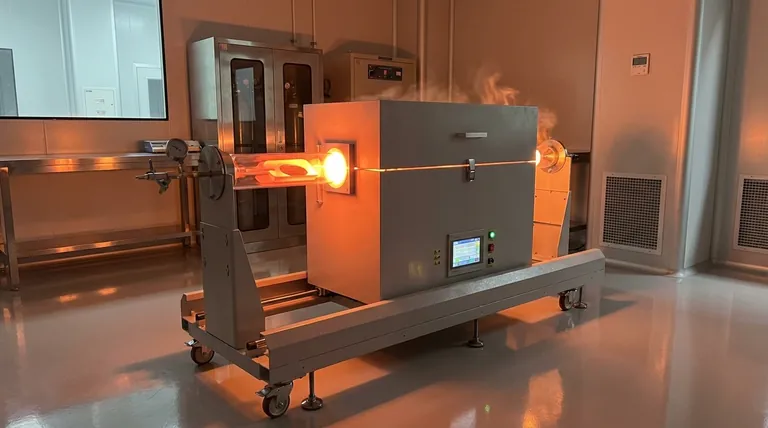
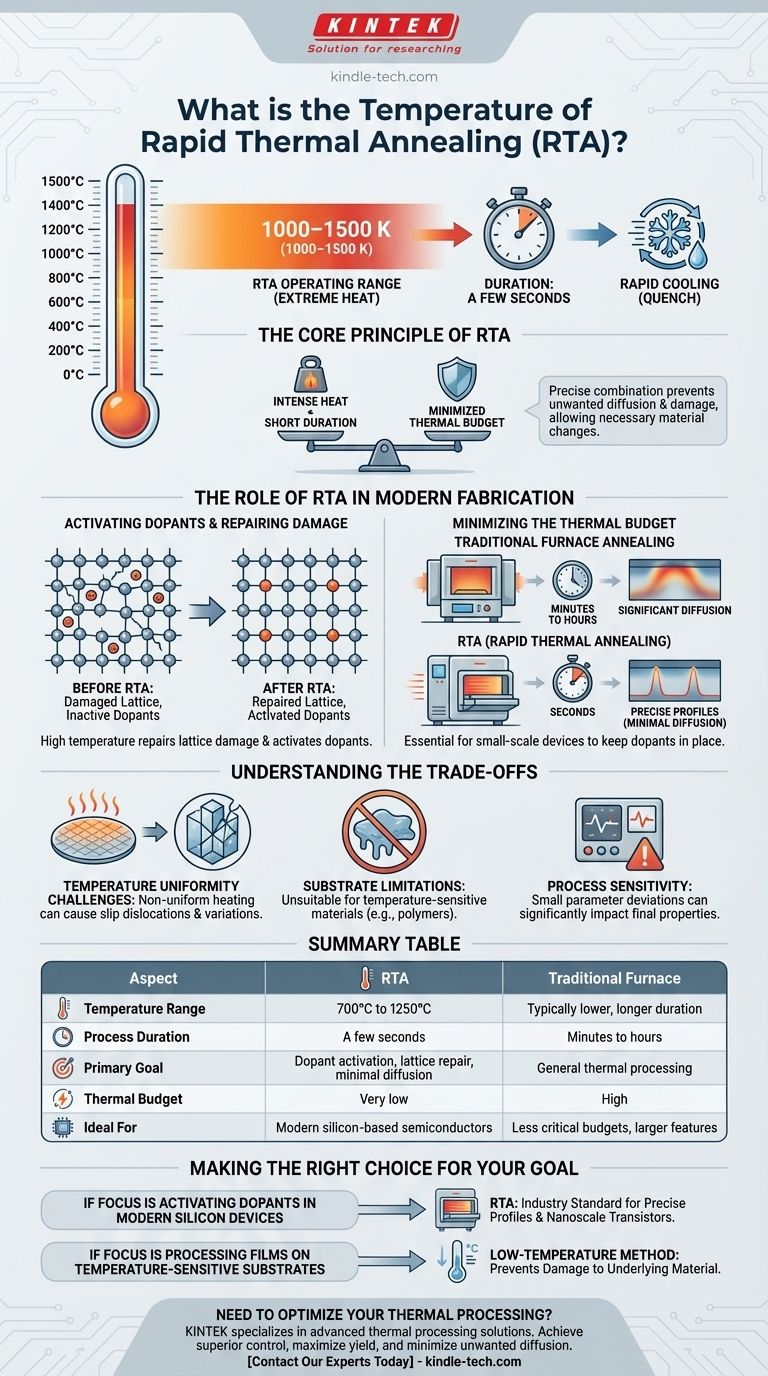
Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA) typically operates at extremely high temperatures, generally ranging from approximately 700°C to 1250°C (1000–1500 K). This intense heat is applied for only a few seconds to activate specific physical or chemical changes in a material, followed by a rapid cooling or "quench" process.
The core principle of RTA is not just its high temperature, but the precise combination of intense heat and extremely short duration. This minimizes the overall "thermal budget," allowing for necessary material changes while preventing the unwanted diffusion and damage that would occur with prolonged heating.

The Role of RTA in Modern Fabrication
To understand why such high temperatures are necessary, we must look at the specific problems RTA is designed to solve in semiconductor manufacturing. It is a tool for delivering a very targeted dose of thermal energy.
Activating Dopants and Repairing Damage
After ions (dopants) are implanted into a silicon wafer to alter its electrical properties, the crystal lattice is left damaged and the dopants are not in electrically active positions.
High-temperature annealing provides the energy needed to repair this lattice damage and allow the dopant atoms to move into the correct substitutional sites in the crystal, thereby "activating" them.
Minimizing the Thermal Budget
The "thermal budget" is the total amount of thermal energy a wafer is exposed to during processing. As electronic components shrink, it is critical that dopants remain exactly where they were implanted.
Traditional furnace annealing, which can take many minutes or hours, would cause these dopants to diffuse or "smear out," ruining the performance of small-scale devices. RTA solves this by completing the anneal in seconds, before significant diffusion can occur.
A Contrast with Low-Temperature Processes
Not all fabrication steps can tolerate high heat. Processes like Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) operate at much lower temperatures, typically from room temperature up to 350°C.
These low-temperature methods are essential when working with substrates or previously deposited layers that would be damaged or destroyed by the extreme heat of RTA. This highlights the trade-off between the thermal energy required for an effect and the thermal stability of the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, RTA is not a universal solution. Its unique characteristics introduce specific engineering challenges that must be managed.
Temperature Uniformity
Heating a wafer by hundreds of degrees in seconds can create temperature gradients across its surface. Non-uniform temperatures can lead to slip dislocations in the crystal and variations in device performance, making process control critical.
Substrate Limitations
RTA is fundamentally unsuitable for temperature-sensitive materials, such as certain polymers or compound semiconductors, which cannot withstand its high operating range. For these applications, low-temperature deposition and annealing techniques are non-negotiable.
Process Sensitivity
The final properties of the material are highly sensitive to both the peak temperature and the duration of the RTA cycle. Small deviations in the process parameters can lead to significant changes in electrical characteristics, requiring sophisticated monitoring and control systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice between a high-temperature, short-duration process like RTA and a low-temperature alternative depends entirely on your material constraints and the desired physical outcome.
- If your primary focus is activating dopants in modern silicon devices: RTA is the industry standard because it provides the necessary energy while preserving the precise dopant profiles required for nanoscale transistors.
- If your primary focus is processing films on a temperature-sensitive substrate: A low-temperature method is required, as the high heat of RTA would damage or destroy the underlying material.
Ultimately, mastering thermal processing requires understanding your material's total thermal budget and selecting the tool that achieves your goal without exceeding that limit.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA) | Traditional Furnace Annealing |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 700°C to 1250°C | Typically lower, but applied for longer |
| Process Duration | A few seconds | Minutes to hours |
| Primary Goal | Dopant activation, lattice repair with minimal diffusion | General thermal processing |
| Thermal Budget | Very low | High |
| Ideal For | Modern silicon-based semiconductors | Less critical thermal budgets, larger features |
Need to optimize your thermal processing for semiconductor fabrication?
Selecting the right annealing technique is critical for achieving precise dopant activation and maintaining material integrity. KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment, including thermal processing solutions tailored for semiconductor R&D and production.
Our expertise can help you:
- Select the right system for your specific material and process requirements.
- Achieve superior process control with precise temperature management.
- Maximize yield and performance by minimizing unwanted thermal diffusion.
Let's discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Contact our thermal processing experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses



















