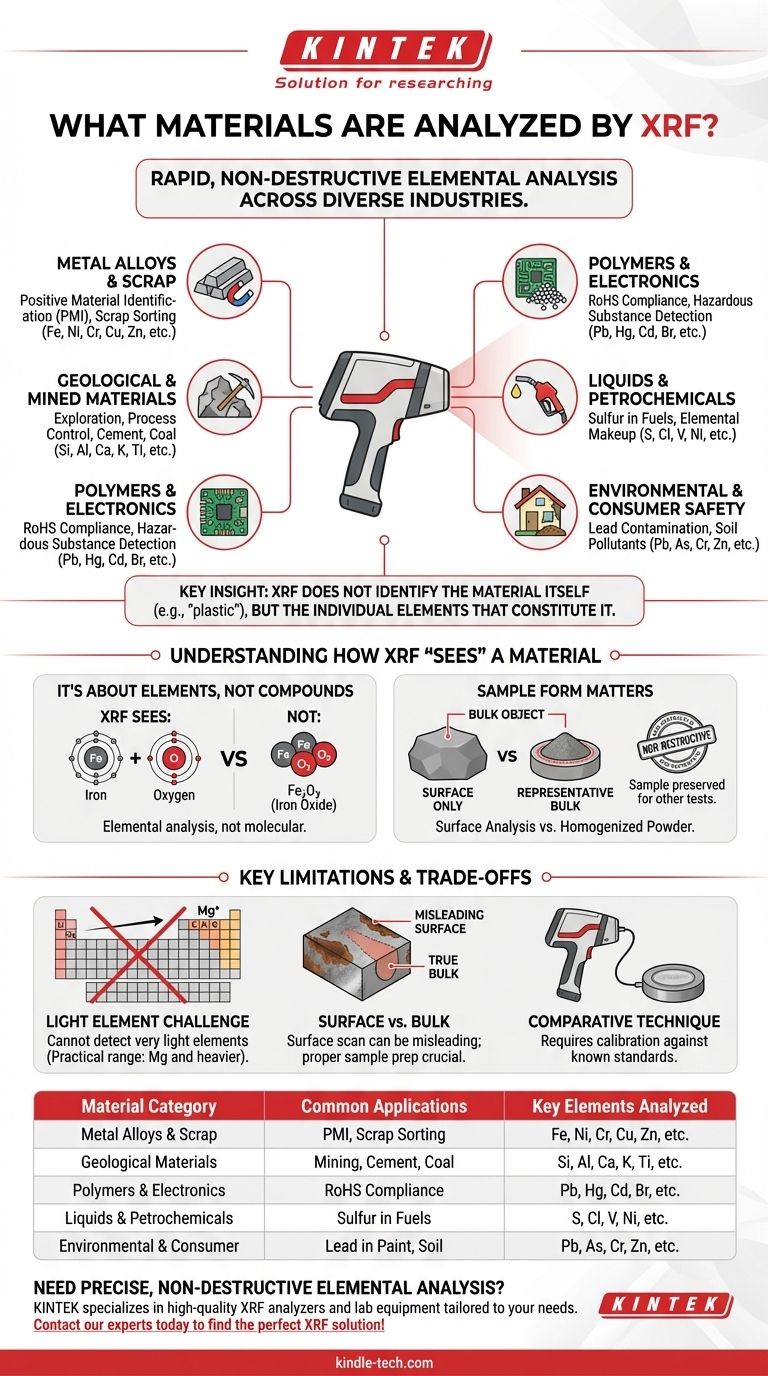
In short, X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) analyzes the elemental composition of an extremely wide range of materials. This includes solids, liquids, and powders, making it a versatile tool for identifying the presence and concentration of elements from magnesium (Mg) to uranium (U) on the periodic table. Common applications range from verifying the grade of metal alloys to detecting heavy metals in plastics and contaminants in soil or consumer goods.
The key insight is that XRF does not identify the material itself (e.g., "plastic"), but rather the individual elements that constitute it. Its power lies in its ability to perform this elemental analysis rapidly and non-destructively across a vast spectrum of sample types.

The Scope of XRF: From Metals to Consumer Products
XRF's versatility makes it a cornerstone technology in numerous industries. Its primary function is to provide rapid, on-site chemical analysis without destroying the sample.
Metal Alloys and Scrap
XRF is fundamental in metallurgy for Positive Material Identification (PMI). It allows for the quick verification of alloy grades in manufacturing and the rapid sorting of different metals in scrap recycling yards.
Geological and Mined Materials
In geoscience, XRF is used for exploration and process control. It helps geologists identify promising areas for mining and allows for real-time quality analysis of raw materials like cement, coal, and other industrial minerals.
Polymers and Electronics
Manufacturers use XRF to ensure compliance with safety regulations, such as the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive. It reliably detects the presence of restricted heavy metals like lead, mercury, and cadmium in plastics and electronic components.
Liquids and Petrochemicals
The technique is not limited to solids. XRF can analyze liquids to determine their elemental makeup, a common application being the measurement of sulfur levels in gasoline and other fuels to meet environmental standards.
Environmental and Consumer Safety
XRF analyzers are frequently used to screen for hazardous elements. This includes testing paint for lead contamination in older homes, checking soil for heavy metal pollutants, and verifying the safety of consumer products.
Understanding How XRF "Sees" a Material
To properly leverage XRF, it's crucial to understand what it measures and how the sample's form affects the results.
It's About Elements, Not Compounds
XRF identifies individual elements. For example, it will detect the presence of Iron (Fe) and Oxygen (O) in a sample, but it will not directly tell you if they are combined as iron(II) oxide or iron(III) oxide. The analysis is elemental, not molecular.
The Importance of Sample Form
Because XRF is primarily a surface analysis technique, the physical state of the sample is critical. A quick scan of a bulk object will only reveal the composition of its immediate surface.
For a true representation of an entire material, samples are often homogenized by being ground into a fine powder and pressed into a standardized pellet. This ensures the reading is consistent and representative of the whole.
A Non-Destructive Method
One of the most significant advantages of XRF is that it is non-destructive. The X-rays used in the analysis do not damage the sample, allowing the material to be preserved for other tests or for its intended use.
Key Limitations and Trade-offs
While powerful, XRF is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is essential for accurate analysis.
The Light Element Challenge
Standard handheld XRF analyzers cannot detect very light elements. The practical detection range begins at magnesium (Mg). This means critical elements in many applications—such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and lithium—are invisible to this method.
Surface vs. Bulk Composition
Relying on a surface scan of a non-uniform material can be misleading. A corroded or plated metal surface, for instance, will give a reading that does not reflect the composition of the underlying alloy. Proper sample selection is paramount.
A Comparative Technique
XRF is a comparative method, meaning its accuracy depends on being calibrated against certified reference materials with known elemental concentrations. The quality of an XRF reading is directly tied to the quality of the standards used to calibrate the instrument.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply XRF effectively, align the technique's strengths with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is rapid quality control or material identification: XRF is an unmatched tool for quickly verifying alloy grades, sorting scrap metal, or screening products on a production line.
- If your primary focus is precise bulk chemical analysis: XRF is highly effective but requires consistent sample preparation, such as grinding the material into a homogenous powder to ensure representative results.
- If your primary focus is detecting very light elements (like carbon in steel): You must use a different analytical technique, as XRF cannot detect elements lighter than magnesium.
By understanding both its broad capabilities and its specific limitations, you can confidently leverage XRF for accurate and efficient elemental analysis.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Applications | Key Elements Analyzed |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Alloys & Scrap | Positive Material Identification (PMI), Scrap Sorting | Fe, Ni, Cr, Cu, Zn, etc. |
| Geological Materials | Mining Exploration, Cement & Coal Analysis | Si, Al, Ca, K, Ti, etc. |
| Polymers & Electronics | RoHS Compliance (Hazardous Substance Detection) | Pb, Hg, Cd, Br, etc. |
| Liquids & Petrochemicals | Sulfur in Fuels, Contaminant Screening | S, Cl, V, Ni, etc. |
| Environmental & Consumer Goods | Lead in Paint, Soil Contamination | Pb, As, Cr, Zn, etc. |
Need precise, non-destructive elemental analysis for your materials?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality XRF analyzers and lab equipment tailored to your specific needs—whether you're in metal fabrication, recycling, environmental testing, or consumer product manufacturing. Our solutions deliver rapid, accurate results to enhance your quality control and compliance processes.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect XRF solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis



















