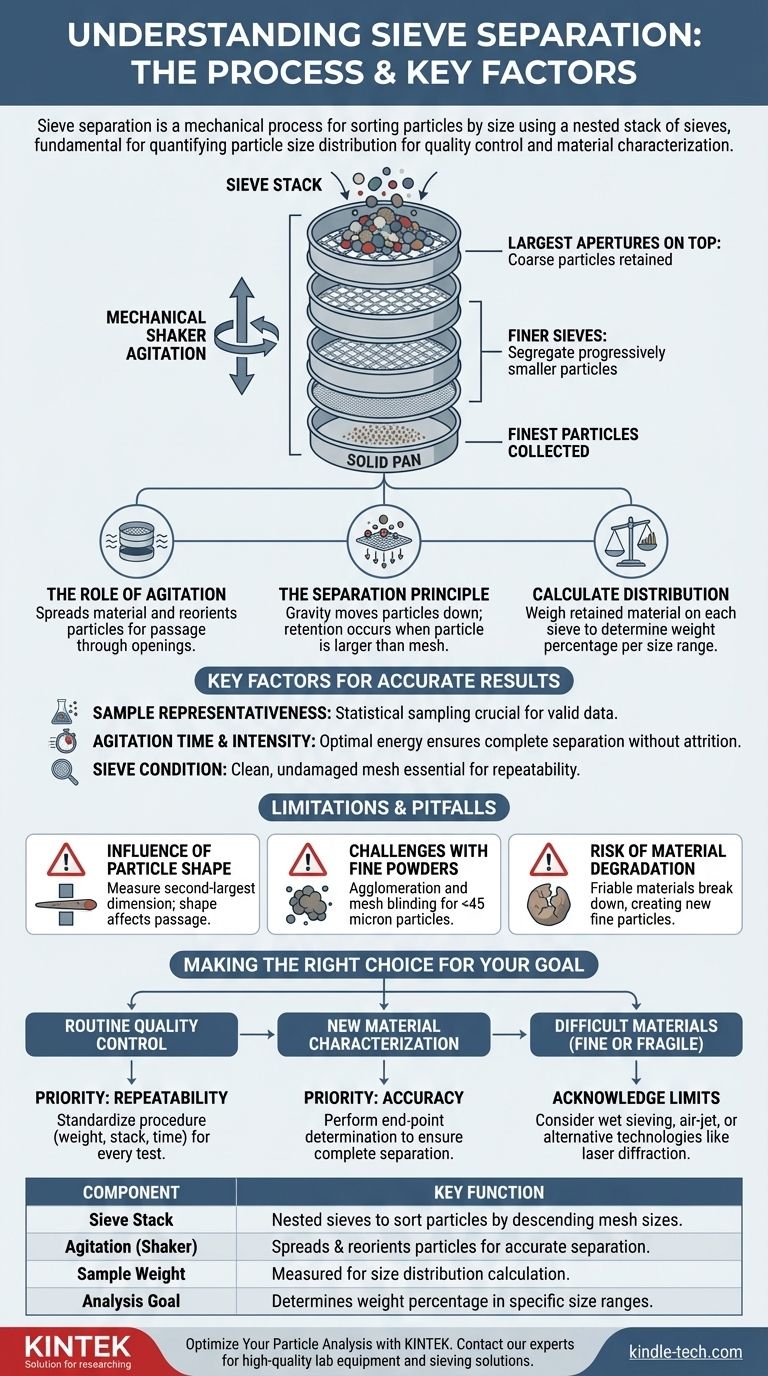
At its core, sieve separation is a mechanical process for sorting particles by size. It involves passing a sample of material through a nested stack of sieves, each with a precisely measured mesh screen of a different size. When the stack is agitated, smaller particles fall through the mesh openings until they are retained by a sieve they are too large to pass through, effectively segregating the sample into different size fractions.
Sieve separation isn't just about sorting; it's a foundational technique for quantifying the particle size distribution of a granular material. The goal is to determine the precise weight percentage of material that falls within specific size ranges, providing critical data for quality control and material characterization.

The Mechanics of Sieve Analysis
Sieve separation, often called sieve analysis, is a highly standardized process. The reliability of the results depends entirely on understanding and controlling the core components of the method.
The Sieve Stack
The primary tool is the sieve stack. This is a column of interlocking sieves arranged in descending order of mesh size.
The sieve with the largest apertures (openings) is placed on top, followed by progressively finer sieves. A solid pan is placed at the very bottom to collect the finest particles that pass through the entire stack.
The Role of Agitation
A sample, carefully weighed, is placed in the top sieve. The entire stack is then agitated, typically using a mechanical sieve shaker.
This agitation is the critical action in the process. It imparts a specific motion—often a combination of vertical tapping and horizontal rotation—that serves two purposes. First, it spreads the material across the mesh surface, and second, it continuously reorients the particles, giving them numerous opportunities to pass through the openings if they are small enough.
The Separation Principle
The separation occurs through a simple physical test. As the stack is shaken, particles move down through the sieves under gravity until they encounter a mesh they cannot fit through.
Once the agitation is complete, the material retained on each sieve is weighed. This data allows for the calculation of the particle size distribution, typically expressed as the weight percentage of the total sample retained on each screen.
Key Factors for Accurate Results
Achieving repeatable and accurate results requires strict control over the testing variables. A small deviation in procedure can lead to a significant error in the final distribution data.
Sample Representativeness
The analysis is only as good as the initial sample. The sample taken for testing must be statistically representative of the entire batch of material. Proper sampling techniques are essential.
Agitation Time and Intensity
The duration and energy of the shaking are critical parameters. Insufficient agitation will result in incomplete separation, with fine particles remaining trapped on upper sieves. Excessive agitation, especially with brittle materials, can cause particle breakdown (attrition), skewing the results toward a finer distribution.
Sieve Condition
The sieves themselves must be in perfect condition. The mesh must be clean, with no blocked or "blinded" apertures. Any damage, such as dents or tears in the mesh, will render the sieve unusable and invalidate the test results.
Understanding the Limitations and Pitfalls
While robust, sieve separation has inherent limitations that are important to recognize. Understanding these helps in interpreting results correctly and deciding when an alternative method may be more appropriate.
The Influence of Particle Shape
Sieving fundamentally measures a particle's second-largest dimension. A long, thin particle may pass through a mesh opening end-on, classifying it as smaller than its actual length would suggest. This is a key reason why sieve analysis results may differ from methods that measure a different dimension, like laser diffraction.
Challenges with Fine Powders
Dry sieving becomes increasingly difficult and less reliable for very fine powders, typically those below 45 microns. These particles tend to agglomerate due to electrostatic forces and are more likely to blind the fine mesh apertures, preventing proper separation.
The Risk of Material Degradation
As noted, friable (easily crumbled) materials can be broken down by the mechanical action of the shaker. This attrition creates new, finer particles that were not present in the original sample, leading to an inaccurate analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this technique effectively, you must align your procedure with your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Prioritize repeatability. Standardize your procedure by using the exact same sample weight, sieve stack, and agitation time for every single test.
- If your primary focus is new material characterization: Prioritize accuracy. Perform an "end-point determination" by running tests for increasing durations until the weight on each sieve no longer changes significantly, ensuring complete separation has been achieved.
- If your primary focus is working with difficult materials (very fine or fragile): Acknowledge the method's limits. Consider alternative techniques like wet sieving, air-jet sieving, or a different technology like laser diffraction to get a more reliable result.
By controlling the process variables, you transform simple sieving from a basic sorting method into a precise and powerful analytical tool.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Separation Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Sieve Stack | Nested sieves with descending mesh sizes to sort particles. |
| Agitation (Shaker) | Spreads and reorients particles for accurate separation. |
| Sample Weight | Measured before and after to calculate size distribution. |
| Analysis Goal | Determines weight percentage of material in specific size ranges. |
Optimize Your Particle Analysis with KINTEK
Accurate sieve analysis is critical for your lab's quality control and material R&D. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including precision sieves and reliable sieve shakers, to ensure your particle size distribution data is consistent and trustworthy.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect sieving solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation



















