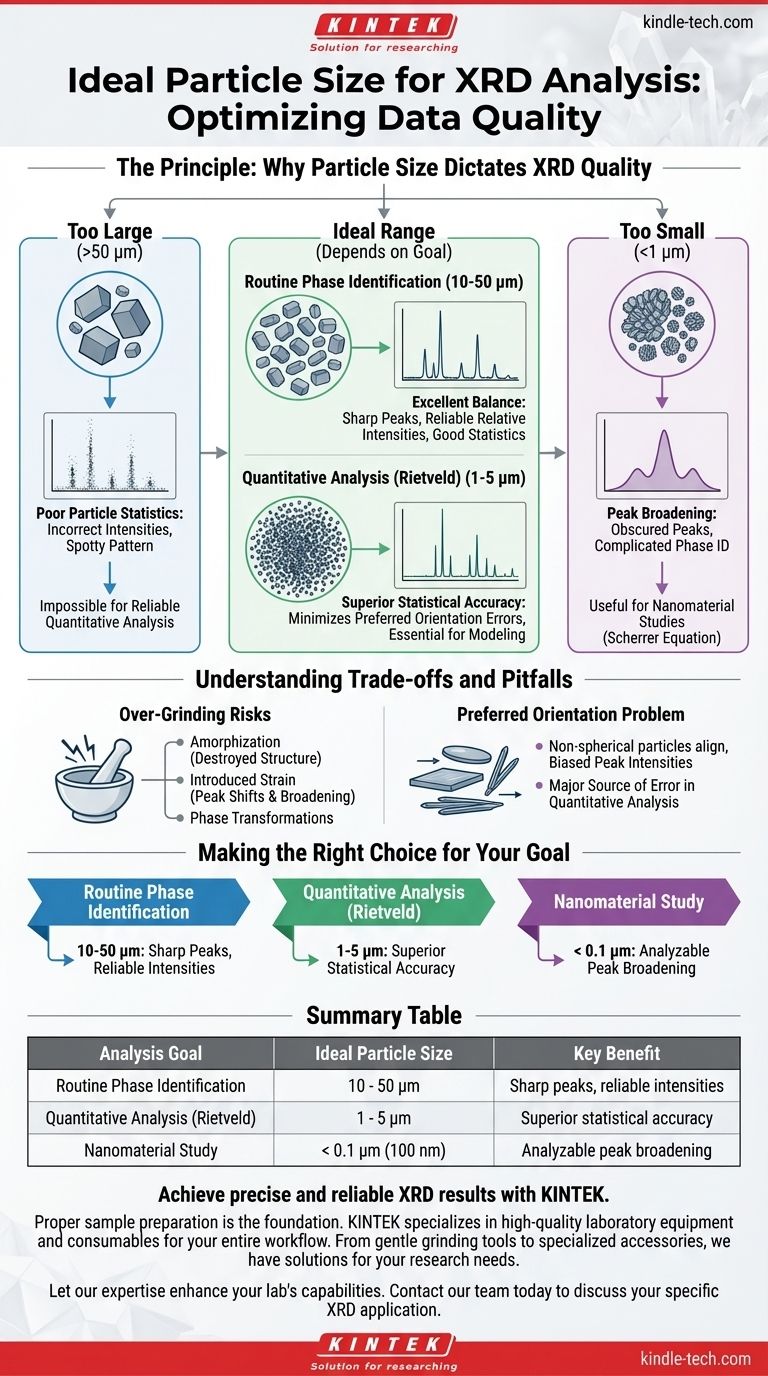
For routine X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, the ideal average particle size is between 10 and 50 micrometers (µm). This range ensures a sufficient number of randomly oriented crystallites are exposed to the X-ray beam. For more demanding quantitative techniques like Rietveld analysis, a smaller particle size of 1 to 5 µm is required to achieve superior statistical accuracy.
The core challenge in powder XRD is sampling a massive number of crystallites in every possible orientation. Particle size is the primary tool to control this, balancing the need for good statistical representation against the risk of introducing unwanted artifacts like peak broadening or sample damage.
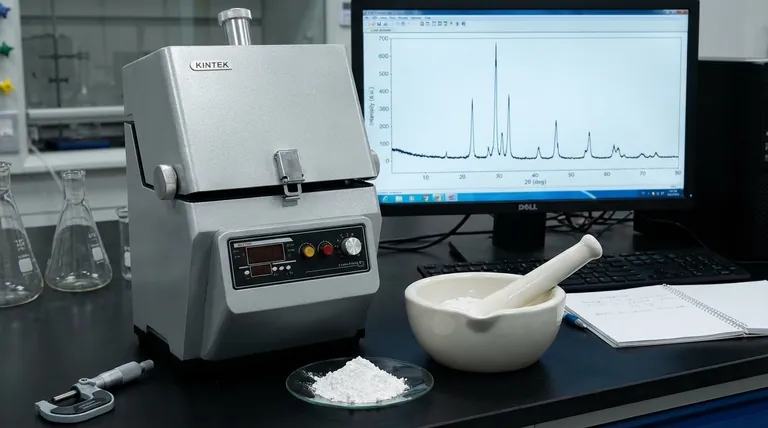

The Principle: Why Particle Size Dictates XRD Quality
Powder XRD works on the assumption that for every possible crystal plane, there are countless tiny crystallites in the sample perfectly oriented to diffract the X-ray beam. The final pattern is the statistical average of all these diffraction events.
The Role of Random Orientation
A "powder" sample is a collection of particles, and each particle can contain one or more crystallites (or grains). To get a high-quality pattern that accurately represents the material's structure, the sample must present a statistically random distribution of these crystallite orientations to the beam.
The Problem with Large Particles (>50 µm)
When particles are too large, the X-ray beam interacts with a relatively small number of crystallites. This results in poor particle statistics.
Not enough crystallites are present to represent all possible orientations. This leads to incorrect peak intensities and a "spotty" or "grainy" diffraction pattern, making reliable phase identification and quantitative analysis impossible.
The Problem with Very Small Particles (<1 µm)
As crystallite size decreases into the sub-micrometer or nanometer scale, a different issue arises: peak broadening.
The diffraction peaks become wider as the size of the coherently scattering domains (crystallites) gets smaller. While this effect is useful for studying nanomaterials (via the Scherrer equation), it is generally undesirable for standard analysis as it can obscure closely spaced peaks and complicate phase identification.
How Your Analysis Goal Defines the Ideal Size
The "best" particle size is not a single number; it depends directly on the data quality you need for your specific experiment.
For General Phase Identification: 10-50 µm
This range is the standard for most routine qualitative work. It strikes an excellent balance.
The particles are small enough to provide good particle statistics for reliable peak intensities, but large enough to avoid significant peak broadening. This ensures sharp, well-defined peaks for easy matching against a database.
For Quantitative Analysis (Rietveld): 1-5 µm
Quantitative methods, such as Rietveld refinement, are extremely sensitive to errors in peak intensity. These analyses mathematically model the entire diffraction pattern to extract detailed structural and compositional information.
Grinding the sample to this finer range dramatically increases the number of crystallites in the irradiated volume. This ensures the intensity data is a highly accurate statistical representation of the material, minimizing errors from preferred orientation and poor statistics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Achieving the right particle size is more than just grinding a sample. You must be aware of the potential downsides of sample preparation.
The Risk of Over-Grinding
Aggressively grinding a sample, especially for long periods, can physically damage it. This can introduce artifacts that are not representative of the original material.
These artifacts include amorphization (destroying the crystal structure), introducing strain (which shifts and broadens peaks), or even inducing phase transformations. Always use gentle grinding methods, such as with a mortar and pestle.
The Problem of Preferred Orientation
Even with the correct particle size, particles with non-spherical shapes (e.g., plates or needles) can preferentially align during sample preparation.
This preferred orientation systematically biases the peak intensities, as certain crystal planes are over-represented. This is a major source of error in quantitative analysis and can sometimes be mitigated by specialized sample packing techniques.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure high-quality data, tailor your sample preparation to your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is routine phase identification: Aim for a particle size of 10-50 µm to get sharp peaks with reliable relative intensities.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis (like Rietveld): Grind your sample finer to the 1-5 µm range to ensure the superior particle statistics necessary for accurate results.
- If you are intentionally studying nanomaterials: Be aware that crystallite sizes below ~0.1 µm (100 nm) will cause significant peak broadening, which itself becomes a key piece of data to be analyzed.
Properly controlling your sample's particle size is the first and most critical step toward producing reliable and accurate XRD results.
Summary Table:
| Analysis Goal | Ideal Particle Size | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Routine Phase Identification | 10 - 50 µm | Sharp peaks, reliable intensities |
| Quantitative Analysis (Rietveld) | 1 - 5 µm | Superior statistical accuracy |
| Nanomaterial Study | < 0.1 µm (100 nm) | Analyzable peak broadening |
Achieve precise and reliable XRD results with KINTEK.
Proper sample preparation is the foundation of accurate X-ray diffraction analysis. Whether you are performing routine phase identification or advanced quantitative Rietveld refinement, using the correct particle size is critical for success.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables designed to support your entire sample preparation workflow. From gentle grinding tools to ensure you avoid damaging your samples to specialized accessories that help mitigate preferred orientation, we have the solutions to help you produce the highest quality data.
Let our expertise enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact our team today to discuss your specific XRD application and find the perfect tools for your research needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
People Also Ask
- What size is a lab mixing mill? A Guide to Matching Capacity to Your Application
- What are the components of a colloid mill? Master the Core Mechanism for Superior Emulsification
- What is the purpose of using a high-purity argon gas system? Ensure Safety and Performance in Magnesium Ball Milling
- How does a ball mill work? Harness Impact and Attrition for Fine Grinding
- What is the function of a high-pressure homogenizer in nanocellulose extraction? Expert Fibrillation Solutions
- What are the advantages of using zirconia grinding jars? Achieve High-Purity Micronization with Zero Contamination
- How does the multi-stage grinding process contribute to the quality of finished nanopowders in solid-state synthesis?
- What is the speed range of a ball mill? Find Your Optimal Grinding Efficiency



















