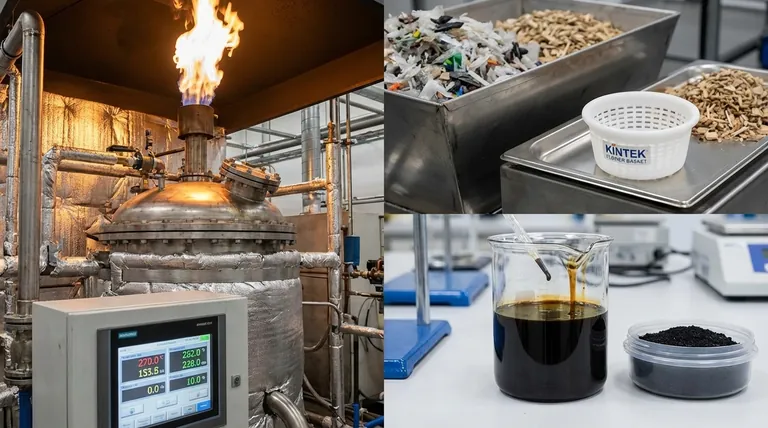
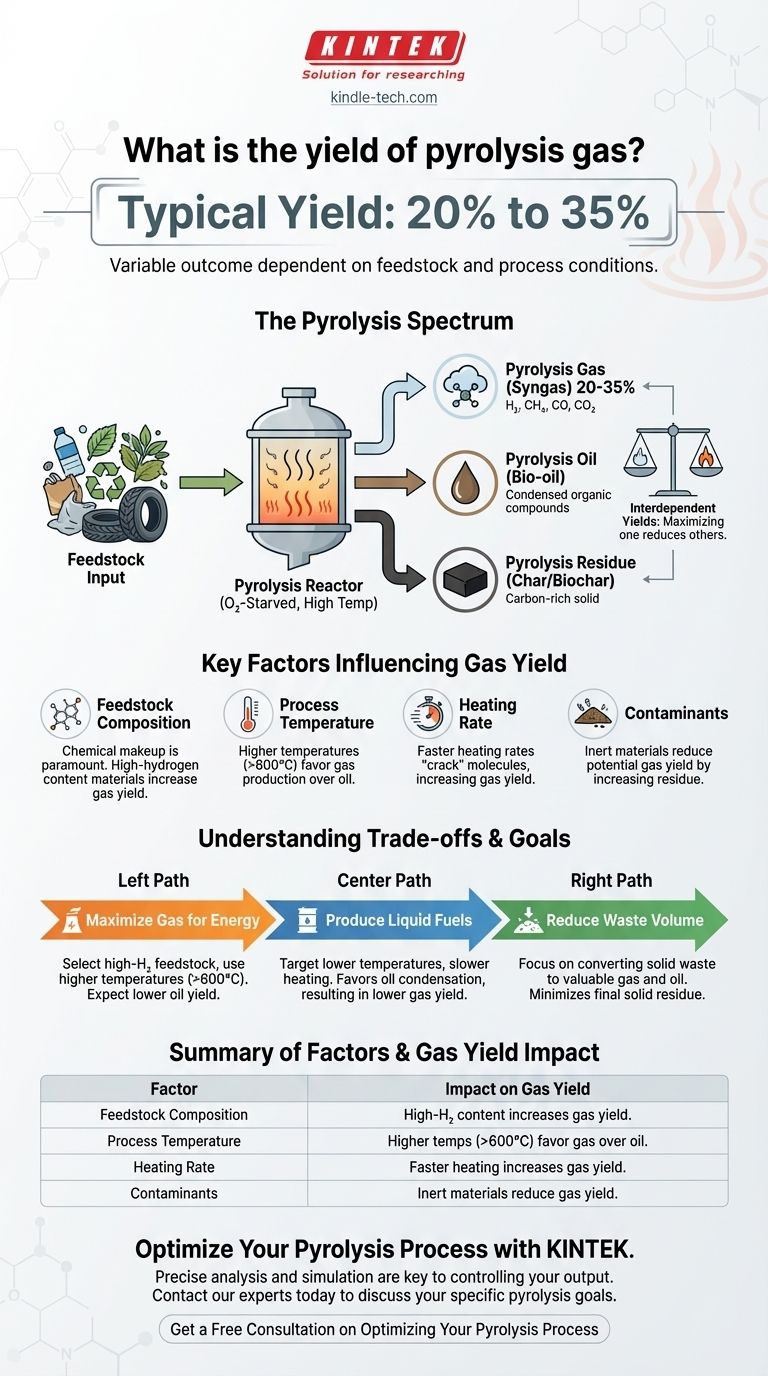
In a typical pyrolysis process, the yield of pyrolysis gas ranges from 20% to 35% of the initial feedstock mass. This figure is not fixed; it is highly dependent on the composition of the material being processed, such as the specific types of plastics in a waste stream, and the precise conditions of the operation.
The yield of pyrolysis gas is a variable outcome, not a static number. The central takeaway is that the composition of the input material (feedstock) and the process temperature are the primary factors that dictate whether you produce more gas, oil, or solid residue.

Why Pyrolysis Yields are a Spectrum, Not a Single Number
To understand the yield of pyrolysis gas, you must first understand the process itself. It's a balancing act between three potential outputs, and you can influence that balance.
The Core Principle of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at high temperatures in an oxygen-starved environment. Because there's no oxygen, the material doesn't combust; it breaks down into smaller, different molecules.
The Three Primary Outputs
This decomposition creates three distinct products:
- Pyrolysis Gas (Syngas): A mix of non-condensable gases like hydrogen, methane, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide.
- Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil): A liquid mixture of various condensed organic compounds.
- Pyrolysis Residue (Char/Biochar): A solid, carbon-rich material.
The yields of these three products are interdependent. An increase in the gas fraction necessarily means a decrease in the oil and/or residue fractions.
Key Factors That Influence Gas Yield
The 20% to 35% range is a general guideline. The actual output is determined by deliberate choices and the nature of your feedstock.
Feedstock Composition is Paramount
The single most important factor is the chemical makeup of what you put in. Different materials break down differently. For example, processing a mixed plastic waste stream will produce a different gas-to-oil ratio than processing uniform agricultural biomass.
Impact of Contaminants
The presence of non-pyrolyzable materials like soil, ash, or metals directly impacts yield. These contaminants do not break down into gas or oil; they simply exit the process as part of the solid residue, lowering the potential yield of the valuable fuel components.
Process Temperature and Speed
Higher process temperatures (e.g., >600°C) and faster heating rates tend to "crack" the larger molecules further, favoring the production of lighter, non-condensable gases. Conversely, lower temperatures and slower heating rates often favor the production of liquid pyrolysis oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing for one output often means accepting a compromise on another. It is impossible to evaluate gas yield in isolation.
The Gas-Oil-Residue Balance
A process designed to maximize gas yield will inherently produce less oil. If your goal is to produce liquid fuel (oil), you would run the system under different conditions that would, in turn, reduce the gas yield. You are always trading one output for another.
The Quality of Other Products
Furthermore, the quality of the co-products matters. Pyrolysis oil, for instance, is often acidic, unstable, and immiscible with conventional fuels. Managing or upgrading this oil is a significant operational and economic consideration that exists alongside the utilization of the gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "ideal" gas yield depends entirely on your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing gas production for energy: You will need to select high-hydrogen feedstocks and run your system at higher temperatures, accepting a lower oil yield.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid fuels: You should target lower-temperature conditions that favor oil condensation, which will naturally result in a gas yield on the lower end of the typical range.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: The key metric is the conversion of solid waste into valuable gas and oil, minimizing the final solid residue that may require disposal.
Ultimately, controlling your pyrolysis output begins with a deep understanding of your input material and precise control over your process parameters.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Gas Yield |
|---|---|
| Feedstock Composition | High-hydrogen content materials (e.g., certain plastics) increase gas yield. |
| Process Temperature | Higher temperatures (>600°C) favor gas production over oil. |
| Heating Rate | Faster heating rates "crack" molecules further, increasing gas yield. |
| Contaminants | Inert materials (soil, metals) reduce potential gas yield by increasing solid residue. |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for maximum efficiency and value?
The yield of pyrolysis gas is a critical factor in your project's economic and operational success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables that help you precisely analyze your feedstock and simulate process conditions to predict and control your output.
Whether your goal is to maximize gas for energy, produce liquid fuels, or reduce waste volume, having the right analytical tools is the first step. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve your specific pyrolysis goals.
Get a Free Consultation on Optimizing Your Pyrolysis Process
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Versatile PTFE Solutions for Semiconductor and Medical Wafer Processing
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What does a layered film mean? Unpacking the Depths of Cinematic Storytelling
- What is silicon carbide used for in semiconductor? A Guide to SiC's Dual Role in Power Electronics & Manufacturing
- Why are PTFE wafer fixtures used after diamond nucleation? Ensure Purity and Protect Fragile Nucleation Layers
- What precautions should be taken to prevent contamination when handling carbon materials? Protect Your Material's Integrity
- Why is PTFE wire used for hanging metal specimens in biodiesel corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Results







