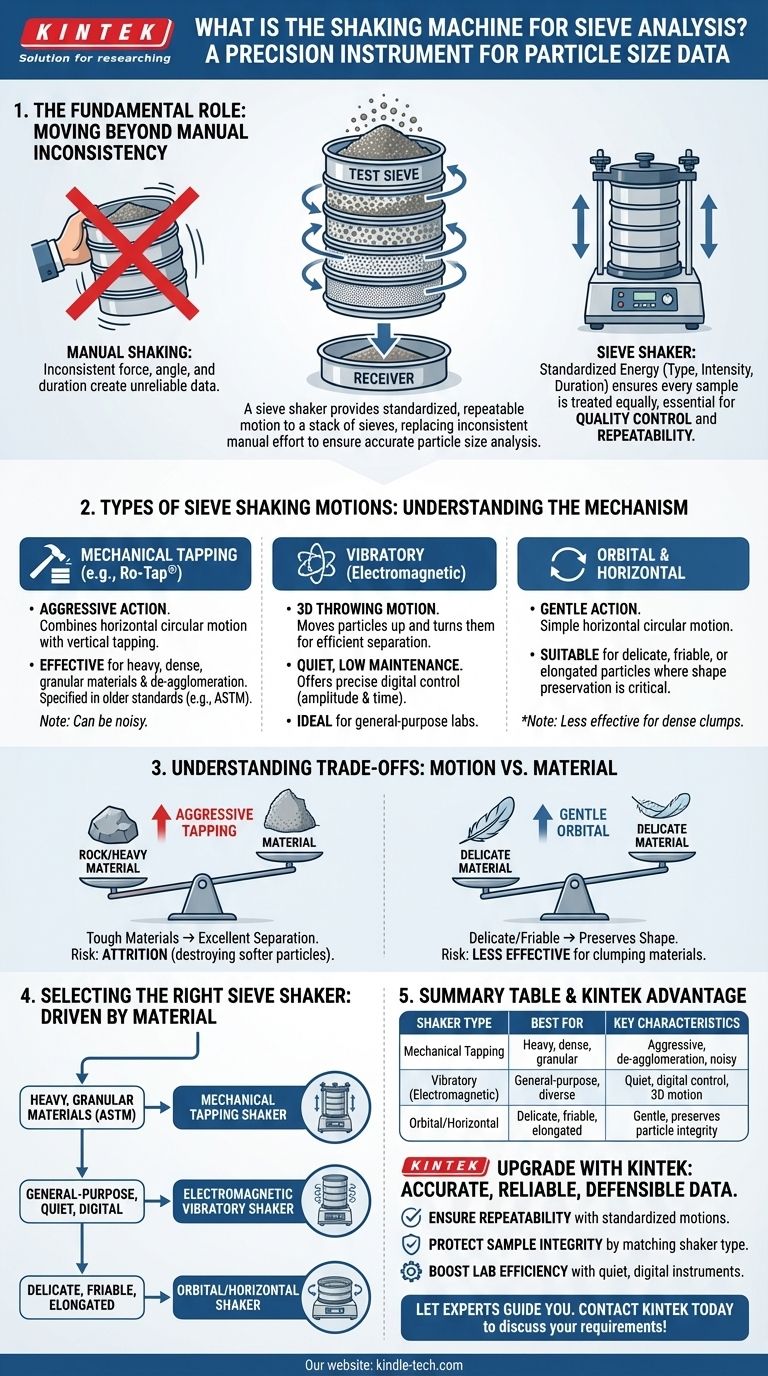
At its core, a shaking machine for sieve analysis is a laboratory device designed for one purpose: to provide a standardized and repeatable motion to a stack of test sieves. Officially known as a sieve shaker, its function is to agitate a granular material, causing particles to find openings and separate by size through the progressively finer mesh of each sieve. This mechanical process removes the inconsistencies and operator-variability of manual shaking.
A sieve shaker is not just a machine for shaking; it is a precision instrument for ensuring the accuracy and repeatability of particle size analysis. Its primary value lies in replacing subjective manual effort with a controlled, consistent energy input, which is the foundation of any reliable test result.
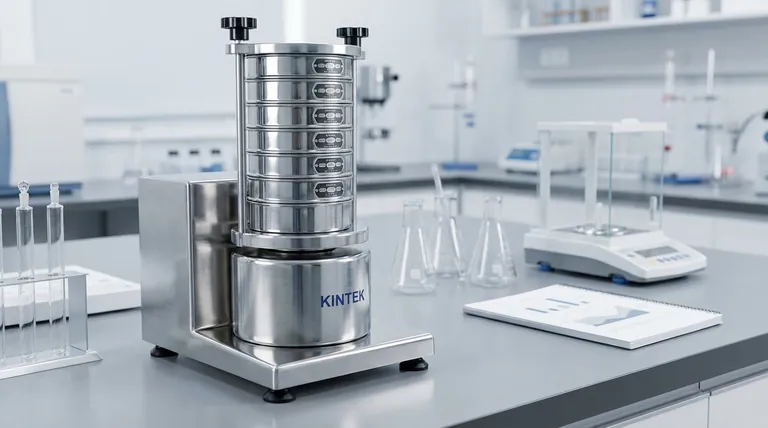

The Fundamental Role of the Sieve Shaker
A sieve analysis, or gradation test, determines the particle size distribution of a material. While you can shake a stack of sieves by hand, the results are nearly impossible to reproduce accurately.
Moving Beyond Manual Inconsistency
Manual shaking is inconsistent. The force, angle, and duration of shaking vary significantly between different operators and even between tests by the same operator. This variability directly impacts how efficiently particles are separated, leading to unreliable data.
The Principle of Standardized Energy
A sieve shaker solves this by applying a precise, repeatable mechanical action. By controlling the type of motion (e.g., tapping, vibrating), the intensity (amplitude), and the duration (time), it ensures that every sample is subjected to the exact same conditions. This standardization is critical for quality control and for comparing results over time or between different labs.
Types of Sieve Shaking Motions
The effectiveness of a sieve analysis depends heavily on the type of motion used to agitate the particles. Different motions are suited for different material characteristics.
Mechanical Tapping (e.g., Ro-Tap®)
This is the traditional and most aggressive method. It combines a jarring, horizontal circular motion with a vertical tapping action from a hammer. This dual-action motion is very effective at de-agglomerating particles and clearing blocked sieve apertures. It is specified in many older industry standards (e.g., ASTM) and is ideal for heavy, dense, or granular materials.
Vibratory (Electromagnetic)
Modern sieve shakers often use an electromagnetic drive to create a 3D throwing motion. This action moves the particles up off the sieve mesh and turns them as they fall back down. This helps each particle present itself to the sieve openings in various orientations, ensuring efficient separation. Vibratory shakers are generally quieter, require less maintenance, and offer precise digital control over amplitude and time.
Orbital and Horizontal
This type of shaker imparts a simple horizontal, circular motion. It is a much gentler action compared to tapping or aggressive vibration. This makes it suitable for needle-shaped, elongated, or friable materials that might be damaged or broken by more vigorous shaking, which would skew the particle size results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sieve shaker involves balancing the needs of your material against operational considerations.
Motion vs. Material Type
The primary trade-off is between aggressive action and particle integrity. A mechanical tapper is excellent for tough materials but can destroy softer or brittle ones (a phenomenon called attrition), falsely increasing the amount of fine particles. A gentler orbital or vibratory motion preserves particle shape but may be less effective for dense materials that tend to clump together.
Noise and Lab Environment
Mechanical tappers are notoriously loud and often require a dedicated sound-dampening enclosure. For a modern, multi-use laboratory, a quiet and compact electromagnetic vibratory shaker is a far more practical choice.
Endpoint Determination and Repeatability
The goal of shaking is to reach the "endpoint," the point at which continued shaking no longer causes a significant amount of material to pass through the sieves. A high-quality shaker with digital time and amplitude control allows you to establish and repeat the exact parameters needed to reach this endpoint consistently, forming the basis of a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP).
Selecting the Right Sieve Shaker
Your choice should be driven by your primary material and testing requirements.
- If your primary focus is heavy, granular materials and compliance with traditional ASTM standards: A mechanical tapping shaker is often the required or preferred instrument.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose lab with diverse materials and a need for quiet, digitally-controlled operation: An electromagnetic vibratory shaker offers the best versatility and user experience.
- If your primary focus is delicate, friable, or elongated particles where shape preservation is critical: A shaker with a gentle orbital or horizontal motion is the most appropriate choice to prevent sample damage.
Ultimately, selecting the right sieve shaker is the first step toward generating particle size data that is not only accurate but also reliable and defensible.
Summary Table:
| Shaker Type | Best For | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Tapping | Heavy, dense, granular materials; ASTM standards | Aggressive action; effective de-agglomeration; noisy |
| Vibratory (Electromagnetic) | General-purpose labs; diverse materials | Quiet operation; digital control; 3D throwing motion |
| Orbital/Horizontal | Delicate, friable, elongated particles | Gentle motion; preserves particle shape and integrity |
Upgrade your lab's particle size analysis with KINTEK.
Choosing the right sieve shaker is critical for generating accurate, reliable, and defensible data. Whether you work with heavy aggregates, fine powders, or delicate materials, KINTEK has the precision lab equipment to meet your needs.
We help you:
- Ensure repeatability with standardized, controlled shaking motions.
- Protect sample integrity by matching the shaker type to your material.
- Boost lab efficiency with quiet, digitally-controlled instruments.
Let our experts guide you to the perfect solution for your laboratory. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sieve analysis requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- Why is the use of high-precision analytical sieve shakers necessary for LPBF? Ensure Perfect Metal Powder Consistency
- How do industrial-grade constant temperature shakers influence the accuracy of data in batch adsorption experiments?
- What is the function of high-energy crushing and sieving systems? Master Mechanical Activation for Mineral Carbonation
- What are the different types of sieving? Dry vs. Wet Methods for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is vibratory sieving? Achieve Precise, Reproducible Particle Size Analysis
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- What is the function of a laboratory shaker during batch adsorption experiments? Optimize Fly Ash Kinetic Research
- How do laboratory shakers ensure accuracy in adsorption studies? Optimize Your Kinetics and Isotherm Data Today



















