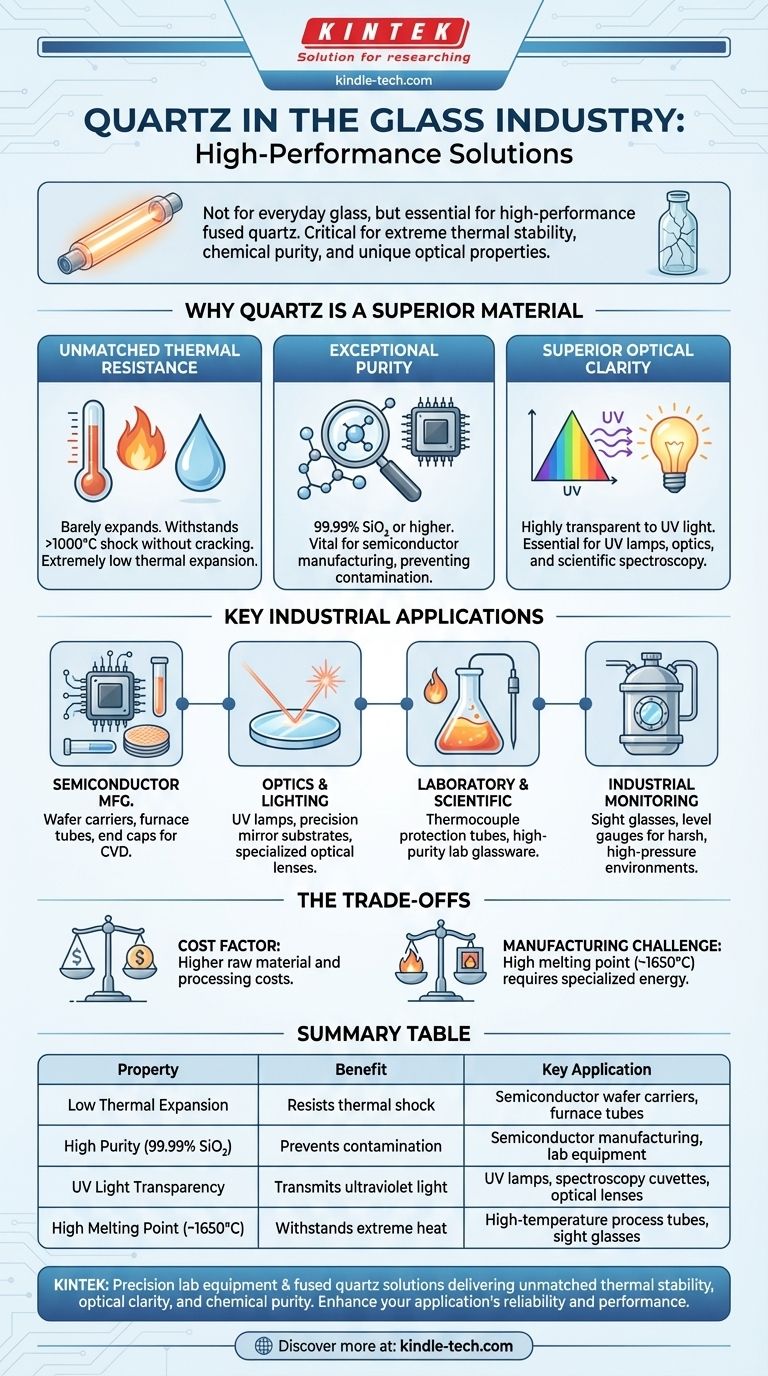
In the glass industry, high-purity quartz is not used for everyday items like bottles or windows; it is the essential raw material for creating high-performance fused quartz glass and silica glass. These specialized materials are critical for demanding applications that require exceptional thermal stability, chemical purity, and unique optical properties that far exceed the capabilities of conventional glass.
The true value of quartz lies in its unparalleled purity and high melting point. These characteristics allow for the creation of fused quartz glass, a material superior to standard glass in its ability to withstand extreme temperatures, resist thermal shock, and transmit UV light, making it indispensable for scientific and industrial technology.
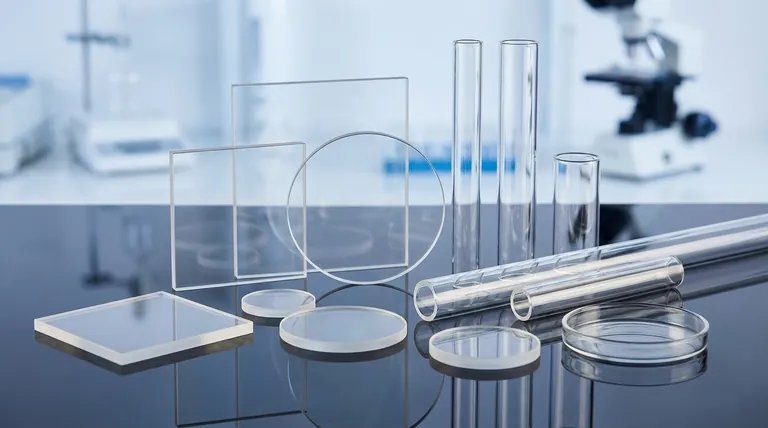

Why Quartz is a Superior Material for Specialty Glass
The decision to use quartz over conventional glass is driven by its unique combination of thermal, optical, and chemical properties. These attributes make it the only viable material for certain high-stakes applications.
Unmatched Thermal Resistance
Fused quartz has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it barely expands or contracts when subjected to radical temperature changes.
You can heat a quartz tube to over 1000°C and plunge it into cold water without it cracking. This resistance to thermal shock is impossible for standard glass.
Exceptional Purity
Industrial quartz can be processed to a purity of 99.99% silica (SiO2) or higher.
This lack of contaminants is critical in industries like semiconductor manufacturing, where even microscopic impurities can ruin a microchip. This purity also ensures consistent performance.
Superior Optical Clarity
Unlike most types of glass, fused quartz is highly transparent to ultraviolet (UV) light.
This property makes it the essential material for creating UV lamps, lenses for UV spectrum optics, and scientific cuvettes used in spectroscopy.
Key Industrial Applications
The properties of fused quartz directly enable its use in some of the world's most advanced technological processes. It is typically manufactured into specific components like tubes, rods, and plates.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
This is one of the largest markets for quartz glass. Its purity and ability to withstand high temperatures are essential for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and diffusion.
Components like process tubes, end caps, transfer carriers, and "boats" that hold silicon wafers are all made from fused quartz.
Optics and Lighting
The UV transmission of quartz is vital for creating high-intensity lamps and specialized optical lenses.
Its thermal stability also makes it the ideal material for precision mirror substrates in telescopes and lasers, as it won't warp with minor temperature fluctuations.
Laboratory and Scientific Equipment
Quartz is used for thermocouple protection tubes, especially when measuring the temperature of molten precious metals, as it is chemically inert and can handle the extreme heat.
Its purity and durability make it ideal for a wide array of laboratory glassware used in high-temperature or high-purity chemical reactions.
Industrial Process Monitoring
In harsh industrial settings, components like sight glasses and level gauges must allow operators to see inside high-pressure or high-temperature vessels.
Quartz provides a clear, distortion-free window that remains stable and reliable under conditions that would cause standard glass to fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its performance is exceptional, fused quartz is a specialized material with practical limitations that make it unsuitable for general use.
The Cost Factor
High-purity quartz is significantly more expensive to source and process than the sand, soda ash, and lime used to make conventional soda-lime glass.
This cost is directly tied to the purity requirements and the more limited supply of suitable raw quartz crystals.
The Manufacturing Challenge
The melting point of quartz is around 1650°C (3000°F), which is much higher than that of standard glass.
Melting and forming quartz requires far more energy and highly specialized equipment, which contributes significantly to the higher cost of the final product. It is inherently more difficult to work with.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting quartz glass is a deliberate engineering choice based on performance requirements. Its use is dictated by environments where other materials would fail.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: Fused quartz is the definitive choice for applications like furnace tubes, thermocouple sheaths, and wafer carriers that must resist extreme heat and thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is optical purity and UV transmission: Specify fused quartz for lenses, windows, and lamps intended for use with ultraviolet light, where standard glass is fundamentally opaque.
- If your primary focus is process purity: The inertness and high purity of quartz glass make it essential for semiconductor processing and laboratory equipment where chemical contamination cannot be tolerated.
Ultimately, choosing quartz is a decision to prioritize performance and reliability in environments where standard glass simply cannot function.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Low Thermal Expansion | Resists thermal shock | Semiconductor wafer carriers, furnace tubes |
| High Purity (99.99% SiO₂) | Prevents contamination | Semiconductor manufacturing, lab equipment |
| UV Light Transparency | Transmits ultraviolet light | UV lamps, spectroscopy cuvettes, optical lenses |
| High Melting Point (~1650°C) | Withstands extreme heat | High-temperature process tubes, sight glasses |
Need high-performance quartz glass components for your lab or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, providing fused quartz solutions that deliver unmatched thermal stability, optical clarity, and chemical purity for semiconductor manufacturing, research labs, and industrial monitoring. Contact us today to discuss how our quartz glass products can enhance your application's reliability and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- 400-700nm Wavelength Anti Reflective AR Coating Glass
- Zinc Selenide ZnSe Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer and Lens
People Also Ask
- What is high temperature quartz? A Guide to Unmatched Thermal Stability & Purity
- What is the temperature range of quartz glass? Master Its Thermal Limits for Demanding Applications
- What are the uses of quartz glass? Essential for Extreme-Temperature and UV Applications
- How does quartz differ from glass? A Guide to Material Selection for Performance
- What is optical quartz? The Ultimate Material for UV and High-Temp Optics







