For producing high-quality compression molded parts, the choice of mold is critical, with semi-positive molds generally offering the best balance of precision, density, and finish. While the simpler flash-type mold is the most common due to its lower cost, achieving top-tier quality in terms of dimensional accuracy and material integrity often requires a more sophisticated design.
The selection of a compression mold is not about finding a single "best" type, but about understanding the engineering trade-offs between part precision, material density, and manufacturing cost. The ideal mold directly aligns with the specific quality requirements of the final component.
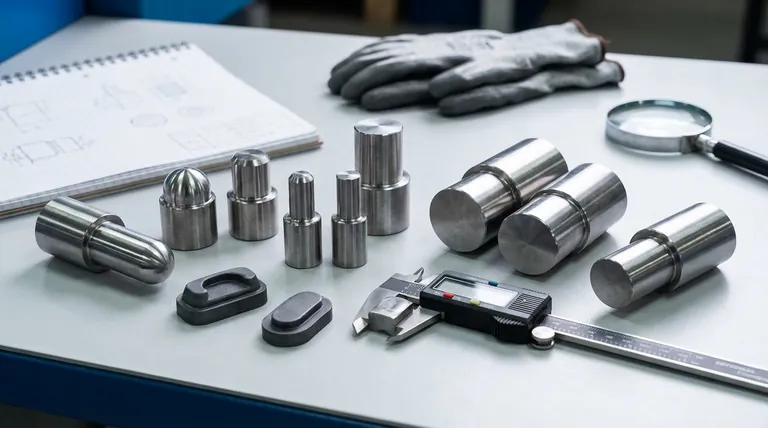

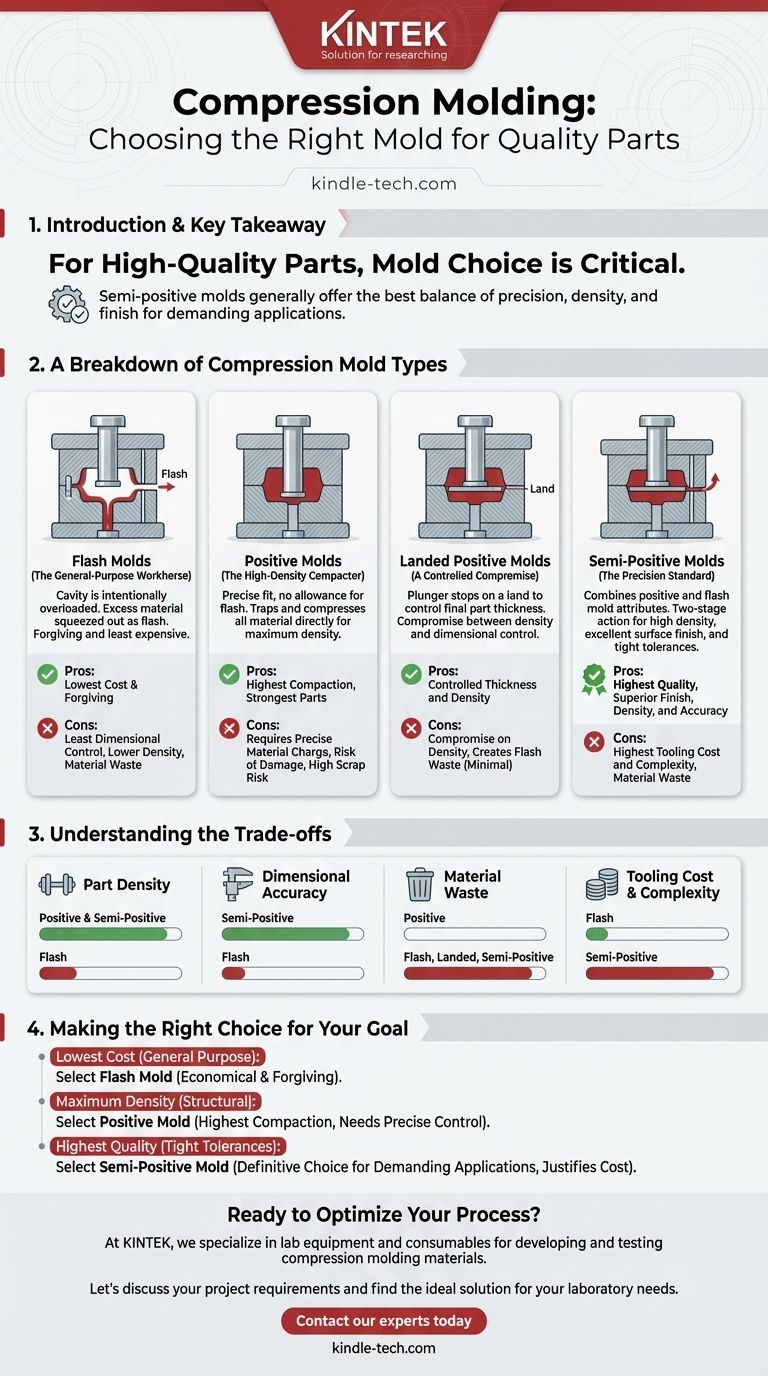
A Breakdown of Compression Mold Types
To understand why one mold is chosen over another, it's essential to examine the fundamental design of each type. Each design controls the flow and pressure of the material differently, directly impacting the final part's characteristics.
Flash Molds (The General-Purpose Workhorse)
A flash mold is designed so that the cavity is intentionally overloaded with material. As the mold closes, the excess material is squeezed out into a small channel around the part, creating a thin layer of "flash."
This is the most common and least expensive type of compression mold to manufacture. It is forgiving of slight variations in the amount of material loaded into the cavity.
Positive Molds (The High-Density Compactor)
In a positive mold, the top and bottom plates fit together precisely, like a piston in a cylinder, with no allowance for flash. All the material placed in the cavity is trapped and compressed directly.
This design achieves maximum material density, as all the force is applied directly to the charge. However, it requires an extremely precise amount of material to avoid either an incomplete part or immense, potentially damaging pressure on the mold.
Landed Positive Molds (A Controlled Compromise)
This design is a variation of the positive mold. The plunger travels under pressure but eventually stops when it makes contact with a "land" or shelf on the cavity plate.
This provides more precise control over the final thickness of the part compared to a standard positive mold, offering a compromise between density and dimensional control.
Semi-Positive Molds (The Precision Standard)
A semi-positive mold combines the best attributes of both flash and positive molds. Initially, the mold acts like a positive mold, directly compressing the material under high pressure.
As the mold closes fully, a small amount of material is allowed to escape as flash. This two-stage action ensures high part density while also allowing trapped air and excess material to vent, resulting in excellent surface finish and tight dimensional tolerances.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a mold type is an engineering decision that balances competing priorities. What constitutes "quality" for one application may be unnecessary for another.
Part Density and Internal Integrity
Semi-positive and positive molds produce the densest parts. By trapping and fully compacting the material, they minimize voids and improve the component's mechanical strength. Flash molds produce the least dense parts because some pressure is lost as material escapes.
Dimensional Accuracy
Semi-positive molds offer the highest degree of dimensional control, particularly over the thickness of the part. The design allows for both high compaction and a final, precise closing position. Flash molds provide the least control over part thickness, as it can vary depending on the amount of material charge.
Material Waste
Flash, landed positive, and semi-positive molds all create flash, which is material waste that must be trimmed in a secondary operation. A perfectly executed positive mold creates zero flash but runs a higher risk of scrap parts from incorrect material measurement.
Tooling Cost and Complexity
The cost and complexity of the molds directly correlate with their precision. The hierarchy is clear:
- Flash Molds: Simplest and cheapest.
- Positive Molds: Require tighter tolerances, moderately expensive.
- Semi-Positive Molds: Most complex and expensive to design and manufacture.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be based on the specific engineering and budget requirements for your component.
- If your primary focus is lowest cost for general-purpose parts: A flash mold is the most economical and forgiving option.
- If your primary focus is maximum material density for structural components: A positive mold delivers the highest compaction, provided you have precise process control.
- If your primary focus is the highest quality with tight tolerances and a superior finish: A semi-positive mold is the definitive choice for demanding applications, justifying its higher tooling cost.
By understanding these fundamental trade-offs, you can select the mold that delivers the precise quality your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Mold Type | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flash Mold | Lowest cost, general-purpose parts | Most economical and forgiving | Least dimensional control, lower density |
| Positive Mold | Maximum material density | Highest compaction, strongest parts | Requires precise material charge, risk of damage |
| Landed Positive Mold | Controlled thickness and density | Compromise on density and dimensional control | Creates flash waste |
| Semi-Positive Mold | Highest quality, tight tolerances | Superior finish, density, and accuracy | Highest tooling cost and complexity |
Ready to select the perfect mold for your high-quality compression molded parts?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for developing and testing materials for compression molding. Our expertise helps you optimize your process for superior results. Whether you're working with plastics, composites, or rubber, the right tools are critical for success.
Let's discuss your project requirements and find the ideal solution for your laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi-Punch Rotary Tablet Press Mold Ring for Rotating Oval and Square Molds
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Carbide Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
People Also Ask
- What is a tablet punching machine called? Choosing the Right Press for Your Production Scale
- What are the advantages of tablet press machine? Achieve High-Speed, Consistent Production
- What does a mould maker do? The Precision Engineer Behind Mass Production
- What components of a tablet press define the size and shape of the tablets? Mastering Die and Punch Tooling
- Which type of tablet press is more suitable for large scale production? Rotary Presses for High-Volume Efficiency


















