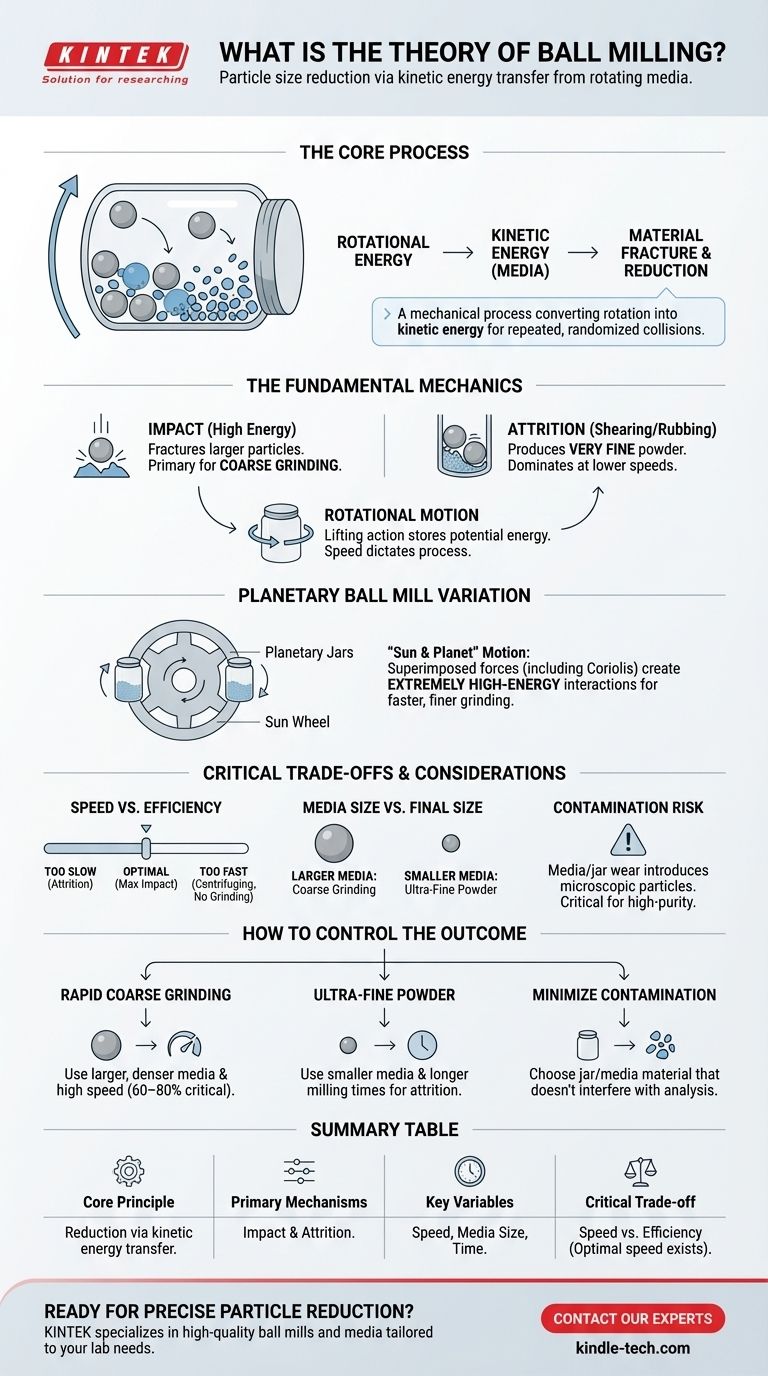
The fundamental theory of ball milling is the reduction of particle size through the transfer of kinetic energy. Inside a rotating container, hard grinding media (balls) are lifted and then fall, repeatedly striking the material and breaking it apart through high-energy impact and frictional attrition.
At its core, ball milling is a mechanical process that converts the rotational energy of a jar into the kinetic energy of internal grinding media. This energy is then delivered to a material through repeated, randomized collisions, causing fractures that reduce it to a fine powder.

The Fundamental Mechanics of Grinding
To understand ball milling, you must visualize two primary forces working in tandem. The process is not simply about crushing; it involves a combination of impact and shearing.
The Role of Rotational Motion
The process begins with the rotation of the grinding jar or vessel. As the jar spins, friction between its inner wall and the grinding media causes the balls and the material to be carried partway up the side of the container.
This lifting action is the crucial first step, as it stores potential energy in the grinding media. The speed of this rotation is a critical parameter that dictates the entire nature of the milling process.
The Power of Impact
Once the balls are lifted to a sufficient height, gravity overcomes the forces holding them to the jar wall, and they fall. They cascade or cataract downwards, striking the material at the bottom of the mill.
This is the impact action. It is a high-energy event responsible for fracturing larger, brittle particles and is the primary mechanism for coarse grinding.
The Finesse of Attrition
In addition to impact, grinding also occurs through attrition. This is a shearing or rubbing action that happens as balls slide and roll against each other and the jar wall, with the material trapped between them.
Attrition is a lower-energy but highly effective process for producing very fine or nano-sized particles. This action dominates at lower rotational speeds when the balls tumble over one another rather than falling from a great height.
Understanding a Key Variation: The Planetary Ball Mill
While simple rotary mills exist, many laboratory applications use a more advanced design to increase efficiency and energy.
The "Sun and Planet" Motion
A planetary ball mill features multiple grinding jars (the "planets") mounted on a larger rotating disc (the "sun wheel"). Crucially, the sun wheel rotates in one direction while the jars rotate on their own axes in the opposite direction.
The Effect of Superimposed Forces
This complex dual-axis rotation superimposes different forces, including Coriolis forces. The result is a dramatic increase in the speed and energy of the grinding balls.
Collisions are no longer simple gravitational impacts. Instead, they become extremely high-energy interactions, allowing for much faster and finer grinding than is possible in a standard rotary mill.
Critical Trade-offs and Considerations
Achieving the desired result with a ball mill requires understanding the key operational trade-offs. The process is not a "one size fits all" solution.
Speed vs. Efficiency
There is an optimal "critical speed" for any given mill. If the rotation is too slow, the balls will simply tumble, relying only on attrition. If the rotation is too fast, centrifugal force will pin the balls and material to the jar wall, and no effective grinding will occur. Maximum impact energy is achieved at a speed just below this critical centrifuging point.
Media Size vs. Final Particle Size
The size of the grinding media directly influences the final particle size. Larger, heavier balls deliver more impact energy and are effective for breaking down large pieces. Smaller balls have more surface area and create more frequent, lower-energy collisions, making them ideal for milling material into an ultra-fine powder.
The Inevitability of Contamination
A practical reality of ball milling is that the grinding media and the jar itself will wear down over time. This wear introduces microscopic particles from the media/jar material into your sample. This is a critical consideration for high-purity applications.
How to Control the Grinding Outcome
Your milling strategy should be dictated entirely by your end goal. The key variables—speed, media, and time—can be adjusted to produce vastly different results.
- If your primary focus is rapid, coarse grinding: Use larger, denser grinding media and operate the mill at a high speed (typically 60-80% of critical speed) to maximize impact forces.
- If your primary focus is producing ultra-fine powder: Use a large number of smaller grinding balls and longer milling times to maximize the effects of attrition.
- If your primary focus is minimizing contamination: Choose a jar and grinding media made of the same material as your sample or a material that will not interfere with your subsequent analysis or application.
Ultimately, mastering the theory of ball milling is about controlling energy transfer to achieve a specific particle size and morphology.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Reduction of particle size via transfer of kinetic energy from grinding media. |
| Primary Mechanisms | Impact (high-energy collisions) and Attrition (shearing/rubbing). |
| Key Variables | Rotational speed, grinding media size, and milling time. |
| Critical Trade-off | Speed vs. Efficiency: An optimal speed exists for maximum impact energy. |
Ready to achieve precise particle size reduction in your lab?
Understanding the theory is the first step; applying it with the right equipment is what delivers results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality ball mills and grinding media tailored to your specific laboratory needs—whether you require rapid coarse grinding or the production of ultra-fine powders.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your efficiency and ensure your grinding outcomes are a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- Hybrid High Energy Vibratory Ball Mill for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a planetary high-energy ball mill? Master Mechanical Alloying for Nickel Nanoparticles
- What are the advantages of a planetary ball mill? Achieve ultrafine powders with speed and precision.
- What is the objective of low-speed ball milling? Enhance Conductivity for Li8/7Ti2/7V4/7O2-Carbon Composites
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in Si-FG preparation? Essential Mechanical Activation and Refinement
- What is the primary function of a planetary ball mill during Mo-La2O3 mixing? Achieve Uniform Powder Dispersion
- What is the primary function of a planetary ball mill for LGPS preparation? Unlock High-Energy Mechanochemical Synthesis
- What is the role of a high-energy planetary ball mill in W-Cu powder preparation? Achieve Superior Material Uniformity
- What is the function of a high-energy planetary ball mill? Unlock Nanoscale Precision in Powder Metallurgy



















