At its core, twin screw extrusion is a continuous manufacturing process that uses two intermeshing, rotating screws inside a heated barrel to process materials. It excels at melting, intensively mixing, and shaping polymers, food products, or chemicals with a high degree of control. This method is the industry standard for creating complex plastic compounds, engineered materials, and textured food products.
The essential advantage of twin screw extrusion over other methods is its unparalleled control and mixing capability. The modular design of the screws allows for precise tailoring of the process to mix multiple ingredients, remove unwanted volatiles, and create highly uniform and specialized materials in a single, efficient operation.
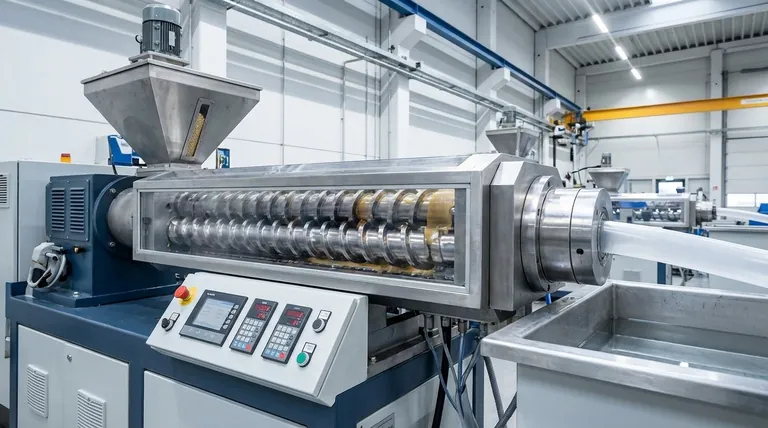

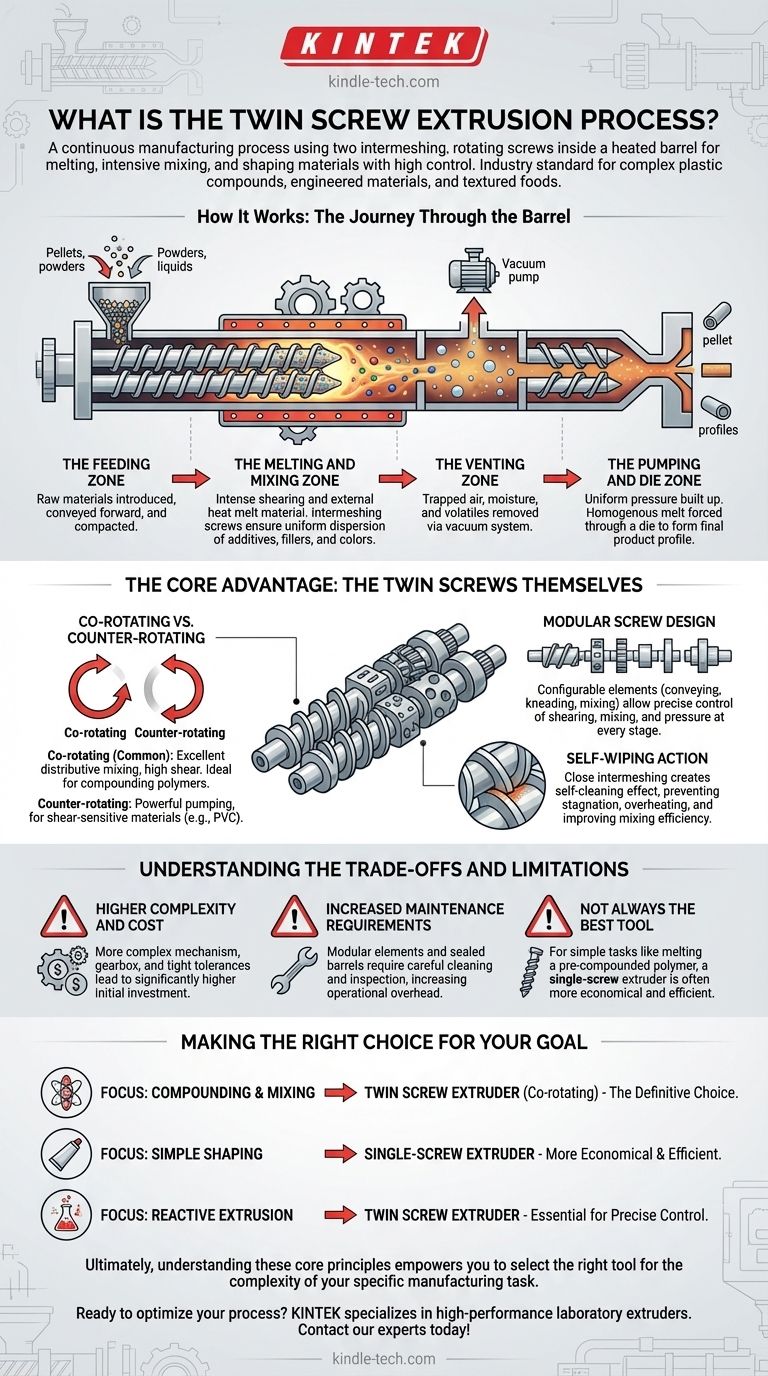
How It Works: The Journey Through the Barrel
The process can be understood as a sequence of distinct zones, each with a specific function. The raw materials—often in pellet, powder, or liquid form—are transformed as they travel from the feed hopper to the final die.
The Feeding Zone
Raw materials are introduced into the extruder barrel through a hopper. The initial screw sections are designed simply to convey this material forward and begin compacting it.
The Melting and Mixing Zone
This is where the transformative work happens. As the material moves along the barrel, external heaters and the intense shearing action generated by the screws melt it into a viscous fluid, or "melt." The intermeshing screws knead and fold the material, ensuring any additives, fillers, or colors are dispersed with extreme uniformity.
The Venting Zone
For many applications, it's critical to remove trapped air, moisture, or other volatile substances from the melt. Specific sections of the barrel can be opened and connected to a vacuum system, allowing these gases to escape before the final product is formed.
The Pumping and Die Zone
In the final section, the screw design changes to build up uniform pressure. This homogenous, pressurized melt is then forced through a shaped opening, known as a die, which forms the final product profile—such as pellets, sheets, tubes, or filaments.
The Core Advantage: The Twin Screws Themselves
The power of this technology lies in the sophisticated interaction between the two screws. This interaction provides process capabilities that are impossible to achieve with a single-screw extruder.
Co-rotating vs. Counter-rotating Screws
Screws can turn in the same direction (co-rotating) or opposite directions (counter-rotating). Co-rotating designs are the most common, as they provide excellent distributive mixing and high shear, making them ideal for compounding polymers with additives. Counter-rotating designs create a powerful pumping action, useful for processing shear-sensitive materials like PVC.
Modular Screw Design
Unlike a single solid screw, the shafts in a twin screw extruder are fitted with various modular elements. These include conveying elements, kneading blocks, and mixing gears. Engineers can arrange these elements in a specific sequence to precisely control the amount of shearing, mixing, and pressure applied to the material at every stage.
Self-Wiping Action
The close intermeshing of the screws creates a self-cleaning effect. As they rotate, one screw wipes the surface of the other, preventing material from stagnating or overheating. This ensures a consistent residence time for the material and significantly improves mixing efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, twin screw extrusion is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Complexity and Cost
Twin screw extruders are mechanically more complex than their single-screw counterparts. The gearbox required to drive two intermeshing shafts, along with the tighter manufacturing tolerances, results in a significantly higher initial capital investment.
Increased Maintenance Requirements
The complexity that provides versatility also demands more rigorous maintenance. The modular screw elements and tightly sealed barrel sections require careful cleaning and inspection, leading to higher operational overhead.
Not Always the Best Tool
For simple tasks like melting a single, pre-compounded polymer to form a pipe or a film, the intense mixing of a twin screw extruder is unnecessary. In these cases, a simpler, more cost-effective single-screw extruder is often the superior choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a twin screw process hinges entirely on the complexity of your material and your final product requirements.
- If your primary focus is compounding and mixing: You must blend polymers with fillers, additives, or multiple colorants. The intensive, controllable mixing of a co-rotating twin screw extruder is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is simple shaping of a single material: You are simply melting and forming a pre-made compound into a final shape (like a tube or sheet). A single-screw extruder is almost always the more economical and efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is reactive extrusion: You need to initiate a chemical reaction within the melt. The precise temperature control and residence time distribution of a twin screw extruder are essential for this advanced application.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles empowers you to select the right tool for the complexity of your specific manufacturing task.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Intermeshing Screws | Two screws rotate inside a barrel. | Provides superior mixing and self-cleaning action. |
| Modular Design | Screw elements can be reconfigured. | Allows precise tailoring of shear, mixing, and pressure. |
| Multiple Process Zones | Includes feeding, melting, venting, and die zones. | Enables complex tasks (e.g., degassing) in one continuous process. |
| Co-rotating vs. Counter-rotating | Screws turn in the same or opposite directions. | Co-rotating: ideal for compounding; Counter-rotating: good for shear-sensitive materials. |
Ready to optimize your compounding or material development process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance laboratory equipment, including extruders, to meet your precise R&D and production needs. Whether you are developing new polymer compounds, engineered materials, or specialty chemicals, our expertise can help you achieve superior mixing uniformity and process efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how the right extrusion technology can accelerate your innovation and improve your product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to utilize PTFE sample holders in electroless nickel plating? Ensure Process Integrity
- Why are PTFE beakers required for hafnium metal ICP-OES validation? Ensure Pure Sample Dissolution
- Why are PTFE laboratory consumables required when testing stainless steel against organic acids? Ensure Data Integrity
- What are the advantages of using PTFE jars for RuTi alloy mixing? Ensure Chemical Purity and High Yield
- What are the advantages of using PTFE molds for WBPUU films? Ensure Purity and Perfect Demolding

















