The short answer is that a vast range of materials can be PVD coated, including most metals, plastics, glass, and ceramics. The true limiting factors are not the materials themselves, but their ability to withstand the heat and vacuum conditions inherent to the PVD process.
The key to determining if a material can be PVD coated is less about the material type and more about its thermal stability and its behavior under a high vacuum. While many materials are compatible, some require special low-temperature processes or preparatory base layers to achieve a successful coating.
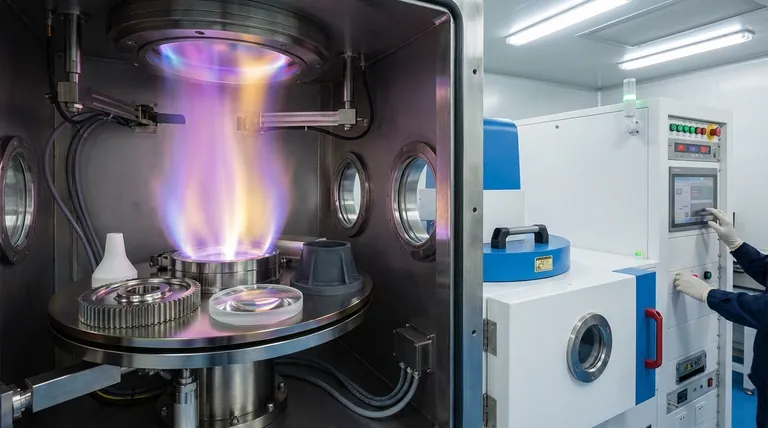

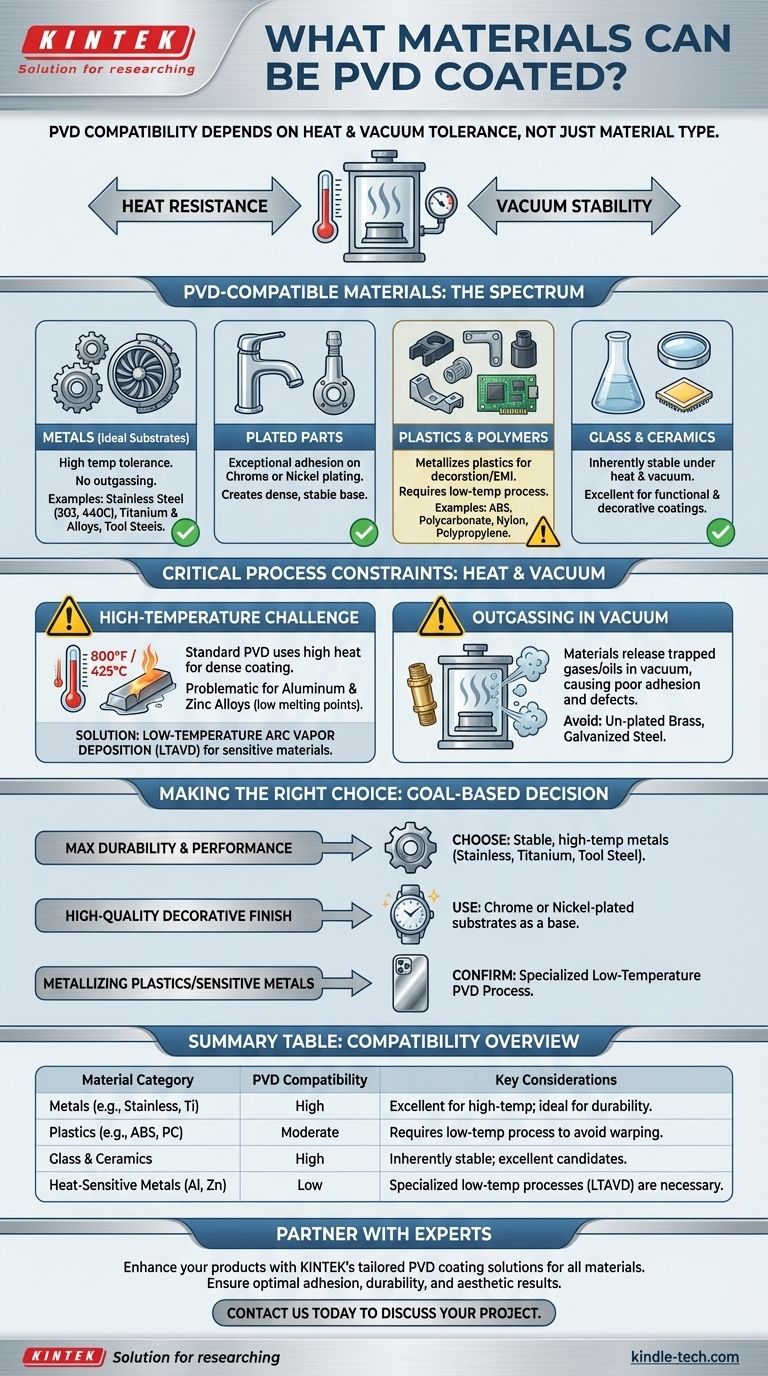
The Spectrum of PVD-Compatible Materials
Physical Vapor Deposition is a versatile coating process, but certain materials serve as better substrates than others due to their inherent stability.
Metals: The Ideal Substrates
The most common and ideal candidates for PVD are metals with high temperature tolerance and stability. They do not degrade or release gasses (outgas) in the vacuum chamber.
These include stainless steels (e.g., 303, 440C), titanium and its alloys, and high-alloy tool steels.
Chrome and Nickel-Plated Parts
PVD coatings exhibit exceptional adhesion to materials that are already plated with chrome or nickel. This preparatory plating creates a dense, stable, and ideal surface for the PVD film to bond with, often resulting in the most durable finish.
Plastics and Polymers
Plastics are frequently PVD coated to "metallize" them, providing a metallic appearance for decorative purposes or functional properties like EMI shielding.
Commonly coated plastics include ABS, polycarbonate (PC), nylon, polypropylene, and various epoxies. These materials require specialized low-temperature PVD processes.
Glass and Ceramics
Both glass and ceramic substrates are fully compatible with PVD coating. Their inherent stability under heat and vacuum makes them excellent candidates for a wide range of functional and decorative coatings.
Critical Process Constraints to Understand
Simply knowing a material can be coated is not enough. You must understand the environmental stresses of the PVD process to avoid failures. The two primary constraints are heat and vacuum.
The High-Temperature Requirement
A standard PVD process heats the substrate to temperatures as high as 800°F (approx. 425°C). This is necessary to ensure a dense, well-adhered coating.
Materials must be able to withstand this temperature without melting, warping, or changing their fundamental properties.
The Challenge of Heat-Sensitive Materials
This high-temperature requirement is why some common metals are problematic. Aluminum and zinc alloys, for example, have low melting points and cannot tolerate a standard PVD process.
The solution is a specialized technique called Low-Temperature Arc Vapor Deposition (LTAVD) or similar processes that operate at much lower temperatures, making it possible to coat these sensitive metals and most plastics.
The Problem of "Outgassing" in a Vacuum
The PVD process takes place in a high vacuum. Some materials, when exposed to a vacuum, release trapped gasses, oils, or water vapor in a process called outgassing.
This is a critical issue because these released contaminants will interfere with the coating process, leading to poor adhesion and defects in the final film. Materials like un-plated brass and galvanized steel are known to outgas, making them unsuitable for PVD coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's goal directly influences the best material choice. Understanding the interplay between the substrate, the process, and the desired outcome is essential.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and performance: Choose stable, high-temperature metals like stainless steel, tool steel, or titanium that can withstand the optimal PVD process conditions.
- If your primary focus is a high-quality decorative finish: Using a chrome-plated or nickel-plated substrate as a base for the PVD coating will provide the best possible adhesion and visual result.
- If your primary focus is metallizing plastics or heat-sensitive metals: Confirm with your coating provider that they offer a specialized low-temperature PVD process designed for these materials.
Ultimately, successful PVD coating comes from matching the right substrate material to the right process.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | PVD Compatibility | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Metals (e.g., Stainless Steel, Titanium) | High | Excellent for high-temperature processes; ideal for durability. |
| Plastics (e.g., ABS, Polycarbonate) | Moderate | Requires low-temperature PVD processes to avoid warping. |
| Glass & Ceramics | High | Inherently stable under heat and vacuum; excellent candidates. |
| Heat-Sensitive Metals (e.g., Aluminum, Zinc) | Low | Specialized low-temperature processes (e.g., LTAVD) are necessary. |
Ready to enhance your products with a durable, high-performance PVD coating? At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored PVD coating solutions for a wide range of materials—from metals and plastics to glass and ceramics. Our expertise ensures optimal adhesion, durability, and aesthetic results for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can bring value to your laboratory or manufacturing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells



















