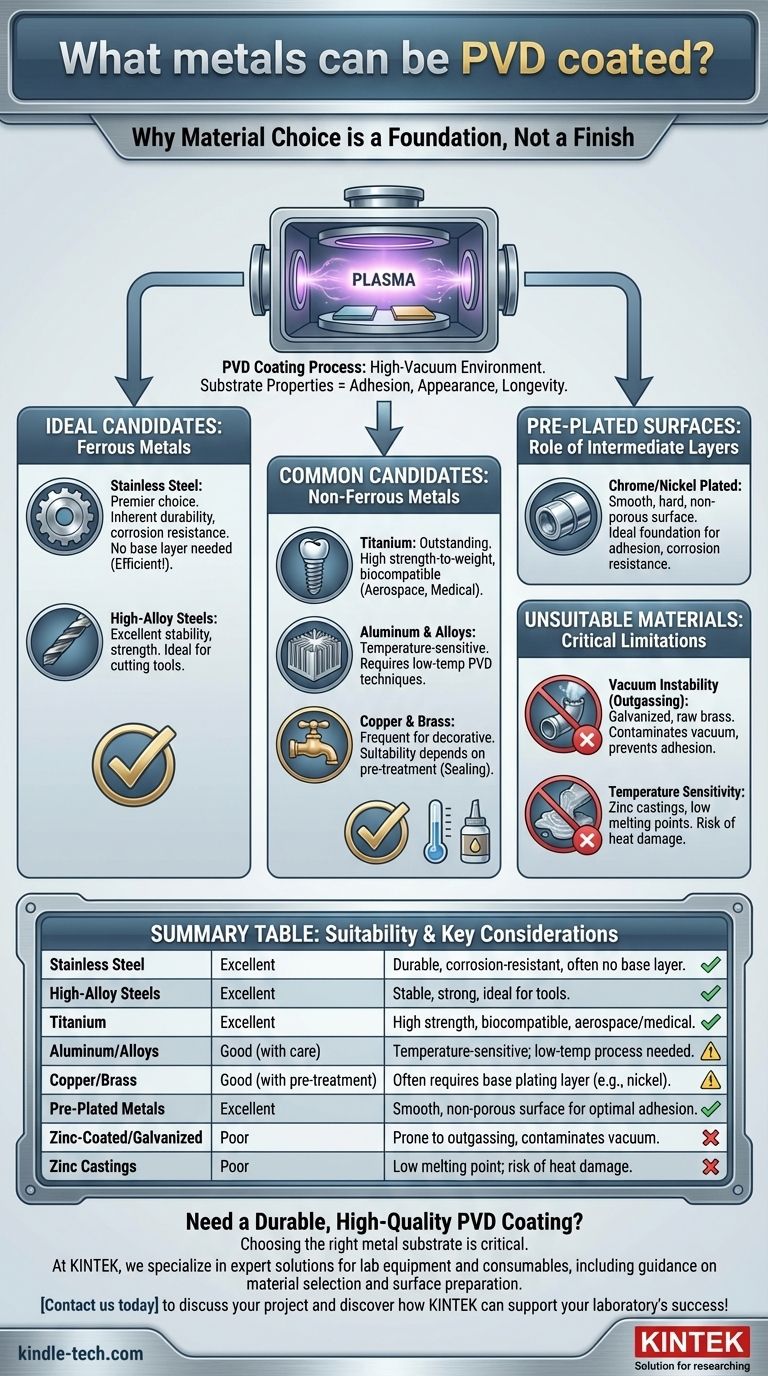
Virtually any metal can receive a PVD coating, but its success and durability are not universal. The most common and suitable candidates include stainless steel, high-alloy steels, titanium, aluminum, and copper alloys. Additionally, metals that have already been plated with materials like chrome or nickel are excellent substrates for PVD application.
The critical factor for a successful PVD finish is not just the type of metal, but its ability to withstand a vacuum environment and its surface preparation. The best results are achieved on materials that are stable under vacuum and have a pristine, non-porous surface.

Why Material Choice is a Foundation, Not a Finish
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) occurs in a high-vacuum chamber. The properties of the base metal, or substrate, directly impact the adhesion, appearance, and longevity of the final coating.
Ideal Candidates: Ferrous Metals
The most reliable and widely used substrates for PVD are often iron-based alloys.
Stainless steel is considered a premier choice. Its inherent durability and corrosion resistance mean it provides an excellent foundation for the coating to bond to.
Crucially, stainless steel generally does not require a base layer of nickel or chrome, which makes the process more efficient and economical.
High-alloy steels, such as high-speed steels used for cutting tools, are also excellent candidates due to their stability and strength.
Common Candidates: Non-Ferrous Metals
Many non-ferrous metals are also compatible, though some require special considerations.
Titanium is an outstanding substrate for PVD, prized in aerospace and medical fields for its high strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility.
Aluminum and its alloys can be coated but are more temperature-sensitive. They often require specialized low-temperature PVD techniques to prevent warping or damage to the substrate.
Copper and brass are also frequently coated, particularly for decorative applications. However, their suitability depends heavily on pre-treatment.
The Role of Pre-Plated Surfaces
Some applications benefit from an intermediate layer between the base metal and the PVD coating.
Metals plated with chrome or nickel create a very smooth, hard, and non-porous surface. This provides an ideal foundation for the PVD layer to adhere to, significantly enhancing both corrosion resistance and final appearance.
Critical Limitations and Unsuitable Materials
Not all metals are suitable for PVD coating in their raw state. The limitations are almost always related to how the material behaves in a vacuum or at elevated temperatures.
The Vacuum Instability Problem
The PVD process requires a deep vacuum. Materials that release gases under these conditions, a process known as outgassing, can disrupt the coating process and lead to defects.
Galvanized materials (zinc-coated steel) and raw brass are classic examples of "vacuum-unfriendly" substrates. The zinc and other elements within these alloys can vaporize in the chamber, contaminating the environment and preventing proper coating adhesion.
The Temperature Sensitivity Factor
While specialized low-temperature PVD processes exist, the standard process involves heat.
Materials with low melting points or those that can be structurally compromised by heat, like zinc castings, require careful process control. If not managed correctly, the part can be damaged before the coating is even applied.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right substrate is the first step toward a successful PVD finish. Your primary goal will dictate the best path forward.
- If your primary focus is durability and process efficiency: Use stainless steel, as it provides superior adhesion and rarely requires an intermediate plating step.
- If your primary focus is coating a lightweight or softer material: Choose aluminum or titanium, but ensure your provider uses the correct low-temperature process to protect the substrate's integrity.
- If your primary focus is a decorative finish on a material like brass: Ensure the part is first properly sealed with a base plating layer, such as nickel, to create a stable and non-porous foundation.
Ultimately, the quality of your base material and its preparation will define the quality of the final PVD coated product.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Suitability for PVD | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Excellent | Durable, corrosion-resistant, often requires no base layer. |
| High-Alloy Steels | Excellent | Stable and strong, ideal for tools. |
| Titanium | Excellent | High strength, biocompatible, great for aerospace/medical. |
| Aluminum/Alloys | Good (with care) | Temperature-sensitive; needs low-temperature PVD process. |
| Copper/Brass | Good (with pre-treatment) | Often requires a base plating layer (e.g., nickel) for best results. |
| Pre-Plated Metals (e.g., nickel/chrome) | Excellent | Provides a smooth, non-porous surface for optimal adhesion. |
| Zinc-Coated/Galvanized | Poor | Prone to outgassing, can contaminate the vacuum chamber. |
| Zinc Castings | Poor | Low melting point; risk of damage from heat. |
Need a Durable, High-Quality PVD Coating?
Choosing the right metal substrate is critical for a successful PVD coating that enhances durability, corrosion resistance, and appearance. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing expert solutions for your lab equipment and consumable needs, including guidance on material selection and surface preparation for optimal PVD results.
Let our expertise ensure your components receive the perfect finish. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot pressing? Choose the Right Powder Metallurgy Process
- What is vacuum lamination? Achieve a Flawless, Durable Finish on Complex Shapes
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density for Advanced Materials
- What is hot press moulding? Achieve Superior Density and Complex Shapes with Heat and Pressure
- What is hot press lamination? The Ultimate Guide to Strong, Durable Material Bonding



















