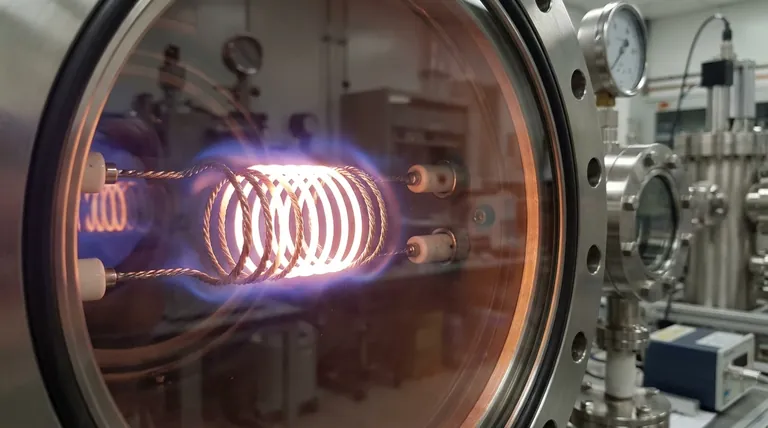
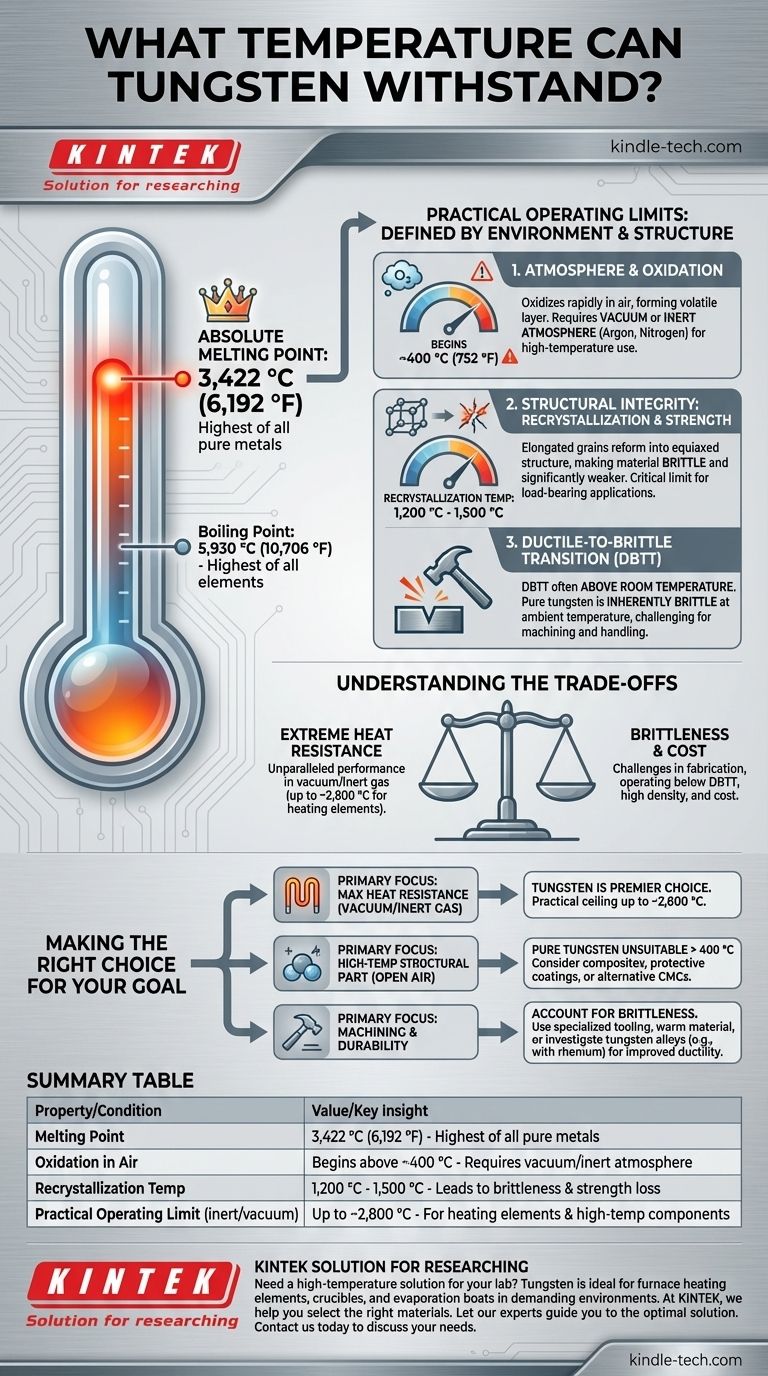
Of all pure metals, tungsten possesses the highest melting point. It can withstand temperatures up to its melting point of 3,422 °C (6,192 °F). This remarkable property is matched only by its boiling point of 5,930 °C (10,706 °F), which is the highest of all known elements.
While its melting point defines the absolute physical limit, the practical temperature tungsten can withstand is almost always lower. This operational ceiling is dictated by the surrounding atmosphere and the structural demands placed upon the material.
Beyond the Melting Point: Practical Operating Limits
To use tungsten effectively, you must understand the factors that constrain its performance well below its melting point. The theoretical maximum temperature is rarely achievable in a real-world application.
The Critical Role of the Atmosphere: Oxidation
Tungsten's primary vulnerability at high temperatures is oxygen. In air, it begins to oxidize rapidly at temperatures above approximately 400 °C (752 °F).
This process forms a volatile oxide layer (tungsten trioxide) that quickly sublimates, or "burns away," causing the material to degrade and fail. For this reason, high-temperature tungsten applications must operate in a vacuum or a protective, inert atmosphere like argon or nitrogen.
Structural Integrity: Recrystallization and Strength
Tungsten's strength is highly dependent on its internal grain structure. When it is manufactured into forms like wire or sheet, the grains are elongated, which imparts strength and ductility.
If heated above its recrystallization temperature (typically 1,200 °C to 1,500 °C), these elongated grains reform into a more uniform, equiaxed structure. This change makes the material significantly more brittle and weaker, even after it cools down. For any application where tungsten must bear a load, the recrystallization temperature is a more critical limit than the melting point.
The Ductile-to-Brittle Transition
A key characteristic of tungsten is its high Ductile-to-Brittle Transition Temperature (DBTT), which is often above room temperature.
This means that at ambient temperatures, pure tungsten is inherently brittle and can fracture easily, much like glass. This makes it challenging to machine and handle without specialized techniques and equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing tungsten for an application involves accepting a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages. Its extreme properties are a double-edged sword.
Extreme Heat Resistance vs. Brittleness
This is the central trade-off of tungsten. You gain unparalleled performance at extreme temperatures, but you must manage its brittleness during fabrication and at any point it operates below its DBTT. Alloying tungsten with elements like rhenium can improve ductility but adds complexity and cost.
High Density and Hardness
Tungsten is one of the densest metals, nearly identical in density to gold. This can be an advantage for applications like radiation shielding or counterweights but is a significant drawback for aerospace applications where weight is a primary concern. Its extreme hardness contributes to its wear resistance but also to the difficulty and expense of machining it.
Cost and Machinability
Due to its hardness and high melting point, tungsten is difficult and costly to extract, refine, and shape into final components. This positions it as a specialty material for applications where no other metal can perform.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select and implement tungsten successfully, you must align its properties with your specific operating environment and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat resistance in a vacuum or inert gas: Tungsten is the premier choice, with a practical operating ceiling for heating elements often reaching 2,800 °C, far beyond other metals.
- If your primary focus is a high-temperature structural part in open air: Pure tungsten is unsuitable above 400°C. You must consider tungsten composites with protective matrices, specialized coatings (like silicides), or alternative materials like ceramic matrix composites (CMCs).
- If your primary focus is an application requiring machining and durability: You must account for tungsten's brittleness. Plan for diamond or carbide tooling, consider warming the material for machining, or investigate tungsten alloys designed for improved ductility.
Understanding these environmental and structural limits is the key to successfully harnessing tungsten's unparalleled thermal capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Condition | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 3,422 °C (6,192 °F) | Highest of all pure metals |
| Oxidation in Air | Begins above ~400 °C | Requires vacuum/inert atmosphere for high-temp use |
| Recrystallization Temp | 1,200 °C - 1,500 °C | Leads to brittleness and strength loss |
| Practical Operating Limit (inert/vacuum) | Up to ~2,800 °C | For heating elements and high-temp components |
Need a high-temperature solution for your lab? Tungsten's extreme heat resistance makes it ideal for furnace heating elements, crucibles, and evaporation boats in demanding environments. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, helping you select the right materials for your specific thermal and atmospheric conditions.
Let our experts guide you to the optimal solution. Contact us today to discuss how our tungsten-based products can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- High Purity Gold Platinum Copper Iron Metal Sheets
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Adjustable Height Flower Basket
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Is tungsten a good heating element? Unlock Extreme Temperatures in Vacuum Environments
- What is the suitability of tungsten as an electrical conducting material for heating applications? Master Extreme High-Temperature Heating
- What are heating elements with tungsten? Unlock Extreme Heat for Vacuum & Industrial Processes
- What is the melting point of tungsten? Discover the Metal That Withstands Extreme Heat
- What happens when tungsten is heated? Harnessing Extreme Heat for Demanding Applications



















