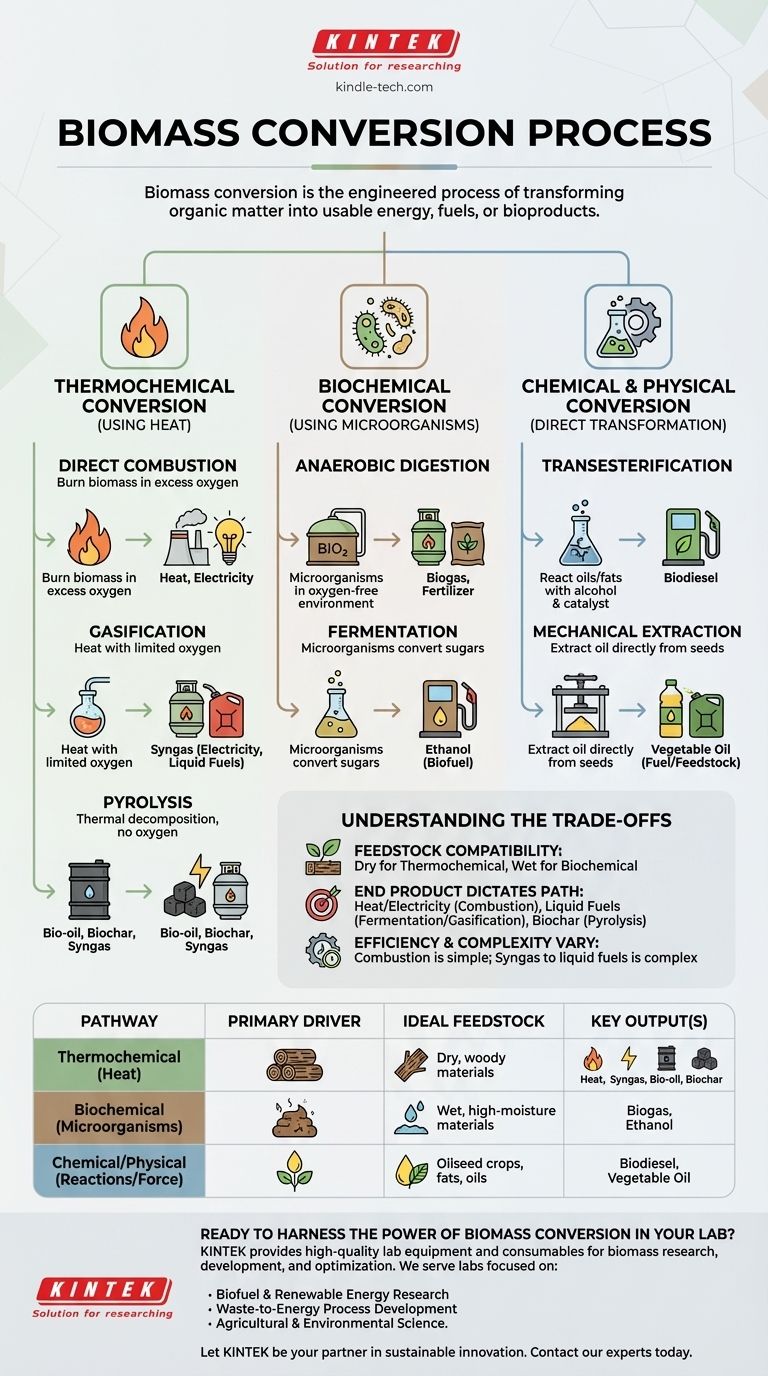
Biomass conversion is the engineered process of transforming organic matter—such as plants, agricultural waste, and wood—into usable energy, fuels, or other valuable bioproducts. It leverages biological and technological principles to unlock the stored chemical energy within these natural materials, turning potential waste into a resource.
The critical insight is not simply that biomass can be converted, but how. The specific conversion method chosen is dictated entirely by two factors: the type of organic material you start with (the "feedstock") and the final product you need to create.

The Core Conversion Pathways
At its heart, biomass conversion involves breaking down complex organic molecules into simpler, more useful ones. There are three primary families of methods used to accomplish this, each suited for different types of biomass and desired outcomes.
Thermochemical Conversion: Using Heat
This category of processes uses heat as the primary driver to break down the chemical structure of biomass. These methods are generally best suited for dry, woody feedstocks like wood chips, straw, or energy crops.
Direct Combustion This is the simplest and most common method. Biomass is burned in the presence of excess oxygen to produce heat, which can be used directly for heating or to create steam that drives a turbine to generate electricity.
Gasification This process involves heating biomass with a limited amount of oxygen. Instead of burning completely, the biomass converts into a mixture of combustible gases known as syngas (synthesis gas), which can then be used to generate electricity or be synthesized into liquid fuels.
Pyrolysis Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass in the complete absence of oxygen. This process yields three primary products: a liquid called bio-oil (or pyrolysis oil), a solid, charcoal-like material called biochar, and a syngas.
Biochemical Conversion: Using Microorganisms
Biochemical processes use the natural metabolic actions of bacteria, yeasts, and other microorganisms to break down biomass. These methods are ideal for feedstocks with high moisture content, such as food waste, manure, and sewage sludge.
Anaerobic Digestion In this process, microorganisms break down biodegradable material in an oxygen-free environment. The primary output is biogas, a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide, which can be burned for heat and power. The remaining solid material, called digestate, is a nutrient-rich fertilizer.
Fermentation Fermentation uses microorganisms (most commonly yeast) to convert the sugars found in biomass into alcohol, primarily ethanol. This is the same fundamental process used to make alcoholic beverages and is a dominant method for producing biofuel for transportation.
Chemical & Physical Conversion: Direct Transformation
This group of processes uses chemical reactions or mechanical force to convert biomass into a finished product, often targeting specific components within the feedstock.
Transesterification This is a specific chemical process used to produce biodiesel. It involves reacting vegetable oils or animal fats with an alcohol (like methanol) in the presence of a catalyst, converting them into fatty acid methyl esters (biodiesel).
Mechanical Extraction Also known as pressing, this physical process is used to extract oil directly from oilseed crops like soybeans, canola, or palm. The extracted oil can then be used directly as a fuel or serve as the feedstock for the transesterification process to create biodiesel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no single "best" conversion process; each pathway comes with its own set of advantages and limitations. The optimal choice is always a function of the raw material and the desired end product.
Feedstock Compatibility is Key
The physical and chemical nature of your biomass is the most important factor. Dry, low-moisture feedstocks like wood are poorly suited for biochemical processes but are ideal for thermochemical methods like combustion or gasification. Conversely, wet waste streams are perfect for anaerobic digestion but inefficient to burn.
The End Product Dictates the Path
Your goal determines the technology. If you need direct heat or electricity, combustion is the most straightforward route. If you need to produce a liquid transportation fuel like ethanol, fermentation is the required process. If your goal is to create biochar for soil amendment, only pyrolysis will achieve that.
Efficiency and Complexity Vary
Some processes are more energy-efficient or technologically mature than others. Direct combustion is a well-established and relatively simple technology. In contrast, converting the syngas from gasification into liquid fuels is a more complex and capital-intensive undertaking.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge, align the technology with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, consistent power generation: Direct combustion of woody biomass or agricultural residues is the most direct and established pathway.
- If your primary focus is managing wet organic waste (e.g., food scraps, manure): Anaerobic digestion is the most effective method for producing valuable biogas while reducing waste volume.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels for vehicles: Fermentation is the standard for ethanol production, while transesterification is the required process for making biodiesel from oils and fats.
- If your primary focus is creating valuable co-products like biochar for agriculture: Pyrolysis is the only process specifically designed to maximize this solid output alongside bio-oil.
By matching the right conversion process to the right organic material, we transform potential waste streams into powerful and sustainable resources.
Summary Table:
| Conversion Pathway | Primary Driver | Ideal Feedstock | Key Output(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermochemical | Heat | Dry, woody materials (wood chips, straw) | Heat, Syngas, Bio-oil, Biochar |
| Biochemical | Microorganisms | Wet, high-moisture materials (food waste, manure) | Biogas, Ethanol |
| Chemical/Physical | Chemical Reactions/Mechanical Force | Oilseed crops, fats, oils | Biodiesel, Vegetable Oil |
Ready to harness the power of biomass conversion in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to research, develop, and optimize biomass conversion processes. Whether you're working on pyrolysis, gasification, fermentation, or transesterification, our reliable tools help you achieve accurate and reproducible results.
We serve laboratories focused on:
- Biofuel and renewable energy research
- Waste-to-energy process development
- Agricultural and environmental science
Let KINTEK be your partner in sustainable innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific biomass conversion needs and discover how our solutions can accelerate your project from feedstock to final product.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs



















