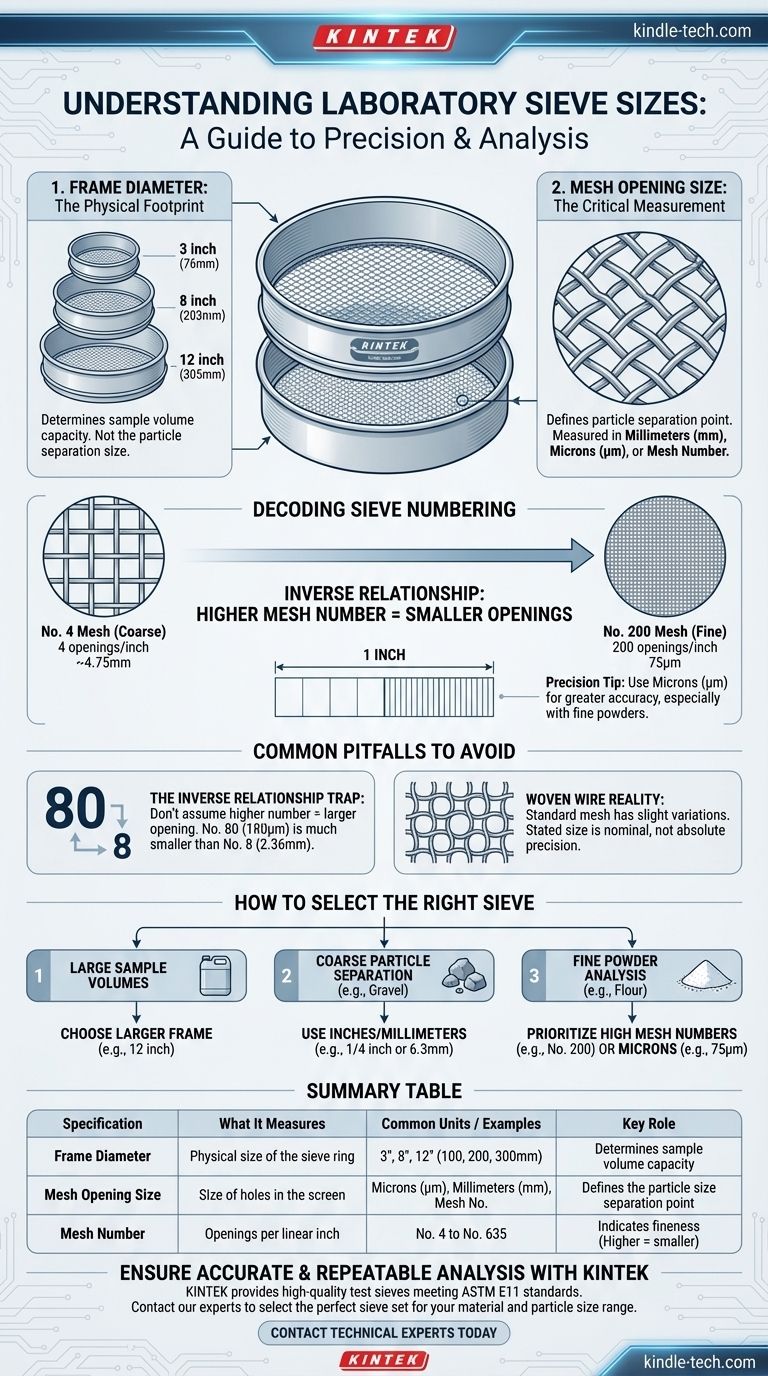
The size of a laboratory sieve is defined by two distinct measurements: the physical diameter of its frame and, more importantly, the opening size of its mesh screen. Sieve mesh openings can range from a very coarse 4 inches (100 mm) for large particles down to an extremely fine 20 microns (or 635 mesh) for powders.
A common point of confusion is mistaking the sieve's frame diameter (e.g., 8 inches) for its particle separation size. The critical specification is the mesh opening size, which dictates the precision of the analysis and is measured in millimeters, microns, or a corresponding "mesh number."

Deconstructing Sieve Dimensions
To select the correct sieve, you must understand its two primary size specifications and the role each plays in a particle size analysis.
Frame Diameter: The Physical Footprint
The frame is the circular metal ring that holds the mesh screen taut. Its diameter determines the amount of surface area available for sieving.
Common U.S. standard sizes are 3 inches, 8 inches, and 12 inches. International standards often use metric equivalents like 100 mm, 200 mm, and 300 mm.
A larger frame diameter allows you to process a larger volume of sample material at one time, which can be critical for bulk analysis.
Mesh Opening Size: The Critical Measurement
This is the most crucial specification, as it defines the size of particles the sieve will separate. It refers to the precise dimensions of the individual holes in the woven wire screen.
This measurement is expressed in several ways, covering a vast range from 4 inches (100 mm) down to 20 microns (µm).
The opening size is what allows particles smaller than the specified dimension to pass through while retaining larger particles on the screen surface.
Understanding Sieve Numbering and Units
The terminology used to describe mesh opening size can be unintuitive. The "mesh number" system is a historical standard that works differently from direct measurements like millimeters or microns.
What "Mesh" Number Means
The term "mesh" or "mesh number" refers to the number of openings in the screen across one linear inch.
For example, a No. 10 mesh sieve has 10 openings per inch. A No. 200 mesh sieve has 200 openings per inch.
This means the relationship is inverse: as the mesh number gets higher, the number of openings increases, and therefore the size of each individual opening gets smaller. A No. 200 sieve has much finer openings than a No. 10 sieve.
The Shift to Microns and Millimeters
For fine powders and applications requiring high precision, describing an opening by its direct measurement is more accurate and universally understood.
A micron (µm) is one-millionth of a meter. Using microns avoids the ambiguity of the mesh number system.
For example, a standard No. 200 mesh sieve has an opening of 75 microns (or 0.075 mm). Specifying "75 microns" is a more direct and precise way to define the separation size.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Navigating these specifications requires awareness of their inverse relationship and the physical nature of the equipment.
The Inverse Relationship Trap
The most common mistake is assuming a higher mesh number means a larger opening. You must remember that higher mesh numbers equal smaller openings.
A No. 8 sieve (2.36 mm opening) will retain much larger particles than a No. 80 sieve (180 µm opening).
Woven Wire vs. Absolute Precision
Standard test sieves use stainless steel woven wire mesh. While manufactured to tight tolerances (like ASTM E11), the weaving process means there will be very slight variations between individual openings.
The stated size (e.g., 75 microns) is a nominal, standardized value, not the absolute measurement of every single hole in the mesh.
How to Select the Right Sieve Size
Your choice depends entirely on the size of the particles you are analyzing and the volume of your sample.
- If your primary focus is processing large sample volumes: Choose a larger frame diameter, such as 12 inches (300 mm), to accommodate more material.
- If your primary focus is coarse particle separation (e.g., gravel, sand): Look for sieves designated by their opening size in inches or millimeters (e.g., 1/4 inch or 6.3 mm).
- If your primary focus is fine powder analysis (e.g., flour, pharmaceuticals): Prioritize sieves with high mesh numbers (e.g., No. 200) or, for greater precision, those specified by their opening size in microns (e.g., 75 µm).
Distinguishing between the frame's physical size and the mesh's opening size ensures you select the correct tool for accurate and repeatable particle analysis.
Summary Table:
| Specification | What It Measures | Common Units / Examples | Key Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frame Diameter | Physical size of the sieve ring | 3", 8", 12" (or 100mm, 200mm, 300mm) | Determines sample volume capacity |
| Mesh Opening Size | Size of holes in the screen | Microns (µm), Millimeters (mm), Mesh Number (e.g., No. 200) | Defines the particle size separation point |
| Mesh Number | Number of openings per linear inch | No. 4 (coarse) to No. 635 (very fine) | Indicates fineness (Higher number = smaller openings) |
Ensure Accurate and Repeatable Particle Size Analysis with the Right Sieves
Selecting the correct laboratory sieve is critical for obtaining reliable data in your quality control, R&D, or production processes. Whether you're analyzing coarse aggregates or fine powders, using the wrong mesh size or frame diameter can lead to inaccurate results and wasted time.
KINTEK is your trusted partner for all your laboratory sieving needs. We specialize in supplying high-quality test sieves and lab equipment that meet international standards like ASTM E11. Our experts can help you:
- Select the perfect sieve set based on your specific material and particle size range.
- Understand the nuances of mesh numbers, micron sizes, and frame diameters.
- Source durable and precise sieves for consistent, repeatable analysis.
Don't let sieve selection uncertainty compromise your results. Contact our technical experts today for personalized guidance and to find the ideal sieves for your laboratory's requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Can sieving be used to separate a solid substance from a liquid substance? Learn the Right Technique for Your Mixture
- How do you clean test sieves? A Gentle Guide to Preserve Accuracy and Extend Sieve Life
- What is the significance of using precision standard sieves for Inconel 625/TiB2? Optimize DLD Powder Quality
- What are the advantages of the sieve method? Achieve Fast, Reliable Particle Size Analysis
- Why is it necessary to process dried SiC mixed powders through sieving equipment? Ensure Uniform Powder Quality
- What materials are required for sieving? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What are three industrial uses for sieving? Ensure Quality and Safety in Your Production Process
- What is a laboratory sieve? A Guide to Precise Particle Size Analysis



















