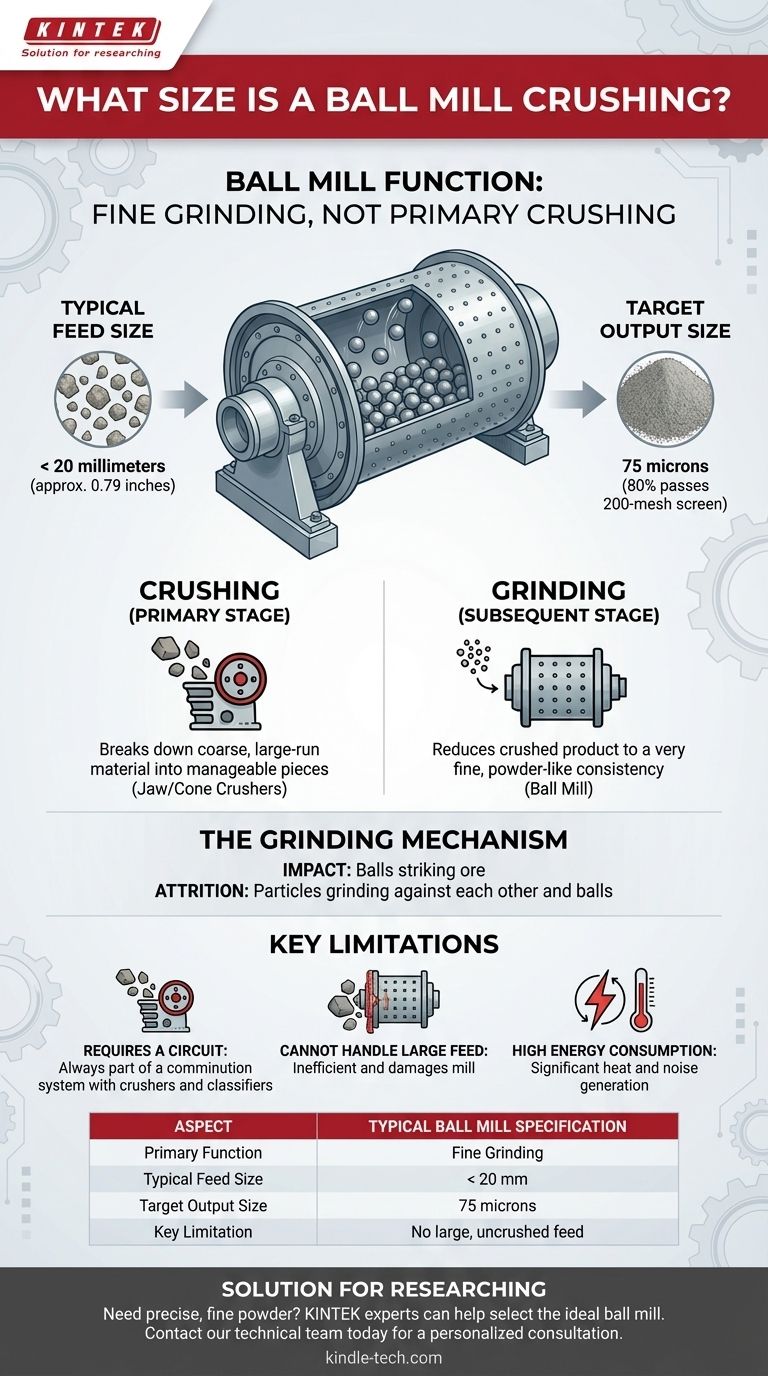
In industrial applications, a ball mill is not used for primary crushing but for fine grinding. It takes pre-crushed material, typically smaller than 20 millimeters, and reduces it to a fine powder. While some large-scale mills can accept feed up to 50mm, their primary function is to grind, not to crush large rocks.
The critical distinction to understand is that a ball mill is a grinding tool, not a crusher. It operates at the final stage of size reduction, designed to turn small particles into a fine powder, not to break large rocks into smaller pieces.

The Role of a Ball mill in Size Reduction
A common point of confusion is the difference between crushing and grinding. While both reduce material size, they operate on vastly different scales and represent different stages in a processing circuit.
Distinguishing Crushing from Grinding
Crushing is the first stage of size reduction. It deals with coarse, large-run material, breaking it down into manageable pieces. This is the work of jaw crushers, gyratory crushers, and cone crushers.
Grinding is the subsequent stage. It takes the product from the crushing circuit and reduces it to a very fine, often powder-like consistency. This is the exclusive domain of mills, like the ball mill.
Typical Feed Size
A ball mill requires a pre-processed feed. The material entering the mill has already been broken down by one or more stages of crushing.
The standard feed size for a ball mill is generally less than 20 millimeters (about 0.79 inches). This ensures the grinding media (the steel balls) can work efficiently.
Target Output Size
The goal of a ball mill is to produce a fine, uniform powder. The exact output size is a critical process parameter tailored to the specific application, such as mineral liberation or preparing material for a chemical reaction.
This output size is often measured in microns or by mesh size. A common target in mineral processing is to grind the material until 80% of it passes through a 200-mesh screen, which corresponds to a particle size of about 75 microns.
The Grinding Mechanism
A ball mill is a large rotating drum partially filled with steel balls. As the drum turns, the balls are lifted on the side of the drum and then cascade or cataract down onto the material.
Size reduction is achieved through two primary forces: impact (balls striking the ore) and attrition (particles grinding against each other and the balls). This continuous action is what produces the extremely fine product.
Understanding the Key Limitations
While powerful, a ball mill is a specialized piece of equipment with specific operational constraints. Understanding these is key to using it effectively.
Not a Primary Crusher
The most significant limitation is that a ball mill cannot handle large feed sizes. Attempting to feed it material larger than its design specifications will result in extreme inefficiency and potential damage to the mill's internal lining.
High Energy Consumption
Grinding is the most energy-intensive part of most mineral processing operations. Ball mills are famously inefficient in their energy use, with a large portion of the consumed electricity being converted into heat and noise rather than useful grinding work.
Requires a Circuit
A ball mill never works in isolation. It is always part of a larger comminution circuit that includes upstream crushers to prepare its feed and often downstream classifiers (like hydrocyclones) to ensure the product meets the required size specification.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The required final particle size dictates whether a ball mill is the right technology for your process.
- If your primary focus is mineral liberation: A ball mill is essential for grinding ore fine enough to separate the valuable mineral particles from the waste rock (gangue).
- If your primary focus is creating a specific surface area: For products like cement or certain pigments, a ball mill provides the necessary grinding to achieve the chemical reactivity required.
- If your primary focus is coarse or intermediate reduction: A ball mill is the wrong tool; you need a primary (jaw) or secondary (cone) crusher instead.
Ultimately, a ball mill is a precision tool for the final, critical step of turning granular material into a fine powder.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Typical Ball Mill Specification |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Fine Grinding (Not Primary Crushing) |
| Typical Feed Size | < 20 millimeters (0.79 inches) |
| Target Output Size | 75 microns (80% passing 200-mesh) |
| Key Limitation | Cannot handle large, uncrushed feed material |
Need to achieve a precise, fine powder for your laboratory or industrial process?
The experts at KINTEK can help you select the ideal ball mill or other size reduction equipment for your specific material and target particle size. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to meet your grinding and processing needs.
Contact our technical team today for a personalized consultation and discover the KINTEK difference in performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the feed size of a ball mill? Optimize Your Grinding Process for Maximum Efficiency
- Why are corundum grinding balls selected for milling boron carbide powders? Ensure High Purity & Chemical Compatibility
- What is the role of a fast sample pulverizer in the ultra-fine grinding of slate powder? Enhance Ceramsite Sintering
- What is the primary purpose of using grinding equipment for Tetradenia riparia extracts? Maximize Leaching Efficiency
- What is the use of a laboratory mill? Achieve Accurate Sample Homogenization for Reliable Results
- What are the operating procedures for a ball mill? Master Speed, Media, and Material for Perfect Grinding
- What is the particle size of a colloid mill? Achieve 1-5 Micron Emulsions for Superior Stability
- What is the function of an agate mortar and pestle in mixing LATP powders? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Synthesis



















