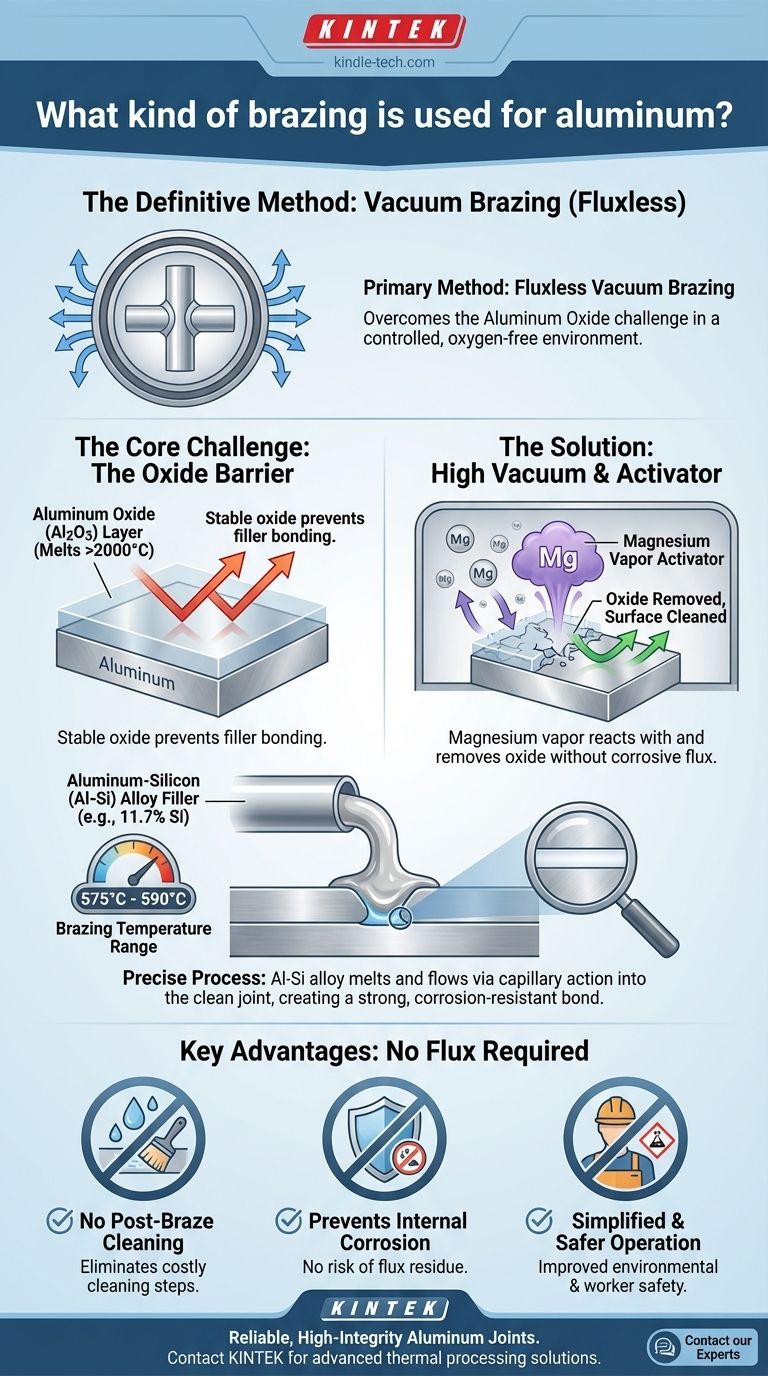
The most common and effective method for brazing aluminum is a fluxless process known as vacuum brazing. This technique is performed in a high-vacuum chamber and uses a specific type of filler metal, typically an aluminum-silicon (Al-Si) alloy. It is purpose-built to overcome the single greatest challenge in joining aluminum: its stable, protective surface oxide layer.
The fundamental challenge in brazing aluminum is its tenacious oxide film (Al2O3), which prevents the filler metal from bonding. Vacuum brazing solves this by using a high vacuum and a metal activator, like magnesium, to remove the oxide layer, enabling a strong, clean joint without needing corrosive chemical fluxes.

The Core Challenge: Overcoming the Oxide Barrier
Brazing aluminum is not like brazing steel or copper. The difficulty lies entirely in the metal's surface chemistry.
The Problem with Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)
Aluminum instantly reacts with air to form a dense, stable, and transparent layer of aluminum oxide (Al2O3).
This oxide film has a melting point over 2000°C, far higher than the aluminum base metal itself. This layer acts as a barrier, preventing the molten brazing filler metal from "wetting" and bonding with the aluminum underneath.
How Vacuum Brazing Solves the Problem
Vacuum brazing is an elegant, multi-pronged solution designed specifically to defeat the aluminum oxide layer without resorting to harsh chemicals.
The Role of High Vacuum
The process is conducted in a vacuum furnace at pressures of 10⁻⁵ mbar or lower. This highly controlled environment minimizes the presence of oxygen, preventing any further oxidation of the parts as they are heated to brazing temperature.
The Function of the Metal Activator
To deal with the existing oxide, a metal activator—most commonly magnesium (Mg)—is introduced into the process.
As the furnace heats up, the magnesium vaporizes. This magnesium vapor actively reacts with the aluminum oxide film, breaking it down and effectively cleaning the surface of the base metal.
The Aluminum-Silicon (Al-Si) Filler Metal
With the oxide barrier removed, the filler metal can do its job. For aluminum, this is typically an aluminum-silicon (Al-Si) alloy.
These alloys, containing 7% to 12% silicon, have a lower melting point than the base aluminum. A standard choice is a eutectic Al-Si alloy with 11.7% silicon, which melts at a precise 577°C.
Once molten, this filler flows via capillary action into the joint, creating a strong, durable, and corrosion-resistant bond upon cooling.
Understanding the Process and Its Advantages
Vacuum aluminum brazing (VAB) is a precise industrial process with distinct benefits over other methods.
Precise Temperature Control
The brazing temperature window is narrow, typically 575°C to 590°C. The melting point of the filler is very close to that of the base metal.
Therefore, modern vacuum furnaces use multiple heating zones to maintain extremely tight temperature uniformity, often within ±5.5°C across the entire workload.
The Major Advantage: No Flux Required
Because the vacuum and magnesium activator handle oxide removal, no chemical brazing flux is needed. This provides several key benefits:
- No Post-Braze Cleaning: Eliminates the complicated and costly step of cleaning corrosive flux residues from the finished part.
- Prevents Internal Corrosion: There is no risk of trapped flux causing hidden corrosion and premature failure in the final assembly.
- Simplified and Safer Operation: Avoids the handling and disposal of aggressive chemical fluxes, improving environmental and worker safety.
Resulting Joint Quality
The resulting joints are known for their high quality. They exhibit excellent strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance that is comparable to the parent aluminum. The color match is also nearly perfect, creating a clean, seamless appearance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a joining method depends entirely on your project's technical requirements, volume, and cost constraints.
- If your primary focus is high-integrity joints and volume production: Vacuum brazing is the definitive choice for critical components like automotive heat exchangers, offering unparalleled consistency and reliability.
- If your primary focus is avoiding high capital investment: Be aware that vacuum brazing requires specialized furnaces, making it less suitable for one-off jobs or prototyping where simpler, flux-based methods might be considered.
- If your primary focus is component longevity and performance: The fluxless nature of vacuum brazing is a significant advantage, as it completely eliminates the risk of future failures caused by flux-induced corrosion.
By understanding how vacuum brazing fundamentally solves the aluminum oxide problem, you can confidently specify a process that produces reliable, high-quality assemblies.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Method | Vacuum Brazing (Fluxless) |
| Core Challenge | Overcoming Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) Layer |
| Solution Mechanism | High Vacuum + Magnesium (Mg) Activator |
| Typical Filler Metal | Aluminum-Silicon (Al-Si) Alloy (e.g., 11.7% Si) |
| Brazing Temperature Range | 575°C – 590°C |
| Major Advantage | No Flux Required, Eliminating Post-Braze Cleaning & Corrosion Risk |
Need reliable, high-integrity aluminum joints for your laboratory or production needs?
KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including vacuum brazing systems and consumables. Our expertise ensures your aluminum assemblies achieve maximum strength, durability, and corrosion resistance without the complications of flux.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific brazing requirements and enhance your product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials
- How is heating done in sintering operation? Master the Core Methods for Dense, Strong Parts
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- What is the sintering time? A Critical Process Variable for Material Density and Strength
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance



















