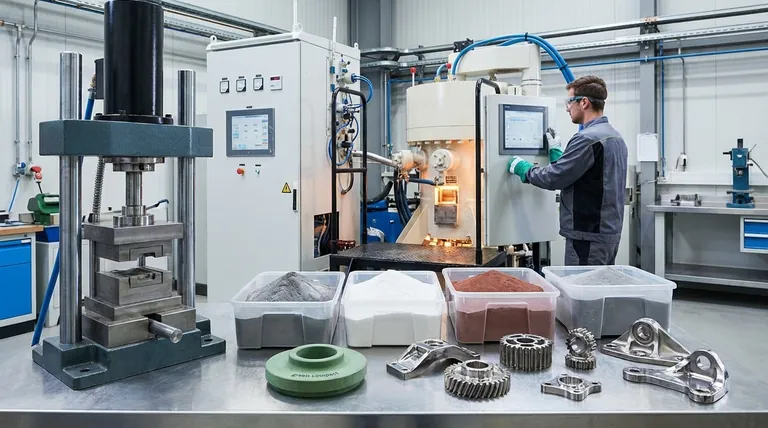
At its core, sintering uses powdered materials—most commonly metals and ceramics—along with heat and pressure. This process transforms loose powder into a solid, unified mass by heating it to a temperature just below its melting point, causing the individual particles to bond and fuse together. The range of materials is vast, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, nickel, and various titanium alloys.
The key takeaway is that sintering is not defined by a single material but by a specific process that uses heat and pressure to bind powders. This method's power lies in its ability to create solid parts from materials, including custom alloys, without ever melting them.

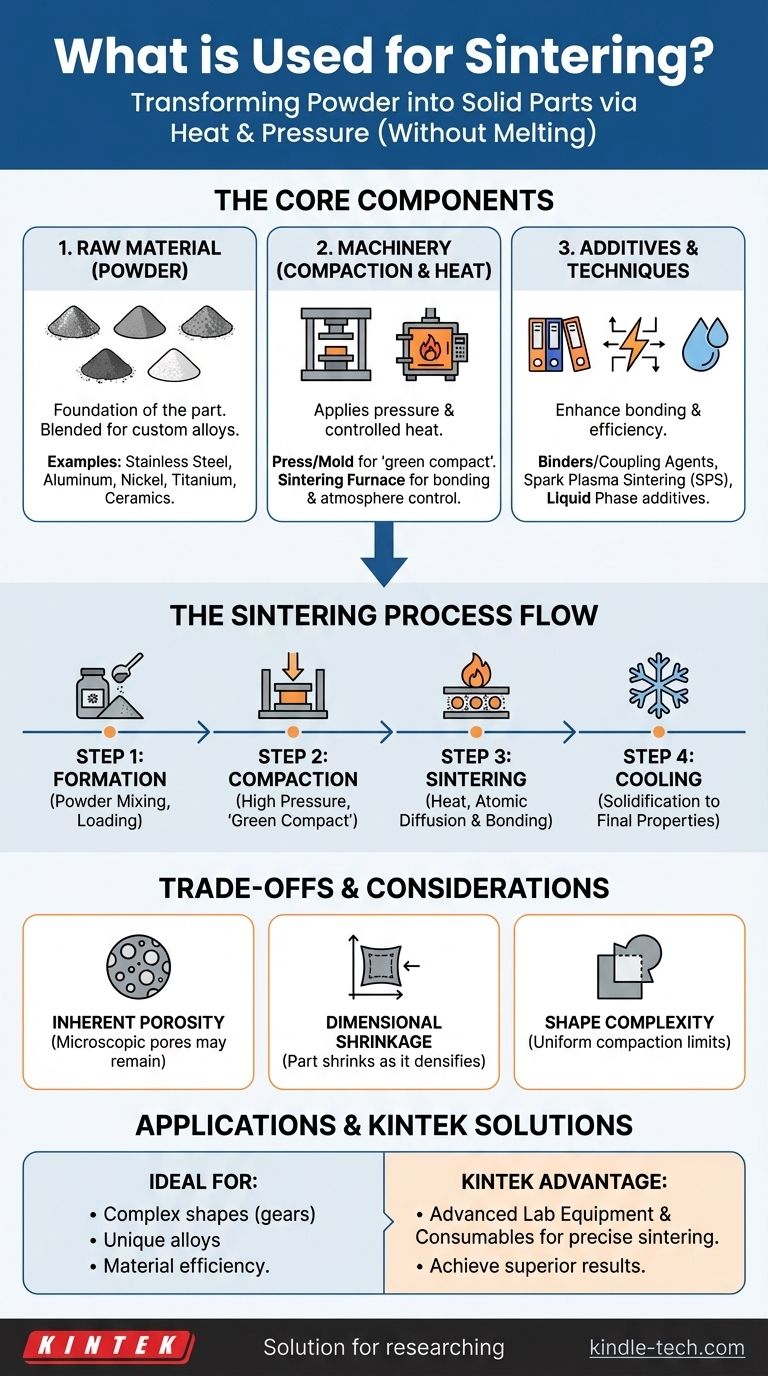
The Core Components of the Sintering Process
To fully understand what is used for sintering, we must look at it as a system involving three key components: the raw material, the machinery, and supplementary additives.
The Raw Material: Powder
The foundation of any sintered part is powder. This provides immense flexibility, as powders of different materials can be blended to create unique alloys tailored to specific needs.
Commonly used powders include metals like stainless steel, aluminum, nickel, copper, and titanium. Ceramic powders are also widely used. The quality and characteristics of the powder directly influence the final properties of the component.
The Machinery: Compaction and Heat
Sintering relies on two critical pieces of equipment to transform powder into a part.
First, a press, mold, or die is used for compaction. This machinery applies high pressure to the powder, forcing it into the desired shape, often called a "green compact."
Second, a sintering furnace provides the controlled heat necessary to bond the particles. This is not a simple oven; it must maintain a specific temperature profile and a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
Specialized Equipment and Additives
Advanced techniques like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) use pressure combined with a powerful electric field. This approach enhances densification, allowing for lower temperatures and faster processing times.
In some cases, binders or coupling agents are mixed with the powder to improve the initial forming process. For liquid phase sintering, a secondary material with a lower melting point is added, which becomes liquid during heating and aids in bonding the primary powder particles.
A Step-by-Step Look at How Sintering Works
The sintering process is a carefully controlled sequence of steps designed to achieve a dense, solid final part.
Step 1: Composition and Forming
The process begins by preparing the powdered material. This can involve mixing primary metal powders to create an alloy or adding lubricants and binding agents. This mixture is then loaded into a mold or die.
Step 2: Compaction
High pressure is applied to the powder within the mold. This compacts the particles tightly together, removing most of the air between them and forming a fragile part that holds its shape.
Step 3: Sintering (Heating)
The compacted part is removed from the mold and placed into the furnace. It is heated in a controlled atmosphere to a temperature below the material's melting point.
At this high temperature, atomic diffusion occurs at the contact points between particles. This causes the particles to chemically bond and fuse, reducing porosity and increasing the part's density and strength.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
After being held at the sintering temperature for a set time, the component is carefully cooled. As it cools, it solidifies into a single, unified mass with its final mechanical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process has inherent characteristics that are important to understand.
Inherent Porosity
Because the material is not fully melted, microscopic pores can remain in the final part. While advanced sintering processes can achieve very high densities, sintered parts may have lower strength than those made by forging or casting.
Dimensional Shrinkage
As the particles fuse and densify, the overall part shrinks. This shrinkage is predictable but must be precisely calculated and accounted for in the initial design of the mold to ensure final dimensional accuracy.
Material and Shape Complexity
The process is highly versatile but depends on the availability of the material in a suitable powder form. Furthermore, extremely complex geometries can be difficult to compact uniformly, potentially leading to variations in density within the part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these components helps you decide when sintering is the right manufacturing process for your goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of complex shapes: Sintering is ideal for manufacturing parts like gears, bearings, and sprockets to near-final dimensions, minimizing material waste and costly machining.
- If your primary focus is creating unique alloys or composites: Sintering's ability to blend different material powders allows for the creation of custom materials that would be difficult or impossible to produce via melting.
- If your primary focus is absolute maximum strength and density: You should weigh sintering against processes like forging or casting, which may be better suited for the most critical, high-stress applications.
Ultimately, sintering is a versatile and efficient manufacturing technology that transforms simple powders into robust, functional components.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Sintering | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Foundation of the part; blended for custom alloys | Stainless steel, aluminum, nickel, ceramic powders |
| Machinery | Applies pressure and controlled heat for bonding | Presses, molds, sintering furnaces |
| Additives/Techniques | Enhances bonding and process efficiency | Binders, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) |
Ready to transform your material concepts into high-performance components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise sintering processes. Whether you are working with custom metal alloys or advanced ceramics, our expertise and reliable solutions can help you achieve superior results with efficiency and accuracy.
Contact us today to discuss your specific sintering needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What critical processing conditions are provided by a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Achieve 98%+ Density.
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- How does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace facilitate the high densification of Al-30%Sc alloys?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics



















