There is no single, universal method for determining the size of a particle. The technique used is chosen based on the material itself, the expected size range of the particles, and whether they are in a dry or liquid state. The most common methods include traditional sieve analysis, Static Light Scattering (also known as laser diffraction), Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), and direct image analysis.
The core principle of particle size analysis is not finding one "best" method, but matching the correct analytical technique to the specific properties of your sample. The size range of your particles is the single most important factor in making this choice.

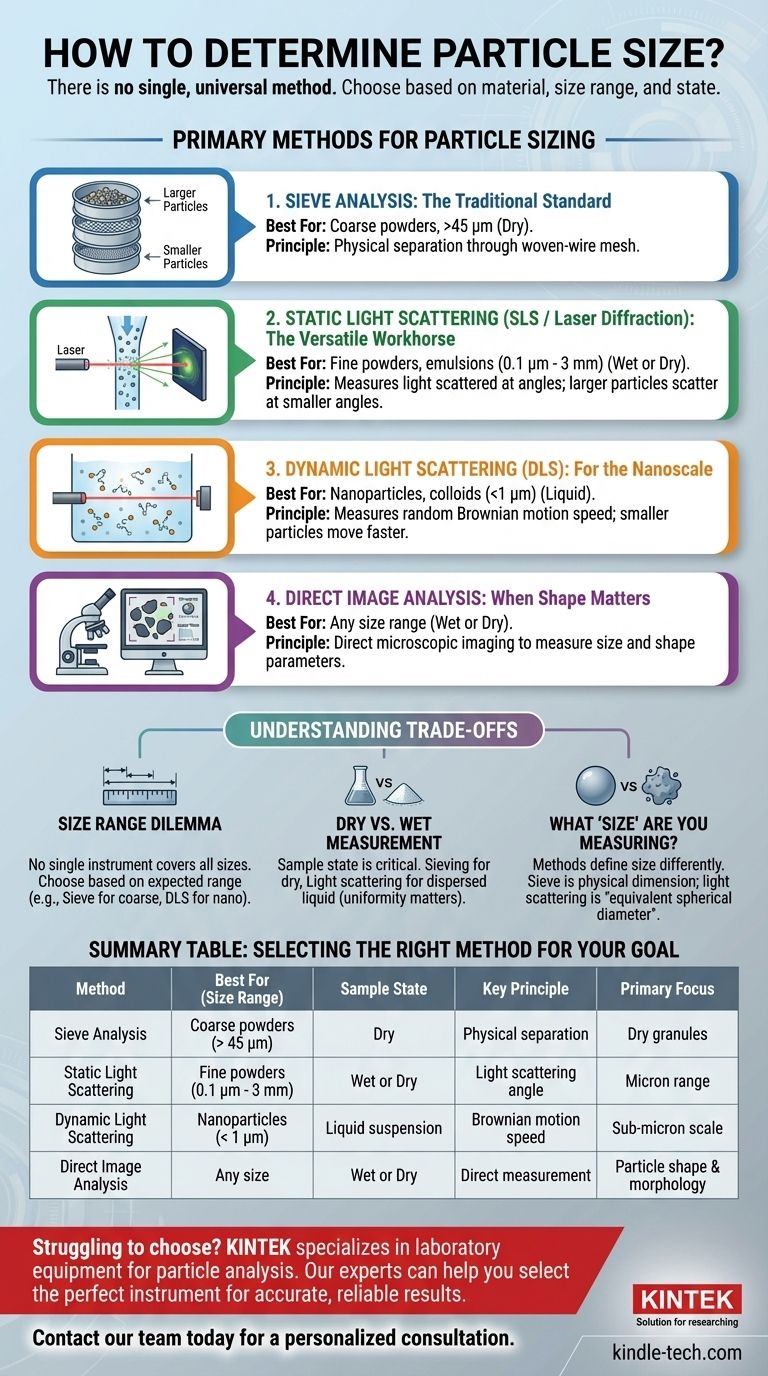
The Primary Methods for Particle Sizing
Each method operates on a different physical principle and is therefore suited for a different type of sample and size range. Understanding these differences is key to getting accurate and relevant data.
Sieve Analysis: The Traditional Standard
Sieve analysis is a straightforward and widely used technique for dry, free-flowing materials. It involves passing a sample through a stack of woven-wire mesh sieves with progressively smaller openings.
The material is separated into different size fractions based on what sieve it is retained on. The weight of each fraction is then measured to determine the particle size distribution.
Static Light Scattering (SLS / Laser Diffraction): The Versatile Workhorse
This is one of the most popular modern methods, especially for particles in the micrometer range. A laser beam is passed through a sample of particles that have been dispersed in a liquid or gas stream.
The particles scatter the light at different angles depending on their size—larger particles scatter light at smaller angles, while smaller particles scatter light at wider angles. A detector measures this pattern, and a computer algorithm calculates the particle size distribution that created it.
Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS): For the Nanoscale
DLS is the preferred method for measuring very small particles, typically below one micron (1µm), suspended in a liquid. This technique doesn't measure the particles directly.
Instead, it measures the random, Brownian motion of the particles in the fluid. Smaller particles move more quickly and erratically, while larger particles move more slowly. By analyzing the fluctuations in scattered light intensity caused by this movement, the DLS instrument calculates the particle size.
Direct Image Analysis: When Shape Matters
This method is exactly what it sounds like: taking microscopic pictures of the particles and using software to measure their dimensions. It can be static (particles on a slide) or dynamic (particles flowing past a camera).
The unique advantage of image analysis is its ability to measure not just size but also shape parameters like aspect ratio, circularity, and surface roughness. This makes it invaluable when the particle's form is as important as its size.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method requires acknowledging the inherent trade-offs between them. Results from two different methods on the same sample may not agree perfectly, because they are fundamentally measuring different properties.
The Size Range Dilemma
No single instrument can cover the entire spectrum of particle sizes.
- Sieve Analysis excels with larger particles, typically from 45 microns up to several millimeters. It is not suitable for very fine powders.
- Laser Diffraction (SLS) covers the broad middle range, often from around 0.1 microns up to 3000 microns (3 mm).
- Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) is specifically for the sub-micron world, excelling with nanoparticles and colloids from a few nanometers up to about 1 micron.
Dry vs. Wet Measurement
The state of your sample is a critical consideration. Sieve analysis is almost always performed on dry powder.
Light scattering techniques require the particles to be uniformly dispersed in a liquid medium. This can be a challenge if particles clump together (agglomerate) or dissolve in the chosen liquid. The goal is to measure the primary particles, not clusters of them.
What "Size" Are You Measuring?
Different methods define "size" differently. Sieve analysis measures the physical dimension that allows a particle to pass through a mesh opening.
In contrast, light scattering methods calculate an "equivalent spherical diameter." This is the diameter of a perfect sphere that would scatter light in the same way as your actual particle. For an irregularly shaped particle, this value may not match its physical dimensions measured with a caliper.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Goal
Base your decision on the physical reality of your sample and the data you need to collect.
- If your primary focus is dry granules or coarse powders (> 45 µm): Sieve analysis is the most direct, cost-effective, and reliable method.
- If your primary focus is fine powders, emulsions, or suspensions in the micron range: Static Light Scattering (Laser Diffraction) offers the best balance of speed, accuracy, and a wide measurement range.
- If your primary focus is measuring nanoparticles or colloids in a liquid (< 1 µm): Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) is the specialized and appropriate tool for the sub-micron scale.
- If your primary focus is understanding particle shape and morphology: Direct Image Analysis is the only method that provides this critical data alongside size distribution.
Ultimately, understanding your sample's properties is the first and most critical step in obtaining a meaningful particle size measurement.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For (Size Range) | Sample State | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sieve Analysis | Coarse powders (> 45 µm) | Dry | Physical separation by mesh size |
| Static Light Scattering (Laser Diffraction) | Fine powders, emulsions (0.1 µm - 3 mm) | Wet or Dry | Light scattering angle |
| Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) | Nanoparticles, colloids (< 1 µm) | Liquid suspension | Brownian motion speed |
| Direct Image Analysis | Any size (with microscope) | Wet or Dry | Direct measurement from images |
Struggling to choose the right particle sizing method for your unique sample? At KINTEK, we specialize in laboratory equipment and consumables for all your particle analysis needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect instrument—from sieve shakers for coarse materials to advanced laser diffraction and DLS systems for fine powders and nanoparticles. Ensure accurate, reliable results that drive your research forward. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover the KINTEK difference in precision and support.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution



















