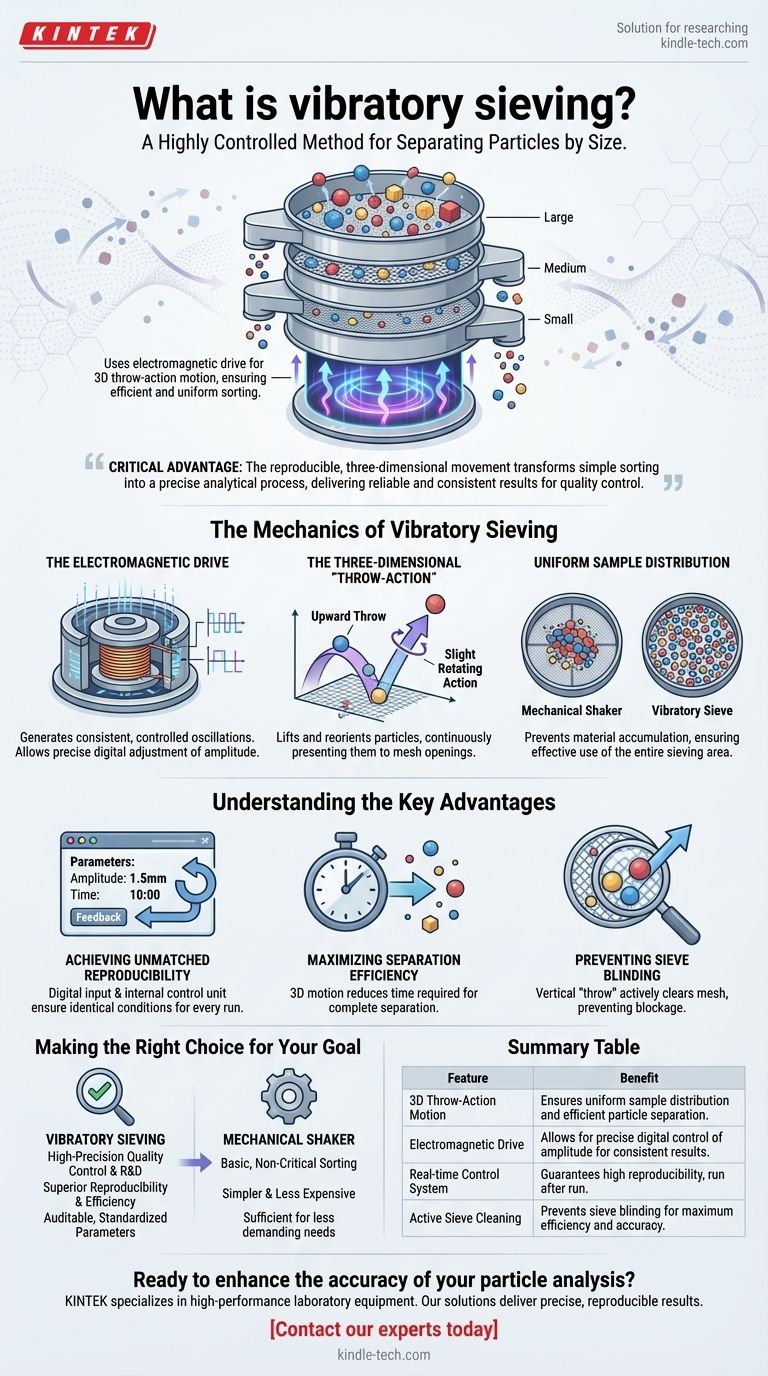
At its core, vibratory sieving is a highly controlled method for separating particles by size. It uses an electromagnetic drive to create a unique three-dimensional throwing motion, which oscillates a stack of sieves to distribute the material evenly and ensure particles are efficiently sorted through the mesh.
The critical advantage of vibratory sieving isn't just the shaking action, but the reproducible, three-dimensional movement. This technique transforms simple sorting into a precise analytical process, delivering reliable and consistent results for quality control and material analysis.

The Mechanics of Vibratory Sieving
To understand its effectiveness, we must look at the specific components and motions that define this technology. Unlike a simple back-and-forth shaker, every aspect of a vibratory sieve is engineered for precision.
The Electromagnetic Drive
The system is powered by an electromagnetic drive. This component generates consistent, controlled oscillations that are transferred to the entire sieve stack.
This is fundamentally different from a basic mechanical motor. An electromagnetic drive allows for precise, digital adjustment of the oscillation's intensity, or amplitude.
The Three-Dimensional "Throw-Action"
The defining feature of this method is its three-dimensional sieving motion. The drive creates an upward throwing movement combined with a slight rotating action.
This 3D path lifts the particles off the sieve mesh, reorients them, and then lets them fall back onto a new position. This process continuously presents particles to the mesh openings in different orientations, maximizing the chance of them passing through if they are small enough.
Uniform Sample Distribution
The result of this 3D motion is an exceptionally uniform distribution of the sample material across the entire surface of the sieve.
This prevents material from accumulating in one spot, which would overload the mesh and lead to inaccurate separation. By spreading the load, the entire sieving area is used effectively, ensuring a faster and more complete separation.
Understanding the Key Advantages
The engineering behind vibratory sieving directly translates into tangible benefits, particularly in professional lab and industrial environments where accuracy is paramount.
Achieving Unmatched Reproducibility
Modern vibratory sievers allow for the digital input of parameters like amplitude and sieving time.
Crucially, an internal control unit continuously measures the actual oscillation and compares it to the set value, making real-time adjustments. This guarantees that the sieving conditions are identical for every run, leading to highly reproducible results essential for quality control and research.
Maximizing Separation Efficiency
The throw-action is far more efficient than simple two-dimensional shaking. By constantly lifting and reorienting particles, it dramatically reduces the time required to achieve a complete separation.
Preventing Sieve Blinding
Sieve blinding occurs when particles that are very close to the size of the mesh openings get stuck, blocking the sieve. The vertical "throw" in vibratory sieving actively dislodges these near-size particles, keeping the mesh clear and the process efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sieving method depends entirely on your specific requirements for precision, repeatability, and material type.
- If your primary focus is high-precision quality control or R&D: Vibratory sieving is the definitive choice due to its superior reproducibility and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is basic, non-critical sorting: A simpler and less expensive mechanical shaker may be sufficient for your needs.
- If your analysis requires auditable, standardized parameters: The digital control and feedback loop of a vibratory sieve provide the necessary process reliability.
Ultimately, choosing a vibratory sieve is an investment in the accuracy and consistency of your particle analysis process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| 3D Throw-Action Motion | Ensures uniform sample distribution and efficient particle separation. |
| Electromagnetic Drive | Allows for precise digital control of amplitude for consistent results. |
| Real-time Control System | Guarantees high reproducibility, run after run. |
| Active Sieve Cleaning | Prevents sieve blinding for maximum efficiency and accuracy. |
Ready to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of your particle analysis?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory equipment, including advanced vibratory sieving systems. Our solutions are designed to deliver the precise, reproducible results that your quality control and R&D processes demand.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving equipment for your specific material and application needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment



















