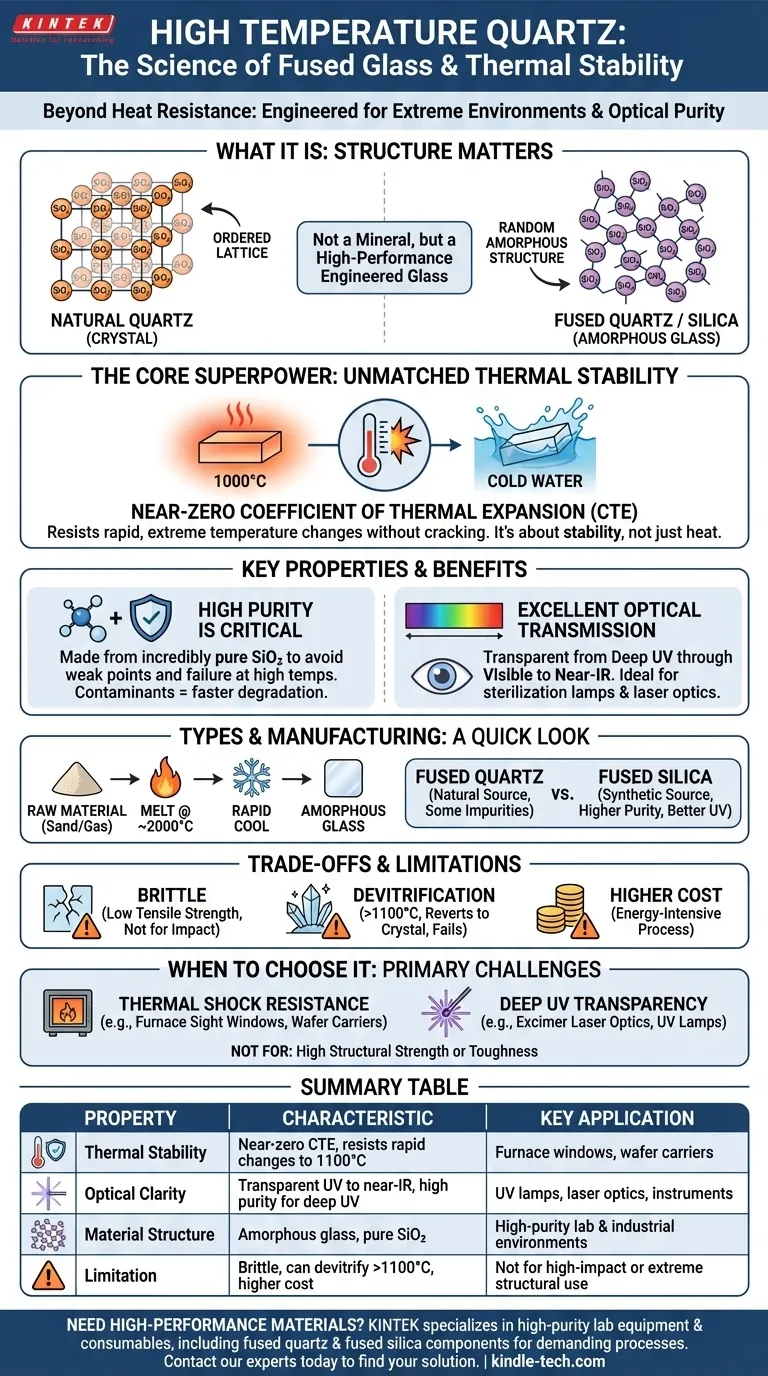
In materials science, the term "high temperature quartz" almost always refers to fused quartz or its higher-purity variant, fused silica. It is not a distinct mineral found in nature, but rather a high-performance amorphous glass engineered by melting extremely pure crystalline quartz. Its defining characteristic is a near-zero coefficient of thermal expansion, which gives it world-class resistance to thermal shock.
The critical insight is that "high temperature quartz" is valued not for its ability to simply withstand high heat, but for its extraordinary stability when subjected to rapid and extreme temperature changes. This property stems directly from its man-made, non-crystalline (amorphous) glass structure.
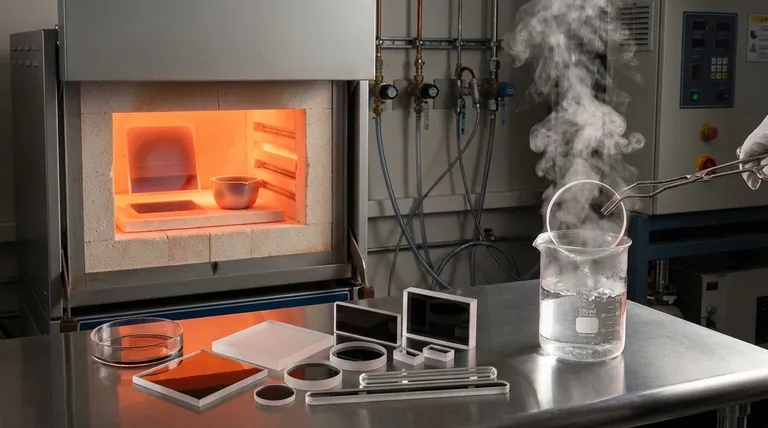

The Defining Properties of High Temperature Quartz
It's Not a Crystal, It's a Glass
The most fundamental concept to grasp is the difference in structure. Natural quartz is a crystal, meaning its atoms are arranged in a highly ordered, repeating lattice.
High temperature quartz, or fused quartz, is a glass. It is made by melting crystalline quartz and cooling it so rapidly that the atoms do not have time to arrange back into an ordered pattern, resulting in a random, amorphous structure.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
This amorphous structure is the source of its primary superpower: an extremely low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE).
While most materials expand significantly when heated and contract when cooled, fused quartz barely changes its size. This is why you can heat a piece of fused quartz to over 1000°C and plunge it into cold water without it cracking.
High Purity is Crucial
The performance of fused quartz is directly tied to its purity. Contaminants, especially metals and alkali ions, create weak points in the glass structure.
These impurities lower the material's softening point and can act as nucleation sites that accelerate failure at high temperatures. This is why manufacturing focuses on using incredibly pure silicon dioxide (SiO₂) as the raw material.
Excellent Optical Transmission
Fused quartz is transparent to a wide spectrum of light, from deep ultraviolet (UV) through the visible spectrum and into the near-infrared (IR) range.
This property, combined with its thermal stability, makes it an essential material for applications like UV sterilization lamps, high-intensity lighting, and optical windows for furnaces and scientific instruments.
How It's Made and Why It Matters
From Sand to High-Performance Glass
The manufacturing process involves heating high-purity silica sand or quartz crystals to approximately 2000°C (3632°F) in an electric arc or flame fusion furnace.
This intense heat breaks down the crystalline structure. The resulting molten material is then cooled to form the amorphous glass we call fused quartz.
Fused Quartz vs. Fused Silica
While often used interchangeably, there is a technical distinction that matters in demanding applications.
Fused Quartz is made by melting naturally occurring, high-purity quartz crystals. It contains slightly more impurities (like aluminum and titanium) inherited from the natural source.
Fused Silica is a synthetic material produced from gaseous silicon compounds like silicon tetrachloride (SiCl₄). This results in a material of much higher purity, offering superior UV transmission and overall performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Brittleness at Room Temperature
Like all glasses, fused quartz is hard but brittle. It has excellent compressive strength but poor tensile strength and is susceptible to fracture from mechanical impact. It is not a suitable material for applications requiring toughness or ductility.
The Process of Devitrification
The primary failure mode at extreme temperatures is devitrification. Over prolonged periods above 1100°C (2012°F), the amorphous glass structure will slowly begin to revert to a stable crystalline state (cristobalite).
This crystallization process makes the material opaque and introduces internal stresses, causing a catastrophic loss of mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance. Surface contamination from fingerprints or atmospheric dust can significantly accelerate devitrification.
Cost Considerations
The high energy requirements for melting quartz and the stringent purity controls make fused quartz and fused silica significantly more expensive than other common technical glasses like borosilicate.
When to Choose High Temperature Quartz
Your material choice depends entirely on the primary challenge you are trying to solve. Fused quartz is a specialized material, not a universal solution.
- If your primary focus is thermal shock resistance: Fused quartz is the industry standard for applications like furnace sight windows, thermocouple protection tubes, and semiconductor wafer carriers that undergo rapid temperature cycling.
- If your primary focus is deep UV transparency: You must specify a high-purity synthetic fused silica, as it is the only practical material for applications like excimer laser optics and UV-EPROM windows.
- If your primary focus is structural strength at high temperatures: You should evaluate technical ceramics like alumina or silicon carbide, which offer superior mechanical toughness and creep resistance compared to the brittle nature of fused quartz.
Ultimately, selecting high temperature quartz is a decision to prioritize supreme thermal stability and optical purity for applications where other materials would crack, warp, or fail.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Near-zero CTE; resists rapid temperature changes up to 1100°C | Furnace windows, wafer carriers |
| Optical Clarity | Transparent from UV to near-IR; high purity for deep UV | UV lamps, laser optics, instruments |
| Material Structure | Amorphous glass (not crystalline); made from pure SiO₂ | High-purity lab and industrial environments |
| Limitation | Brittle; can devitrify above 1100°C; higher cost | Not for high-impact or extreme structural use |
Need a high-performance material for extreme thermal or optical applications? KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including components made from fused quartz and fused silica. Our materials ensure superior thermal shock resistance, optical clarity, and longevity for your most demanding laboratory processes. Contact our experts today to find the right solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of quartz glass? Essential for Extreme-Temperature and UV Applications
- What temperature does quartz glass melt at? Understanding Its Softening Point and Practical Limits
- How does quartz differ from glass? A Guide to Material Selection for Performance
- What are the thermal properties of quartz? Unlocking Extreme Temperature Stability for Your Lab
- What is the temperature range of quartz glass? Master Its Thermal Limits for Demanding Applications



















