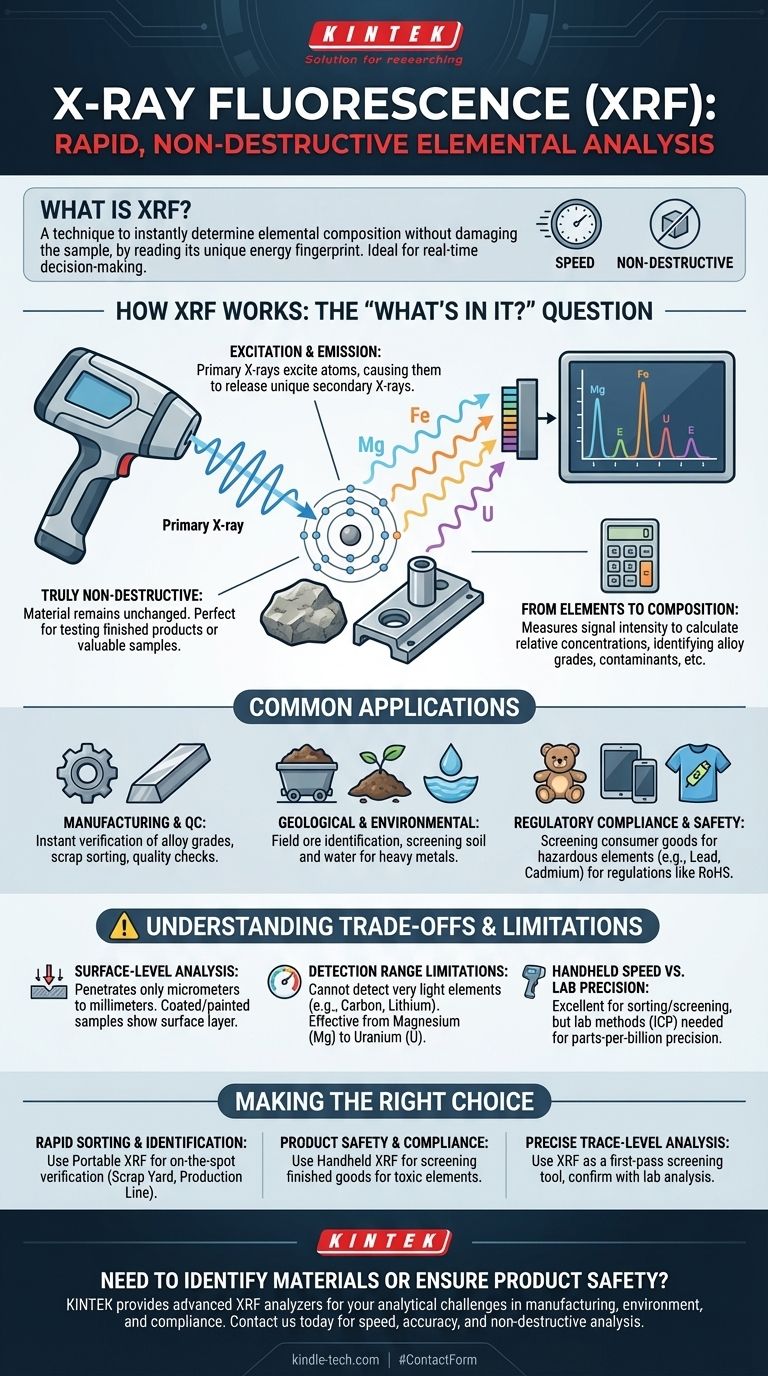
In short, X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) is an analytical technique used to rapidly determine the elemental composition of a material without destroying it. By bombarding a sample with X-rays, an XRF analyzer can read the unique energy "fingerprint" of the elements within, from magnesium all the way to uranium. This allows you to instantly identify what a material is made of.
While many lab methods can identify elements, XRF's core value is its speed and non-destructive nature. It provides immediate, actionable answers in the field or on the factory floor, making it an indispensable tool for real-time decision-making where damaging the sample is not an option.

How XRF Answers the "What's In It?" Question
At its core, XRF is a method for elemental identification. It doesn't just tell you if an element is present; it can also quantify how much is there, allowing you to understand the complete makeup of a sample.
The Fundamental Principle: Excitation and Emission
An XRF analyzer directs a primary beam of X-rays at the sample. This energy excites the atoms within the material, causing them to release their own secondary X-rays, known as fluorescence.
Each element emits these secondary X-rays at a unique and predictable energy level. The analyzer's detector measures these energies, effectively reading the elemental signature of the material.
A Truly Non-Destructive Method
Because this process only involves X-rays interacting with the sample's atoms, the material itself is left completely unchanged and undamaged. This is critical when testing finished products, valuable historical artifacts, or samples that must be preserved for other tests.
From Elements to Composition
Identifying the elements is the first step. By measuring the intensity of the signal for each element, the analyzer's software calculates their relative concentrations. This allows you to confirm the grade of a metal alloy, check for contaminants, or verify the composition of a mineral.
Common Applications: Where XRF Delivers Value
XRF's speed and portability have made it a standard tool across numerous industries. Its applications are best understood by the problems it solves.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
In manufacturing, knowing the exact composition of metals is non-negotiable. XRF provides instant verification. It is used for sorting incoming scrap metal, identifying alloy grades on the production line, and performing final quality assurance checks before a product ships.
Geological and Environmental Analysis
Geologists and miners use portable XRF analyzers in the field to identify promising ore deposits and guide exploration efforts. For environmental work, XRF is used to quickly screen soil, water, and dust for heavy metal contaminants like lead, arsenic, and mercury.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety
Consumer product safety is a major application. XRF is used to screen toys, electronics, and apparel for restricted or hazardous elements like lead (Pb) in paint, cadmium (Cd) in plastics, and mercury (Hg) in other components, ensuring compliance with regulations like RoHS.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No technology is a universal solution. Being an effective advisor means acknowledging where XRF excels and where it falls short.
It's a Surface-Level Analysis
XRF can only analyze the immediate surface of a material, typically penetrating only a few micrometers to millimeters depending on the material's density. If a sample is coated, painted, or corroded, the analysis will only reflect the surface layer, not the bulk material underneath.
Detection Range Limitations
Standard handheld XRF analyzers cannot detect very light elements. The periodic table coverage generally starts at magnesium (Mg). This means crucial elements in some materials, such as carbon, lithium, beryllium, and oxygen, are invisible to XRF.
Handheld Speed vs. Lab Precision
While incredibly fast for sorting and screening, portable XRF may not offer the same level of precision as slower, more complex laboratory methods like Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP). For applications requiring parts-per-billion sensitivity, XRF is a powerful screening tool but lab analysis is the final authority.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right analytical tool depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is rapid material sorting and identification: XRF is an unparalleled tool for on-the-spot verification in a scrap yard, on a receiving dock, or on a production line.
- If your primary focus is ensuring product safety and compliance: Handheld XRF provides a fast, non-destructive way to screen for restricted toxic elements like lead or cadmium in finished goods.
- If your primary focus is precise, trace-level chemical analysis: Use XRF as an excellent first-pass screening tool, but plan to confirm your results with more sensitive laboratory methods for definitive quantification.
Understanding both the capabilities and the inherent limitations of XRF is the key to using it effectively to solve your analytical challenges.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Capability | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Analysis Type | Elemental Identification & Quantification | Determines 'what' and 'how much' of an element is present |
| Method | Non-Destructive (X-ray Fluorescence) | Leaves sample intact; ideal for finished goods or artifacts |
| Speed | Real-time Results (Seconds) | Enables immediate decision-making in the field or on-site |
| Primary Applications | Quality Control, Material ID, Safety Compliance | Versatile for manufacturing, geology, and consumer product safety |
| Key Limitation | Cannot Detect Light Elements (e.g., Carbon, Lithium) | Best for elements from Magnesium (Mg) to Uranium (U) |
Need to identify materials or ensure product safety quickly and without damage?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced XRF analyzers and lab equipment to meet your specific analytical challenges. Whether you're in manufacturing needing rapid alloy verification, in environmental services screening for contaminants, or ensuring regulatory compliance for consumer goods, our solutions deliver the speed, accuracy, and non-destructive analysis you require.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our XRF technology can bring precision and efficiency to your laboratory or field operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Barium Fluoride BaF2 Substrate Window
People Also Ask
- Why KBr is used in IR spectrophotometry? A Key to Transparent Sample Analysis
- Why is my hydraulic press not holding pressure? Diagnose and Fix Common Leaks
- What is a hydraulic press in simple words? Harness Immense Force for Shaping and Crushing
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press essential for LATP solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure High-Density Ion Conductivity
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- How are samples prepared for XRF analysis? Achieve Accurate and Reliable Results
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- How does a press machine work? Harnessing Force Multiplication for Industrial Power



















