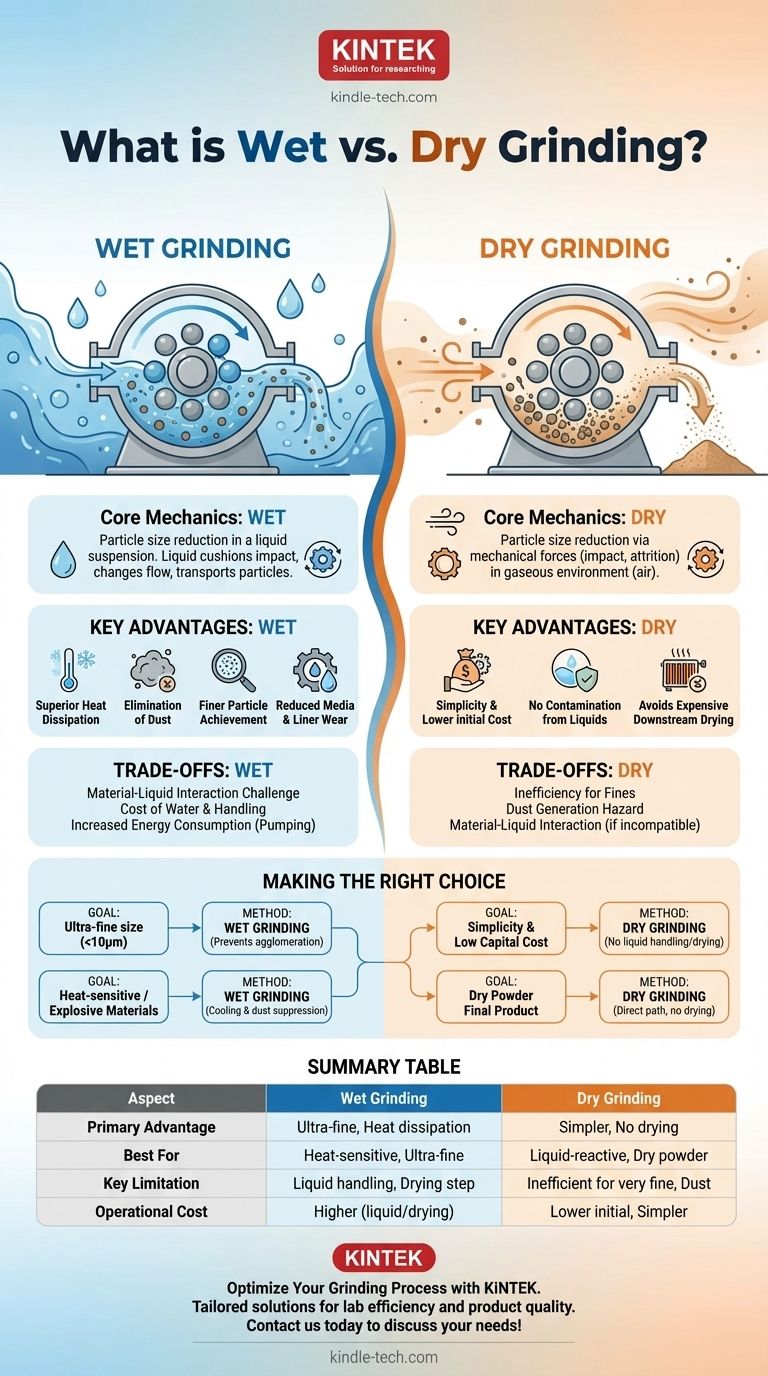
In materials processing, wet grinding is the method of reducing the particle size of a solid material while it is suspended in a liquid, typically water. Conversely, dry grinding is the process of particle size reduction without the use of any liquid, relying solely on mechanical forces in a gaseous environment, usually air. The choice between them is a critical engineering decision with significant downstream consequences.
The fundamental choice between wet and dry grinding is not about which is universally superior, but which method aligns with your material's properties, your target particle size, and your operational constraints. Wet grinding excels at producing ultra-fine, consistent particles, while dry grinding offers simplicity and lower processing costs.

The Core Mechanics of Each Method
To understand the applications, we must first understand the fundamental differences in how each process works. This distinction goes far beyond the mere presence of a liquid.
How Dry Grinding Works
Dry grinding is a process of comminution (particle size reduction) driven by mechanical forces like impact, attrition, and compression in the absence of a liquid.
The material is fed into a mill, such as a ball mill or hammer mill, where grinding media or internal components break the particles down. This method is straightforward and avoids the complexity of handling slurries.
How Wet Grinding Works
Wet grinding involves creating a slurry by mixing the solid material with a liquid, often water or a solvent, before feeding it into a mill.
The liquid serves multiple purposes. It cushions the impact forces, changes the material's flow characteristics inside the mill, and acts as a transport medium for the particles.
Key Advantages of Wet Grinding
The introduction of a liquid medium provides several distinct technical advantages that make it the required choice for many advanced applications.
Superior Heat Dissipation
Grinding generates a significant amount of heat due to friction. The liquid in wet grinding is an excellent coolant, absorbing and dissipating this heat, which is critical for processing heat-sensitive materials that could otherwise melt or chemically degrade.
Elimination of Dust
Dry grinding, especially of fine materials, can create hazardous airborne dust. Wet grinding completely eliminates this problem, leading to a safer working environment and preventing product loss to dust collection systems.
Finer Particle Achievement
For producing ultra-fine particles (in the micron or sub-micron range), wet grinding is almost always superior. The liquid medium prevents fine particles from clumping back together—a phenomenon known as agglomeration—which often limits the effectiveness of dry grinding.
Reduced Media and Liner Wear
The liquid acts as a lubricant between the grinding media (e.g., steel or ceramic balls) and the mill liner, reducing the rate of wear and lowering long-term operational costs.
Key Advantages of Dry Grinding
Despite the technical benefits of wet grinding, dry grinding remains widely used due to its significant practical and economic advantages.
Simplicity and Lower Initial Cost
Dry grinding systems are mechanically simpler. They do not require the pumps, tanks, seals, and liquid handling infrastructure associated with wet grinding, resulting in lower capital investment.
No Contamination from Liquids
The process is pure. For materials that would react with, dissolve in, or be contaminated by a liquid, dry grinding is the only viable option.
Avoids Expensive Downstream Drying
Perhaps the most significant advantage is the elimination of downstream processing. If the final product must be a dry powder, wet grinding necessitates a costly and energy-intensive drying step, which dry grinding completely bypasses.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Choosing a method requires an objective assessment of its inherent challenges. Neither process is without its downsides.
The Challenge of Material-Liquid Interaction
The primary limitation of wet grinding is chemical compatibility. If your material is soluble in the grinding liquid or reacts with it, the process is not feasible.
The Hidden Cost of Water
For wet grinding, the liquid isn't free. It requires handling, potential treatment before use, and often costly disposal or recycling, adding operational complexity and expense.
The Inefficiency of Dry Grinding for Fines
The primary limitation of dry grinding is its inefficiency at very fine sizes. As particles get smaller, the forces of attraction cause them to agglomerate and stick to the grinding media, severely reducing the process efficiency.
Increased Energy Consumption in Wet Grinding
While it can be more efficient at producing fine particles, the overall energy consumption of a wet grinding circuit, especially when factoring in pumping the slurry, can sometimes be higher than a comparable dry grinding process for coarser targets.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision must be driven by a clear understanding of your end goal. The optimal choice is the one that best serves your final product specification and operational reality.
- If your primary focus is achieving the finest possible particle size (<10 microns): Wet grinding is almost always the correct choice, as it prevents agglomeration and allows for more efficient fine grinding.
- If your primary focus is process simplicity and minimizing capital investment: Dry grinding is the clear winner, as it eliminates the entire liquid handling and drying circuit.
- If you are processing heat-sensitive or potentially explosive materials: Wet grinding provides essential cooling and dust suppression, making it the safer and more effective option.
- If your final product absolutely must be a dry powder and cannot be contaminated: Dry grinding is the most direct and logical path, avoiding any risk from liquid interaction or the high cost of drying.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental physics of each process transforms the choice from a guess into a strategic engineering decision.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Wet Grinding | Dry Grinding |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | Produces ultra-fine particles; excellent heat dissipation | Simpler setup; no downstream drying required |
| Best For | Heat-sensitive materials; ultra-fine particle sizes | Materials that react with liquids; dry powder end products |
| Key Limitation | Requires liquid handling and potential drying step | Inefficient for very fine particles; dust generation |
| Operational Cost | Higher due to liquid handling and drying | Lower initial cost; simpler operation |
Optimize Your Grinding Process with KINTEK
Whether you're processing heat-sensitive materials or require ultra-fine particles, selecting the right grinding method is crucial for your lab's efficiency and product quality. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering tailored solutions for all your grinding needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can help you achieve superior particle size reduction and enhance your laboratory's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a laboratory ball mill in HE-O-MIEC preparation? Master High-Entropy Material Synthesis
- What function does an Agate Mortar and Pestle serve in Na3OBr synthesis? Achieve Pure Solid-State Electrolytes
- What are the disadvantages of producing a laboratory sample from a gross sample by crushing and grinding? Avoid Contamination and Data Errors
- What role does a high-energy ball mill play in mechanical alloying for HEAs? Optimize Solid-State Diffusion & Refinement
- How is an agate mortar utilized in the preparation of LiMn2O4 cathode composite materials? Optimize Battery Performance
- Why is the wet milling mode preferred for Fe-Cr-Mo-C alloy powder? Ensure Data Integrity for Neutron Diffraction
- Why use agate grinding jars for silver vanadium oxide? Ensure Purity in Battery Material Milling
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a sag mill? A Guide to Primary vs. Secondary Grinding



















