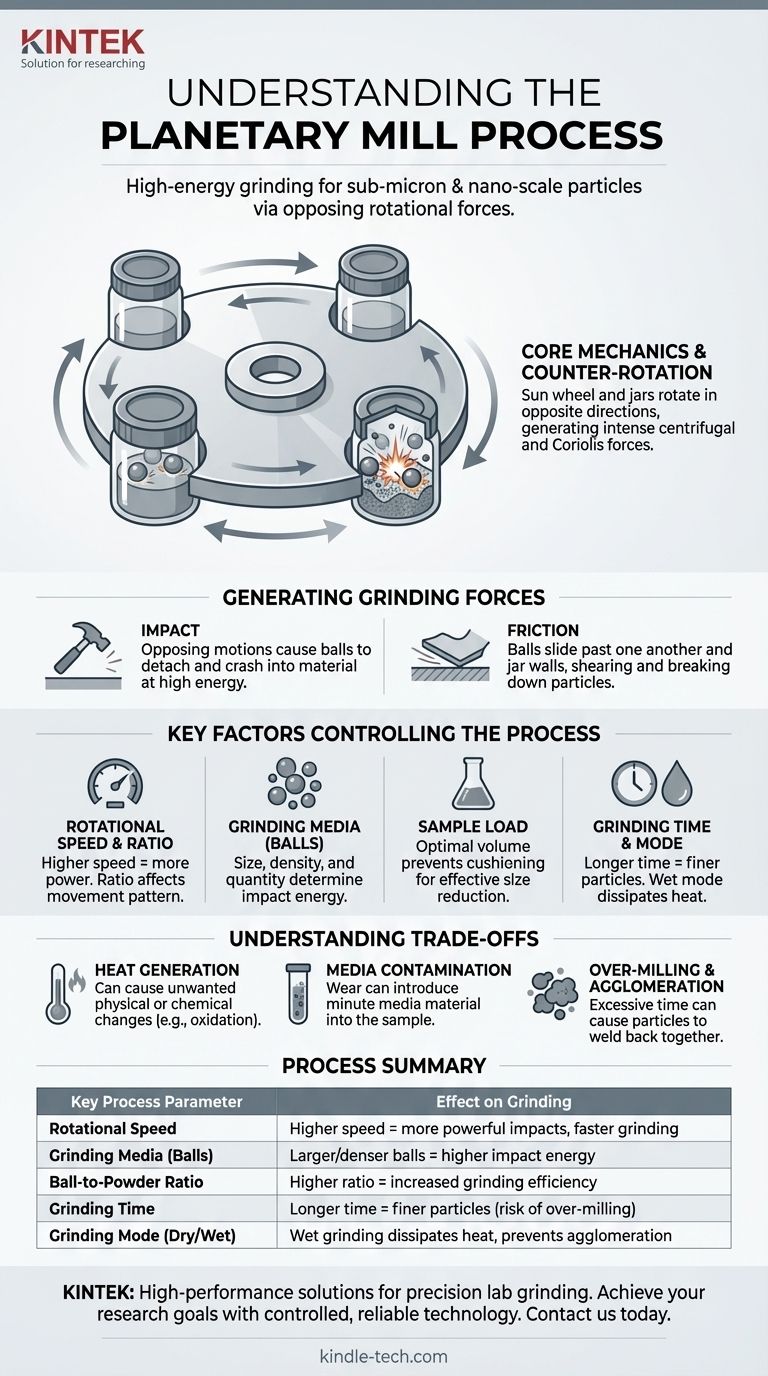
In essence, a planetary mill is a high-energy grinding device that reduces materials to a very fine powder. It achieves this by subjecting the material to intense forces generated by the simultaneous rotation and revolution of grinding jars, similar to how planets revolve around the sun. The core process relies on the counter-rotation of a main disc and the grinding jars, which creates powerful collisions between grinding media (balls) and the sample material.
The defining characteristic of a planetary mill is its use of opposing rotational forces. This creates a powerful Coriolis effect, causing grinding balls to repeatedly detach and fly across the jar's interior, generating the extreme impact and friction needed for effective pulverization.

The Mechanics of High-Energy Grinding
To truly understand the process, we must look at the components and the forces they generate. The elegance of the planetary mill lies in its simple design that produces complex, powerful grinding dynamics.
The Sun Wheel and the Planets
The main system consists of a large, rotating central disc, often called the sun wheel. Mounted on this sun wheel are one or more grinding jars, which act as the "planets."
These jars, along with the grinding balls inside them, are typically made from extremely hard materials like hardened steel, zirconia, or tungsten carbide to withstand the intense forces and minimize contamination.
The Principle of Counter-Rotation
The critical action occurs because the sun wheel and the grinding jars rotate in opposite directions. For example, as the sun wheel turns clockwise, the jars on it will spin counter-clockwise.
This opposition in movement is the key to the mill's high efficiency. It prevents the contents of the jar from simply being pinned against the wall by centrifugal force.
Generating Grinding Forces
The counter-rotation creates a powerful combination of two primary grinding forces:
- Impact: The opposing motions cause the grinding balls to repeatedly detach from the inner wall of the jar, accelerate across its diameter, and crash into the material on the opposite wall with tremendous energy.
- Friction: As the balls slide past one another and rub against the jar walls and sample material, intense frictional forces are generated, further breaking down the particles.
The combination of these high-frequency impacts and shearing friction is what allows planetary mills to achieve particle sizes down to the sub-micron or even nanometer scale.
Key Factors Controlling the Grinding Process
The final result of the milling process is not accidental. It is controlled by a set of precise, adjustable parameters that allow you to tailor the outcome to your specific material and goals.
Rotational Speed and Ratio
The speed of the sun wheel is the primary control for the amount of energy put into the system. A higher speed results in more powerful impacts and faster grinding. The speed ratio between the sun wheel and the grinding jars is also a critical factor that dictates the movement pattern of the balls.
Grinding Media (Balls)
The characteristics of the grinding balls are crucial. This includes their size, density, and the quantity used (often called the charge ratio). Larger, denser balls produce higher-impact energy. A higher ball-to-powder mass ratio generally increases grinding efficiency.
Sample Load
The amount of material you place in the jar significantly affects the outcome. Overfilling the jar will cushion the impacts and drastically reduce grinding efficiency. Finding the optimal sample volume is key to effective size reduction.
Grinding Time and Mode
Longer grinding times naturally lead to finer particles, but there is often a point of diminishing returns. The process can also be done dry or wet. Wet grinding, where a liquid solvent is added, helps to dissipate heat and prevent particles from re-agglomerating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the planetary milling process involves inherent trade-offs that every operator must manage. Ignoring these can lead to poor results or damaged samples.
Heat Generation
The immense energy input generates significant heat. This can cause unwanted physical or chemical changes in the material, such as oxidation or phase transitions. For temperature-sensitive materials, this is a primary concern.
Contamination from Media
Even the hardest grinding media will wear down over time. This wear introduces minute amounts of contamination from the balls and jar into your sample. For applications requiring ultra-high purity, this is a critical limitation to consider.
Over-Milling and Agglomeration
Milling for too long can be counterproductive. After reaching a certain fineness, particles may begin to weld back together due to the high impact energy, a process known as agglomeration. This can actually increase the effective particle size.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
You must adjust the milling parameters based on your desired outcome. The goal is to balance grinding efficiency against potential negative effects like heat and contamination.
- If your primary focus is rapid size reduction: Use high rotational speeds, larger or denser grinding balls, and a high ball-to-powder mass ratio.
- If your primary focus is maintaining material purity: Carefully match the jar and ball material to your sample, or use a material far harder than your sample to minimize wear. Consider shorter milling times.
- If your primary focus is processing temperature-sensitive materials: Use lower speeds, implement programmed grinding pauses to allow for cooling, or perform wet grinding by adding a suitable liquid agent.
By mastering these principles, you can leverage the planetary mill as a precision instrument for advanced material processing and synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Key Process Parameter | Effect on Grinding |
|---|---|
| Rotational Speed | Higher speed = more powerful impacts, faster grinding |
| Grinding Media (Balls) | Larger/denser balls = higher impact energy |
| Ball-to-Powder Ratio | Higher ratio = increased grinding efficiency |
| Grinding Time | Longer time = finer particles (risk of over-milling) |
| Grinding Mode (Dry/Wet) | Wet grinding dissipates heat, prevents agglomeration |
Ready to Achieve Precision Grinding in Your Lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance planetary mills and lab equipment, designed to meet the rigorous demands of material science and research. Whether you need to reduce particles to the nanoscale, synthesize new materials, or maintain sample purity, our solutions deliver controlled, high-energy grinding with minimal contamination.
We provide:
- Durable planetary ball mills with precise speed control
- A wide range of grinding jar and ball materials (including zirconia, tungsten carbide, and hardened steel) to suit your application
- Expert support to help you optimize parameters for your specific materials and goals
Contact us today at #ContactForm to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your research capabilities with reliable, efficient grinding technology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a planetary high-energy ball mill? Master Mechanical Alloying for Ni-Co-Al Superalloy Powders
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in Al-LLZ lithium garnet preparation? Optimize Solid-State Electrolyte Synthesis
- What is the primary function of a planetary ball mill for LLZTO targets? Achieving High-Energy Pulverization
- Why are high-intensity planetary ball mills preferred for reducing the crystallinity of lignocellulose?
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in SHS? Optimize Powder Activation for Superior Alloy Synthesis



















